Volume 18 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 899-925Jutila, L., Layek, R., Javanshour, F., George, L., Sarlin, E., and Kanerva, M. (2023). "Effects of pine rosin on the degradation of mechanical performance in flax-reinforced polymeric composites after soil burial at low temperatures," BioResources 18(1), 899-925.AbstractArticlePDF
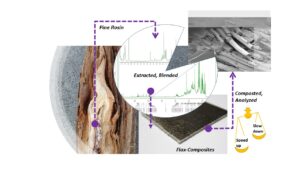
The effect of pine rosin (RO) was studied relative to the biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA), starch-based polymer (Mater-Bi), and PLA-flax composites. It was hypothesized that rosin can alter – either speed up or slow down – biodegradation in plastics depending on the specific species of polymer. The biodegradation was brought about by soil burial over 56 days. First, the effect of rosin was studied alone without any effects of soil burial. Second, the effects of soil burial were studied in terms of biodegradation. The results showed that RO increased the degree of crystallinity (+100%) and Young’s modulus (+14%) of PLA. For Mater-Bi, RO decreased the strength by 22% and led to brittleness (56% lower ultimate strain) of the specimens. After 56 days of soil burial, the presence of RO in PLA was found to speed up the degradation when compared to pure PLA (the decrease of strength was 9.3% and 6.6%, respectively). For Mater-Bi, the RO blending led to 2.1% slower biodegradation of strength during 56 days of soil burial. The effect of RO, in terms of affecting the biodegradation, was comparable in flax-reinforced and non-reinforced PLA. The strength of the fiber-matrix bonding remained equal for RO-impregnated fibers compared to the as-received flax fibers.
- Researchpp 926-936Pe III, J., Mun, J., and Mun, S. (2023). "Thermal characterization of kraft lignin prepared from mixed hardwoods," BioResources 18(1), 926-936.AbstractArticlePDF
Thermal characterization of kraft lignin (KL) prepared from mixed hardwoods was conducted to determine their thermal and thermo-oxidative stability, glass transition temperature (Tg), pyrolysis products composition, and syringyl/guaiacyl ratio. Two milled wood lignins (MWLs) from acacia (MWL-aca) and mixed hardwoods (MWL-mhw), the same hardwood species employed in the production of KL, were also characterized for comparison with KL. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) indicated that KL had higher thermal and thermo-oxidative stability than MWLs. Based on differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), the Tg of KL was 63.2 °C, while MWLs gave similar values near 165 °C. The syringyl (S), guaiacyl (G), p-hydroxyphenyl (H) composition of KL acquired from pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS) at 675 °C was 48:44:8 (S/G ratio 1.07), while MWL-aca and MWL-mhw were 31:60:9 and 46:48:6, respectively.
- Researchpp 937-948Korpela, A., Tanaka, A., and King, A. W. T. (2023). "A comparative study of the effects of chemical crosslinking agents on NBSK handsheet properties," BioResources 18(1), 937-948.AbstractArticlePDF
Chemical crosslinking is an established method for improving the wet performance of paper. In the chemical crosslinking process, covalent bonds are formed between cellulosic surfaces. The formed intra- and inter-fiber bonds increase the paper’s wet strength and reduce its water absorptivity. The majority of published studies concern crosslinking treatments with glyoxal, citric acid (CA), or with 1,2,3,4-butanetetra-carboxylic acid (BTCA). The most severe disadvantage of the crosslinking treatments with glyoxal, CA, and BTCA is that the formed crosslinks make the fibers and the paper more brittle. This downside effect has largely impeded the utilization of crosslinking in paper and paperboard making. In the present study, handsheets made from Nordic bleached softwood kraft pulp (NBSK) were crosslinked with methylated 1,3-dimethylol-4,5-dihydroxyethylene urea (mDMDHEU), which is commonly used in cotton fabric finishing. Similar to using glyoxal and citric acid, crosslinking with mDMDHEU notably increased the handsheet wet strength and decreased the water absorption. Compared to the use of glyoxal or CA, the crosslinking with mDMDHEU did not make the handsheets that brittle. These results suggest that mDMDHEU could be a more viable crosslinking agent for improving the wet performance of paper products.
- Researchpp 949-959Zhu, X., Xue, Y., Qi, P., Lan, Q., Qian, L., Shen, J., Gao, Y., Li, J., Mei, C., and Li, S. (2023). "Bearing capacity of L-shaped latticed joints connected by welding of screw-fitted dowels," BioResources 18(1), 949-959.AbstractArticlePDF
Three kinds of L-shaped latticed joint were designed to study the shear bearing capacity of joints prepared by welding of wooden dowels prepared with self-tapping screws. The results showed that such composite dowels in all specimens showed varying degrees of bending and splitting on the surface of the beech dowel after the shear test. The bending bearing capacity of the joint was the bending moment at the geometric center of the four composite dowels. The shear force of each composite dowel generated from the bending moment was equal with the same direction. The ultimate standard value of the theoretical loading force (F) was equal to 4.44 kN and the calculated design value (Fd) was equal to 2.96 kN. The errors between the standard and design value and test value of 3.94 kN were 11.2% and 24.9%, respectively. The theoretical value was relatively consistent with the test value. If the calculated design value was applied to estimate the ultimate bearing capacity of the joint, it was on the conservative side.
- Researchpp 960-979Ghahrani, N., Ramezani, O., Kermanian, H., Vatankhan, E., and Koosha, M. (2023). "Valorization of old corrugated container to dissolving pulp," BioResources 18(1), 960-979.AbstractArticlePDF
As an alternative raw material for various cellulose derivatives, the current research studied the processing of old corrugated container (OCC) in the subsequent stages of homogenization (soda cooking) and purification (bleaching with hypochlorite). The properties were characterized in four different categories including chemical composition or purity, accessibility, reactivity, and structural features. Alkali delignification and a bleaching sequence of HEHEHEA were selected for homogenization and purification of pulp followed by characterization of the pulp properties. The dissolving pulp exhibited the following properties: yield, 78%; cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin content, 90.5%, 7.76%, and 0.3%, respectively; alpha cellulose, 70%. Pulp reactivity measured with two experiments showed Fock reactivity value of 85.67% as well as iodine sorption value (ISV) of 94.95 g/g; accessibility represented by two tests of water retention (WRV) and alkali retention capacity (ARC) with 6.87 for the first and 6.1% for the latter, degree of polymerization (DP), 913.4; crystallinity index, 76.95%; and brightness, 72.87%. FTIR spectroscopy and Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (BET) isotherms were utilized to examine the modifications of OCC to dissolving pulp. The results indicated that the dissolving pulp produced from OCC as a raw material is suitable for DP applications of cellulose derivatives.
- Researchpp 980-990Wang, S., Chai, X., Niyitanga, E., and Liu, Y. (2023). "Optimizing the conditions of anaerobic fermentation in pig manure to produce volatile fatty acids and its efficiency in killing root-knot nematodes," BioResources 18(1), 980-990.AbstractArticlePDF
To concurrently control root-knot nematodes and treat pig manure and further clarify the mechanism of anaerobic digestion slurries on nematodes, the optimal conditions for producing volatile fatty acids (VFAs) were studied, and the relationship between the carboxyl group in anaerobic fermentation and the mortality rate of root-knot nematodes was also researched. When the fermentation condition parameters were set as initial pH=10.0, temperature of 25 °C, and total solid (TS) loading of 15%, the largest quantity of VFA production was obtained through orthogonal experiments and range analyses. When the concentration of VFA in the anaerobic fermentation slurry was enhanced to 3.2 g/L, the rate of root-knot nematode mortality was up to 43.3% and was significantly different from that of the control. However, after the concentration of VFA reached 4.3 g/L, no significant difference was observed for the treatments with even higher concentrations of VFA. This indicated that the pig manure slurry with anaerobic digestion exhibited a limited range to kill root-knot nematodes. The results of this study provide a theoretical basis for producing acid from anaerobic digestion in pig manure and for slurry applications.
- Researchpp 991-1007Pang, S., Ahn, K., Oh, J., Lee, H., Kang, S., and Oh, J. (2023). "Fire resistance of structural wooden walls covered by gypsum and diatomite board," BioResources 18(1), 991-1007.AbstractArticlePDF
The fire resistance of structural wooden walls covered with fire-resisting boards was investigated. A 49-mm-thick gypsum board (No. 1 and No. 2), a 24-mm-thick diatomite (No. 3), and a combination of gypsum and diatomite board (No. 4 and No. 5) were theoretically designed for 2-h fire resistance. As a result, when the gypsum board was fixed to the wood studs with nails (No. 1), there was no damage after 2 h, as predicted. When diatomite boards were used on the surface to face the fire (No. 3 and No. 4), the diatomite boards were destroyed after approximately 50 min because of the cracks of the diatomite board. However, when the diatomite board (6 mm) was placed inside the gypsum board (30 mm), the specimen (No. 5) showed a fire resistance of more than 2 h. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the thickness of the gypsum board using the diatomite board by avoiding placement of the diatomite board in direct contact with heat.
- Researchpp 1008-1024Bai, X., Xu, D., Sun, W., and Diao, Z. (2023). "Physico-mechanical properties of Sapindus mukorossi seed," BioResources 18(1), 1008-1024.AbstractArticlePDF
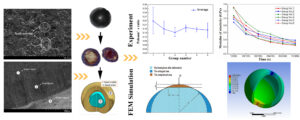
This work characterized physical and mechanical properties of Sapindus mukorossi seed to explore the mechanical behaviors of the seed during compression in a roll crusher. A new method that combines simulations and calculations with experimental data obtained using a three-dimensional optical measurement system for the measurement of the Poisson ratio and elasticity modulus of the hollow-sphere seed hull was proposed. The modulus of elasticity was derived from a mechanics formulation and verified in a computer simulation based on experimental data. Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectrometry were conducted to reveal the mesostructure and components of the seed hull. The results revealed that the average densities of the S. mukorossi seed shell and kernel were respectively 1.49 and 1.07 × 103 kg/m3, the average Poisson’s ratio was 0.185, and Young’s modulus ranged from 1.3 to 0.3 GPa. These values had little dispersion, demonstrating both the consistency of the processing techniques and the stability of the material properties. The given properties of the S. mukorossi can be used as a theoretical basis for the optimized processing of this biomass material. The proposed method provides a new direction in the study of the mechanical properties of biomaterials.
- Researchpp 1025-1040Kaçamer, S., and Budakçı, M. (2023). "Application parameters of water transfer printing on wood-based panel surfaces," BioResources 18(1), 1025-1040.AbstractArticlePDF
Optimum application values of the Water Transfer Printing (WTP) technique were determined on various wood-based panel surfaces. For this purpose, 8-mm-thick, glossy white, acrylic-coated medium-density fiberboard (MDF) panels (high gloss panels), polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-coated MDF panels, MDF Lam ready-to-use panels, and cellulosic, polyurethane, acrylic, and water-based paint applied MDF panels were used. An automatic immersion system with pool was designed and produced. A 30-μm-thick carbon patterned WTP film was applied on sample panel surfaces prepared with the help of this device at four immersion angles (0º, 15º, 30º, and 45º), four immersion speeds (50 cm/min, 100 cm/min, 150 cm/min, and 200 cm/min), and four immersion times (5 to 10 s, 20 to 30 s, 50 to 60 s, and 80 to 90 s). The optimum parameters of the WTP technique regarding the temperature and relative humidity of the application environment, water temperature, laying method, dissolution time, amount of activator, spray gun angle and tip clearance, air pressure, as well as immersion angle, speed, and time were determined using the measurement and observation method. According to the optimum parameters obtained in the study, the WTP technique was successfully applied to all wood-based panel surfaces.
- Researchpp 1041-1051Dias, R. R., Alves, M. C. S., Deus, P. R., and Vieira, F. H. A. (2023). "Variables influencing the production of door jambs from Pinus taeda EGP panels," BioResources 18(1), 1041-1051.AbstractArticlePDF
The influence of coverslip width and the physical arrangement of growth rings were studied relative to laterally glued Pinus taeda wood panels (EGP) used in the manufacture of door jambs, according to the requirements of ABNT-NBR 15.930 (2011). The goal was to determine the combination providing the best physical performance of the product. The experiments used the complete factorial design for two factors and four levels, i.e., 32, 56, 75, and 112 mm width coverslips, and rings arrangement of radial, tangential, cross coverslips, and ones with finger joints. A total of 48 EGP door jamb specimens (3 for each combination) measuring 2120 x 220 x 32 mm, with moisture content between 8% and 12% and apparent density between 400 and 600 kg.m-3 were used. Statistical analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to investigate the influence of factors and their interactions on the following responses: visual aspect, moisture, density and dimensional (width and thickness) variations. It was found that both factors and their interactions influenced the level of significance of 1% on shape deviations. The best results were for panels produced with 32 and 56 mm coverslips, with cross or radial arrangement.
