Volume 18 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 748-766Xu, F., and Cho, B.-U. (2023). "Preparation and optimization of porous regenerated cellulose microspheres from cellulose tetraethyl-ammonium/urea solution for adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye," BioResources 18(1), 748-766.AbstractArticlePDF
Porous regenerated cellulose microspheres (RCMs) have attracted increasing attention due to their wide range of applications from medical carriers to environmental remediation. Here, porous RCMs were synthesized for adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye using a simple emulsification–acid coagulation–oven-drying technique after dissolving pulp cellulose with a degree of polymerization (DP) of approximately 1500 in tetraethylammonium hydroxide (TEAOH)/urea solvents at room temperature. The RCMs with controllable size (20 to 224 µm) and high pore volume (8.24 to 10.20 mL/g) were prepared by varying the dosage of the surfactant polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate (polysorbate 80). Moreover, the viscosity of the cellulose solution steadily decreased with storage time due to the decrease in cellulose DP, but the effect on the particle size and morphology of RCMs was negligible, which could be advantageous to the scalable production of RCMs. When used as an adsorbent for cationic methylene blue dye removal, it showed high adsorption efficiency (1 h to achieve equilibrium, 24.5 mg/g), stability, recyclability, and reusability.
- Researchpp 767-777Özlüsoylu, İ., and İstek, A. (2023). "Effects of surface lamination process parameters on medium density fiberboard (MDF) properties," BioResources 18(1), 767-777.AbstractArticlePDF
Medium density fiberboard (MDF) is widely utilized in furniture production. Most MDF in such applications has a surface laminate layer. The lamination process improves the physical and mechanical properties of the boards. The temperature, press time, and pressure values applied during the lamination process affect such properties. In this work, the lamination process was carried out using a constant temperature (180 °C), four different press times (18, 20, 22, and 24 s), and three different pressures (25, 30, and 35 kg/cm2). The raw weight of the decor paper was 90 g/m2 and UF and MF glues were used in its production. The properties of the laminated panels were then determined for each variation. In general, the water absorption and thickness swelling properties were improved at the lower pressure and higher press times. The internal bonding strength exhibited a linear change at different press times depending on increasing pressure values, whereas the changes in the bending strength and modulus of elasticity in bending were not statistically significant. It was concluded that the BS increased with rising pressure in the short-term lamination process and that the effect of the pressure on the BS declined with increasing press time.
- Researchpp 778-791Lin, P., Ko, C., Chang, F., Tu, S., and Lin, C. (2023). "Oxidation behavior and decomposition kinetics of mixed-waste biomass material," BioResources 18(1), 778-791.AbstractArticlePDF
In Taiwan, approximately 379,000 automobiles and 588,000 motorcycles were recycled in 2019. Rigid polyurethane foam is one of the principal components of auto shredder residue. The amount of rigid polyurethane foam from the recycling of waste vehicles is 8,000 to 10,000 tons/year. In this study, waste Cryptomeria wood was mixed with waste rigid polyurethane foam to form derived fuels. The oxidation behaviors of the wood mixed with waste rigid polyurethane foam-derived fuels were investigated. The characteristics of the derived fuel made from wood mixed with waste rigid polyurethane foam showed that the ash content was less than 2.5% and its calorific value reached 21.9 MJ/kg. According to the Friedman equation, the activation energies of the wood mixed with 5%, 15%, and 30% of waste rigid polyurethane foam pellets were 212, 220, and 188 kJ/mol, respectively. The thermal conversion efficiencies of the wood mixed with 5%, 15%, and 30% of waste rigid polyurethane foam pellets were 30.2% to 48.1% by a water boiling test. The results showed that waste Cryptomeria mixed with waste rigid polyurethane foam-derived fuels is suitable for use as an alternative renewable energy fuel.
- Researchpp 792-803Kuzmina, N., Menshchikov, S., Mohnachev, P., Zavyalov, K., Petrova, I., Ozel, H. B., Aricak, B., Onat, S. M., and Sevik, H. (2023). "Change of aluminum concentrations in specific plants by species, organ, washing, and traffic density," BioResources 18(1), 792-803.AbstractArticlePDF
One of the most critical problems throughout the world is air pollution, causing the death of millions of individuals annually, and it is reported that 90% of the global population breathes polluted air. Among the components of air pollution, the most harmful ones are the heavy metals, which can remain non-degraded in nature for a long time, bio-accumulate in living organisms, and be toxic or carcinogenic at low concentrations. Hence, monitoring and reducing heavy metal pollution in the air are high-priority research topics. Heavy metals can accumulate within various organs of plants grown in an environment with an increased level of heavy metal pollution. The metal analyses on these organs can provide insight into the heavy metal pollution in the air. In the present study, the concentrations of aluminum (Al), one of the most important heavy metals, were determined in the different organs of five plant species grown in regions with different traffic densities. Remarkable changes were observed in the Al concentrations in all the organs of species, which were examined here by organ and traffic density. The highest values were obtained from the organs of plants grown in no-traffic regions.
- Researchpp 804-826Yorur, H., Ozcanan, S., Yumrutas, H. I., and Birinci, E. (2023). "Renewable hybrid roadside barrier: Optimization of timber thickness," BioResources 18(1), 804-826.AbstractArticlePDF
Researchers have recently focused on new and original roadside barriers that prioritize aesthetic, and environmental concerns by employing natural materials. In this study, the safety performance (Acceleration Severity Index (ASI), Theorical Head Impact Velocity (THIV)), structural performance (Working Width (W), Exit Angle (α)), and failure analysis (visual deformation) of a newly developed Renewable Hybrid Barrier (RHB) system at different timber thicknesses were tried to be determined by pendulum crash test and Finite Element (FE) models. The FE models were calibrated and validated based on pendulum crash test results, and then the most suitable timber thickness in terms of safety and structural performance was determined via FE analyses. The results revealed that as the timber thickness decreased, the safety parameters, such as ASI and THIV, decreased, thus the barrier safety increased. However, it was observed that the deflection and deformations in the barrier increased as the timber thickness decreased. In this sense, the safest and the most structurally durable barrier was determined through conducting virtual optimization tests. Studies on diversification of the usage areas of natural/renewable materials should be increased in the future.
- Researchpp 827-843Zhang, D., Shen, L., Zhu, X., Zhang, S., Gong, M., and Gao, Y. (2023). "Comparative study on connection properties of shear bolt and screw of thin cross-laminated timber panel," BioResources 18(1), 827-843.AbstractArticlePDF
Cross-laminated timber (CLT), a wood product with excellent shear resistance, is often used in modern timber constructions. Using the standards ASTM D1761-12 (2020) and NDS-2012 (2012), this study investigated the connection properties of shear bolts and screws in CLT panels. The specimens were made from spruce-pine-fir lumber and installed on a test platform using one high-strength bolt or eight screws, and then an upward load was applied to the top of the specimen. The results showed that the bolt connection provided a higher ultimate bearing capacity and elastic stiffness. The bolt exhibited virtually no deformation, and the CLT panel did not noticeably deteriorate when the connection was damaged. The distance between the bolt hole and the bottom of the CLT specimen and the angle between the outer-layer grain direction of the CLT panel and the load direction were both measured. Changes in the ductility coefficient value had an obvious effect on the connection performance of the shear bolts when the outer-layer grain direction of the CLT panel was consistent with the load direction. Contrastingly, when the outer-layer grain direction of the CLT panel was perpendicular to the load direction, the effect was negligible, and the yield load was nearly unchanged.
- Researchpp 844-854Pang, L., Lv, S., Li, K., Ding, L., and Hao, Y. (2023). "Parameter optimization for the biodiesel of Xanthoceras sorbifolium oil and determination of fatty acid methyl ester," BioResources 18(1), 844-854.AbstractArticlePDF
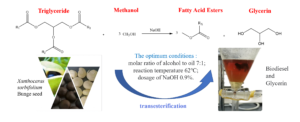
Biodiesel was prepared from Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge oil and methanol by transesterification with NaOH as the catalyst. The central composite design (CCD) was utilized to optimize its process, and Design Expert software was applied to perform a fitting regression. The best process conditions were determined as: NaOH 0.9%, molar ratio of methanol and oil 7:1, and reaction temperature 62 °C. Under these conditions, the yield of biodiesel was 89.0%. The composition of Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge oil-based biodiesel was ascertained by qualitative and quantitative analysis using gas chromatography.
- Researchpp 855-868Zou, Y., Zhang, W., Yuan, S., Zhang, J., and Chen, H. (2023). "Effects of different pretreatments combined with steam explosion on the properties of bamboo fibers," BioResources 18(1), 855-868.AbstractArticlePDF
Bamboo pretreatment is a key technology for the preparation of bamboo fibers (BFs) for composites. This study examined the properties of BFs prepared by steam explosion (SE) BFs following pretreatment by enzyme, alkali, and salt. The microstructure, functional groups, crystallinity, and surface chemical elements of BFs were characterized by environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results indicated that bamboo could be separated into fiber bundles through SE after pretreatment. The separation of BFs pretreated by enzyme and alkali were better, but colloid remained and was able to stick the fibers together. Through performing different pretreatments before SE, the lignin and hemicellulose of BFs were partially removed, and alkali pretreatment had the best effect on lignin removal. The crystal structure of the BFs did not change significantly, and the crystallinity of BFs was highest at 2 MPa and 6 min when pretreated by alkali. The XPS results showed that the effect of alkali pretreatment at 2 MPa for 6 min was the best.
- Researchpp 869-883Wang, J., Zhang, K., Sheng, J., Ren, H., Gong, J., Wang, Y., Pan, D., Wang, X., and Hao, Y. (2023). "Investigation on walnut kernel oil extraction using different methods," BioResources 18(1), 869-883.AbstractArticlePDF
Extraction of oil from walnut kernel as raw material was explored using the method of pressing. Soxhlet and ultrasonic-assisted extractions of walnut oil, its evaluation index, the extraction process optimization by single factor experiment, the physical and chemical properties of oil, fatty acid composition, element composition, and the main functional group analysis were studied. The results showed that walnut kernel could be extracted effectively with petroleum ether. The optimal extraction conditions of walnut oil by ultrasonic assisted extraction were as follows: solid/liquid ratio of 1:11 (g/mL), ultrasonic power 180 W, extraction time 60 min, and the extraction efficiency of walnut oil was 59.13%. The optimal extraction conditions of walnut oil by Soxhlet were solid to liquid ratio of 1:7, temperature of 76 °C, time of 4 h, and the extraction efficiency of walnut oil was 58.3%. The extraction efficiency of pressing was 43.2%. Walnut oil mainly contains phosphorus, zinc, magnesium, potassium, calcium, and other elements. The fatty acids of walnut oil mainly consist of palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, cis-linoleic acid, cis,cis,cis-9,12,15-octadecanotrienoic acid and other fatty acids. The cis linoleic acid accounted for the highest proportion in GC content, and the content of both was more than 90%.
- Researchpp 884-898Prasetia, D., Purusatama, B. D., Kim, J.-H., Jang, J.-H., Park, S.-Y., and Kim, N.-H. (2023). "Qualitative anatomical characteristics of the virgin cork in Quercus variabilis grown in Korea," BioResources 18(1), 884-898.AbstractArticlePDF
To provide information on the identification and quality evaluation of Q. variabilis virgin cork from Korea, the qualitative anatomical characteristics of the virgin cork were observed by optical and scanning electron microscopy and compared with those of Q. suber reproduction cork from Portugal. Q. variabilis showed a narrower growth ring than Q. suber. A dark-brown zone with sclereids was found only in Q. variabilis cork. The lenticular channel in Q. variabilis is larger than that in Q. suber. Q. variabilis virgin cork showed a distinct growth ring boundary and an abrupt transition from earlycork to latecork with a few rows of latecork cells. Q. suber reproduction cork showed an indistinct growth ring with a gradual transition from one to two rows of latecork cells. In the earlycork, Q. suber showed mild corrugation, while Q. variabilis displayed significant corrugation with collapsed and distorted cork cells. The lenticular channel in Q. variabilis virgin cork was surrounded by thick-walled cells filled with compact lenticular filling tissue. Q. suber reproduction cork had an opening with loose lenticular filling tissue surrounded by thick-walled cells. Prismatic crystals, thick-walled sclereid cells, and fiber-sclereids were found only in Q. variabilis. A few trabeculae were found in both cork samples.
