Volume 18 Issue 1
Latest articles
 Award Winner: 2023 BioResources Early Career Investigator Award
Award Winner: 2023 BioResources Early Career Investigator Award
Baral, N. R., Banerjee, D., Mukhopadhyay, A., Simmons, B. A., Singer, S. W., and Scown, C. D. (2024). “Integration of genome-scale metabolic model with biorefinery process model reveals market-competitive carbon-negative sustainable aviation fuel utilizing microbial cell mass lipids and biogenic CO2,” BioResources 19(3), 4056-4086.Hubbe, M. A. (2024). “Artists, papermakers, and the future,” BioResources 19(3), 4053-4055.- Researchpp 1052-1071Arabi, M., and Dahmardeh Ghalehno, M. (2023). "Suitability of thin-layer drying models for halogen lamp drying of sugarcane bagasse," BioResources 18(1), 1052-1071.AbstractArticlePDF
The drying process of bagasse particles was investigated in this study using an artificial neural network (ANN) and 18 thin-layer drying (TLD) models. These models are used for investigating kinetics and understanding engineering parameters involved in the drying process of food and agricultural products. Bagasse particles were studied at 105 to 135 °C and an initial moisture content of 180% (based on the dry weight) using a halogen moisture analyzer. The results showed that an increase in the temperature decreased the bagasse drying period and increased the constant drying. The whole drying process of bagasse happened in a falling drying rate period. The fitness of drying curves on semi-experimental TLD models based on statistical parameters, including root mean square error (RMSE), sum of square errors (SSE), and coefficient of determination (R2) showed that the Hii et al. model had the highest coefficient of determination and the lowest error percentage. The ANN predicted changes in the bagasse moisture content through time more accurately than the Hii et al model. Also, the results demonstrated that the selected ANN model and a number of semi-empirical models with less than 3 adjustable parameters provided good agreement and can be considered promising tools to predict drying kinetic of bagasse particles.
- Researchpp 1072-1095Pang, S.-J., Lee, H. S., and Oh, J.-K. (2023). "Lateral load carrying capacities of particleboard shear walls made by gluing with timber studs," BioResources 18(1), 1072-1095.AbstractArticlePDF
Particleboard shear walls were developed and their lateral load carrying capacities were evaluated. The shear walls were made by connecting particleboards and timber studs with polyurethane (PUR) or nails. Seven types of particleboard shear wall specimens were manufactured by varying the wood species, size of the timber studs, and number of particleboards. The size of the shear wall specimens was 2.4 m × 2.7 m, and the bottom of the shear wall was fixed to the steel frame of the test equipment using hold-downs and angle brackets. As a result, the lateral load carrying capacities of the glued particleboard shear wall (73.4 to 75.6 kN/m) were 3.2 times higher than that of the typical light-frame shear wall and higher than the experimental data of the cross-laminated timber (CLT) wall in the CLT handbook. All glued specimens failed at the hold-down and angle bracket, and there was no damage at the glue layer between a particleboard and timber studs. The shear performance with different combinations of species, stud size, and number of particleboards was not significantly different, and the shear strength of the nailed specimen was approximately 20% lower than that of the glued specimen.
- Researchpp 1096-1114Liu, E., Guo, Z., Shi, Y., Qi, B., Wang, Y., and Jiang, Y. (2023). "Simulation of cattle stomach processes applied to the fermentation of mixed manure and straw," BioResources 18(1), 1096-1114.AbstractArticlePDF
The cattle stomach was considered as the basis for simulating a proposed operation. Microenvironmental degradation mechanisms are understood to be key to the efficient utilization of straw and other resources. Through dynamic tracking of the change law of heat generated by microbial degradation of straw in the cattle stomach, this study used an orthogonal test to explore the optimal ratio of feeding feed, the degradation mechanism in the microenvironment, and the characteristics of cattle manure and straw anaerobic fermentation. The results showed that the number of days of fermentation and the ratio of straw and cattle manure had a significant impact on methane gas production, and the mixture ratio was 1:3, at 26 °C; within 20 days, the cumulative gas production was up to 78.9 L. The results also showed that rumen microorganisms, cattle manure, and mixed straw fermentation can be used at different ratios to obtain the change of methane production, and determine the best ratio to achieve the maximum gas production.
- Researchpp 1115-1127Kazemi Karchangi, Z., and Behrooz, R. (2023). "Preparation of microcrystalline cellulose using cotton yarn waste from the textile industry and evaluation of its characteristics," BioResources 18(1), 1115-1127.AbstractArticlePDF
In order to protect the environment and cellulose resources, yarn wastes from the textile industry, which contains a considerable amount of cellulose, can be used to produce microcrystalline cellulose. In this study, yarn waste was milled via a ball mill and was subjected to acid hydrolysis using sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid at different times. It was characterized through various tests to determine the particle size, degree of polymerization, bulk and tap density, water soluble substances, ash content, moisture absorption capacity, infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and thermogravimetric analysis. The Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy analysis showed that the chemical compositions of all the samples were the same. The X-ray diffraction measurement showed an increase in crystallinity after acid hydrolysis. The thermogravimetric analysis showed that prepared microcrystalline cellulose via acid hydrolysis had good temperature resistance. The results obtained showed that the cotton waste from textiles was able to produce cellulose microcrystalline at a pharmacy standard level.
- Researchpp 1128-1140Zhang, Y., Lin, X., Hu, C., and Yun, H. (2023). "Activated carbon from melamine-impregnated paper," BioResources 18(1), 1128-1140.AbstractArticlePDF
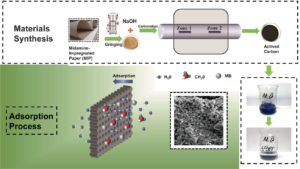
Activated carbon was prepared from waste melamine-impregnated paper (MIP) by pyrolysis with activation by NaOH. The adsorption parameters such as carbonization temperature (300, 350, 400, 450 °C), NaOH to C ratio (2:1, 3:1, 4:1, 5:1), and initial methylene blue (MB) dye concentration (20 to 600 mg/L) were studied. The adsorption results were fit by the Langmuir isotherm model and pseudo-second order kinetics. It was found that the activated carbon from MIP had a maximum adsorption capacity of 497 mg/g at 400 °C (carbonization temperature) and NaOH to C ratio (2:1). The highest removal of methylene blue (MB) via activated carbon was 99.4%. The π-π interaction between dye molecules and MIP active carbon was proposed to be a primary driving force for dye adsorption. This activated carbon adsorbent based on MIP was shown to be highly promising for water decontamination applications.
- Researchpp 1141-1154Chung, M.-J., and Wang, S.-Y. (2023). "Properties of cross-laminated oriented bamboo scrimber board (CL-OBSB)," BioResources 18(1), 1141-1154.AbstractArticlePDF
Physical and mechanical properties were evaluated for cross-laminated oriented bamboo scrimber board (CL-OBSB). Results of non-destructive testing revealed a linear relationship of parallel grain content with ultrasonic-wave velocity, dynamic modulus of elasticity (DMOEu), tap-tone velocity, and DMOEt values. In terms of the ratio of parallel grain, CL-OBSB 80%(//) possessed the highest modulus of elasticity and modulus of rupture values along with the greatest strength. The high grain content compressed in a parallel direction contributed to superior strength performance. Regarding the perpendicular compressive (C┴) strength, because both the CL-OBSB 40%(//) configuration and CL-OBSB have a mid-layer consisting of 60% parallel grain, CL-OBSB 40%(//) holds the largest C┴ value. Furthermore, the shear bond strength (S) showed that the S// value was 1.03 times that of the S┴ value with a wood failure frequency of 97%. After the dimensional stability test, the water absorption and volumetric swelling of the four CL-OBSB types ranged between 15.3% and 17.7% and 9.5% to 10.6%, respectively. In conclusion, the orthogonal configuration of CL-OBSBs can improve balance expansion and contraction in different directions, thus increasing its dimensional stability.
- Researchpp 1155-1165Yalçın, İ., and Esen, R. (2023). "Adhesive type’s effects on adhesive strength of densified reinforced laminated wood obtained from black poplar (Populus nigra L.)," BioResources 18(1), 1155-1165.AbstractArticlePDF
Wood material is the most critical indoor and outdoor building element that has not changed since ancient times. Previous studies have determined that the mechanical properties of tree species with low industrial importance, such as poplar wood, can be improved when they are subjected to the densification process. In addition, it has been determined in studies that the lamination process has a positive effect on the mechanical properties of the wood material. This study aimed to assess the impact of the glue type on the bonding strength during the lamination process of the densified black poplar (Populus nigra L.) using reinforcement material. Wood materials were subjected to densification at 140 °C for 10 min. Then, the densified boards were laminated in 3 layers with a reinforcement element (Kevlar®®, fiberglass, and carbon fiber) between the two wooden boards. It was determined that the best result was obtained with the combination of Akfix polyurethane resin type and carbon fiber reinforcement material (8.49 N/mm2).
- Researchpp 1166-1176Zhu, X., Xue, Y., Qi, P., Lan, Q., Qian, L., Shen, J., Gao, Y., Li, J., Mei, C., and Li, S. (2023). "Flexural properties of wooden nail friction welding of laminated timber," BioResources 18(1), 1166-1176.AbstractArticlePDF
The properties of single shear specimens connected by wooden nail frictional welding and twist nails were studied. The single shear properties of the specimens connected by wooden nail welding were lower than that of the twist nail specimens. The single shear capacity of the wooden nail welding specimen was determined by calculating the method of design value of the bearing capacity of the pin connection. Furthermore, the flexural properties of the wooden nail welding laminated timber were analyzed. Due to the larger diameter of the wooden nails compared with the twist nails, the wooden nail welding laminated timber in the elastic phase had higher stiffness. The elastic modulus of the wooden nail welding laminated timber exceeded the average elastic modulus of the constituent lumber pieces by 9.46%. The number of wood lumbers in wooden nail welding laminated timber had little effect on the elastic modulus of laminated timber, but the nail spacing had a certain effect. Therefore, in future research, it is recommended to use the construction method of twist nail connection to design the wooden nail welding laminated timber. In addition, the nail spacing should refer to the GB 50005 (2003) standard and the wood structure design manual.
- Researchpp 1177-1184da Silva, W. M., Zanuncio, A. J. V., Carvalho, A. G., de Castro, V. R., Carneiro, A. C. O., and Araújo, S. O. (2023). "Drying of eucalyptus logs from plantations with different spacing between trees," BioResources 18(1), 1177-1184.AbstractArticlePDF
The adoption of dense plantations can reduce the drying time of the logs, by optimizing this step. This study evaluated the drying of eucalyptus wood from plantations with different spacing (3 × 4; 3 × 3; 2 × 3; 1 × 3 m). Five trees were selected per treatment. Logs were removed from the base and at 50% and 100% of commercial height for drying evaluation for 60 days. The diameters of the eucalyptus trees from plantations with wider spacing were bigger, and the productivity per hectare was not affected by the spacing between trees. The planting spacing did not affect the initial moisture, which was higher for those removed from the top of the trees. The logs from the base from the denser spacing showed a drying rate 2.5 times higher than the same logs from the treatment with greater spacing, reducing the final moisture from 37.2 to 18.8%. The logs removed from the top of the trees reached the equilibrium moisture after the drying period. The reduction in the planting spacing reduced the wood moisture and the difference in this parameter between the logs removed from the base and top of the eucalyptus trunks.
- Researchpp 1185-1205Kılınç, İ., Budakçı, M., and Korkmaz, M. (2023). "The use of environmentally friendly abrasive blasting media for paint removal from wood surfaces," BioResources 18(1), 1185-1205.AbstractArticlePDF
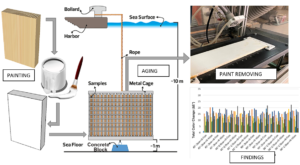
This study determined some physical changes that occur on wood surfaces aged in a marine environment resulting from the removal of coatings using environmentally friendly media blasting. Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) wood coated with water-borne and synthetic paints was exposed to a marine environment for 100 days. The aged paint layers were removed using five different media (sodium bicarbonate, hazelnut shell granules, corncob granules, walnut shell granules, and apricot kernel granules), varying blasting angles (45° and 90°), blasting distances (7 and 10 cm), air pressures (2 and 2.5 bar), and nozzle diameters (0.5 and 0.8 mm) using an automated blasting cabinet. The results showed that corn cob granules and sodium bicarbonate were less effective than other media for removing paint layers at the application parameters. The samples were tested for hardness, gloss, and total color change. Samples exhibited a remarkable total color change and gloss increase when the blasting distance was increased from 7 cm to 10 cm, while their hardness decreased. The highest gloss value was obtained on surfaces blasted with a nozzle diameter of 0.5 cm. Surfaces blasted with a nozzle diameter of 8 mm, however, yielded the highest total color change and hardest values.
