Volume 20 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 10370–10389Chen, J., Chang, X., Li, X., Xue, G., and Ding, Y. (2025). "Research on age-friendly kitchen cabinet design based on the Kano-QFD-FBS model," BioResources 20(4), 10370–10389.AbstractArticlePDF
In home-based elder care, kitchen cabinets serve a critical function in the daily lives of older adults. However, most cabinets currently available in the Chinese furniture market are designed for young and middle-aged users, neglecting the specific requirements of the elderly population. To improve user satisfaction with age-friendly kitchen cabinet products, this study proposed a conceptual design method based on the Kano-QFD-FBS integration model. First, customer requirements were identified through behavioral observation and in-depth interviews, then systematically categorized and prioritized using the Kano model. Subsequently, Quality Function Deployment (QFD) was employed to translate customer requirements into actionable design requirements. Finally, the seven key design elements derived from this process were incorporated into the Function-Behavior-Structure (FBS) model to determine the product’s structural components. This integrated approach enables a precise mapping from customer requirements to design elements, facilitating the development of age-friendly kitchen cabinet concepts. The study demonstrates the feasibility and effectiveness of the Kano-QFD-FBS model in age-friendly design research, providing valuable guidance and innovative perspectives for age-friendly kitchen design in China.
- Researchpp 10390–10405Liu, X., and Wang, W. (2025). "Evaluating perceptual quality of office chair surface materials through visual-tactile synesthesia assessment," BioResources 20(4), 10390–10405.AbstractArticlePDF
In the context of increasing demands for health, comfort, and aesthetic quality in office environments, this study investigated how surface materials of office chairs influence users’ emotional responses through visual–tactile perception. Ten typical office chair surface material samples were sourced from manufacturers and evaluated in a controlled laboratory setting. Participants provided feedback via a semantic differential questionnaire, designed using the Kawakita Jiro (KJ) method and expert screening. Visual-tactile evaluation data were analyzed using SPSS software, employing factor analysis to explore perceptual groupings and latent emotional dimensions. Results showed four material clusters aligned with different user needs, including support, comfort, skin-friendliness, and breathability. Factor analysis extracted four core dimensions: physical comfort, thermal-affective feedback, quality–breathability trade-off, and material essence. To further support material selection, a method was established using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to clarify the weight of each perceptual factor. This study integrated Kansei engineering with visual-tactile synesthesia theory to construct a multidimensional evaluation framework, providing implications for the design of office chairs with greater attention to emotional and health-related factors.
- Researchpp 10406–10413Yan, J., Liu, J., Feng, K., Luo, J., Wang, Y., and Zhang, N. (2025). "Preparation of carbon quantum dots from traditional Chinese medicine residues and their application in metal ion detection," BioResources 20(4), 10406–10413.AbstractArticlePDF
The disposal of residues from traditional Chinese medicine results in resource waste and poses non-negligible environmental concerns. While the synthesis of carbon dots (CDs) from green raw materials has been widely studied, the use of Chinese medicine residues (CMR) which are rich in ligno-cellulosic components as a carbon source for CDs preparation remained largely unexplored. Notably, converting CMR into carbon dots (CMR-CDs) offered a dual benefit: it enhanced resource utilization and mitigated the environmental impact of these waste materials. In this study, CMR-CDs were synthesized via a simple, eco-friendly one-step hydrothermal method for metal ion detection. The CMR-CDs demonstrated highly selective fluorescence quenching toward Fe³⁺, with a strong linear correlation (R² = 0.999) between fluorescence intensity and Fe³⁺ concentration (0 to 516 μmol/L). The detection limit was determined to be 6.0 μmol/L. These findings suggest that CMR-CDs hold significant potential for rapid and sensitive Fe³⁺ detection in future applications, while also highlighting the value of ligno-cellulosic waste in sustainable nanomaterial synthesis.
- Researchpp 10414–10424Samariha, A., and Khademieslam, H. (2025). "Effects of nanoclay and coupling agent on mechanical properties of Picea flour/polypropylene/nanoclay composite," BioResources 20(4), 10414–10424.AbstractArticlePDF
In this research, effect of nanoclay cloisite 30B and Coupling agent MAPP on mechanical properties of wood plastic composite that produced from picea flour/ poly propylene/ nanoclay inspected. for this propose, we used picea wood flour in constant level of 40%, MAPP in two levels of 2% and 4% and nanoclay in 4 levels of 0, 1, 3 and 5%. Next, wood plastic nano composite constructed by using of injection moulding method, and mechanical tests containing tensile, bending and impact performed on samples. Results showed that tensile strength and flexural strength and flexural modulus of composite enhance by increasing nanoclay and MAPP. Structural studies of wood plastic nano composite by diffraction of x ray also showed that distribution of nanoclay particles in polymer field is intercalation, and distance of between layers increase by enhancing of nanoclay particles amount.
- Researchpp 10425–10446Liu, Y., Li, J., and Hu, W. (2025). "Aesthetic preferences of Minnan folk wooden altar table," BioResources 20(4), 10425–10446.AbstractArticlePDF
The Minnan region in China boasts a rich religious culture, giving rise to the distinctive Minnan folk wooden altar table (MFWAT). This study investigated the MFWAT’s artistic characteristics and aesthetic preferences using Kansei Engineering (KE) and eye tracking (ET). The Semantic Differential (SD) method assessed perceptual evaluations, while eye tracking (ET) tests analyzed design elements via heat maps and areas of interest (AOI). Preference ratings complemented the objective measures. Factor analysis indicated that perceptual imagery comprised two principal components: stable-lightweight/dignified-relaxed and simple-complex/ceremonial-practical. Eye movement metrics showed decorative components (AOI-3) attracted significantly more attention than leg-foot (AOI-2) and panel components (AOI-1). Sample GA1 achieved the highest preference score, supporting the eye tracking (ET) findings. Decorative components were the most dominant elements. This integration of subjective and objective methods revealed MFWAT’s aesthetic characteristics and provides references for modern wooden furniture’s innovative design.
- Researchpp 10447–10459Bülbül, R., Ates, A. O., İmirzi, H. Özgür, Döngel, N., and Gökdemir, A. (2025). "Mechanical properties of laminated and aramid fiber-reinforced laminated wood elements," BioResources 20(4), 10447–10459.AbstractArticlePDF
The mechanical performance of laminated panels manufactured from beech (Fagus orientalis) wood was enhanced by reinforcement with aramid fibers. Specimens were organized into three primary groups: (i) a solid (control) group, (ii) laminated groups composed of two and three layers without aramid reinforcement, and (iii) laminated groups incorporating one or two layers of aramid fiber reinforcement. Results of compressive strength tests revealed that both laminated and aramid-reinforced laminated specimens exhibited improved performance compared to the control group. Static bending strength was improved by lamination alone, and inclusion of aramid reinforcement in the lamination interface gave further enhancement. Lamination by itself did not yield a statistically significant improvement in the modulus of elasticity in static bending. A significant increase in the modulus of elasticity was observed only when aramid fibers were embedded in the lamination interface. Moreover, dynamic bending strength was substantially improved by the incorporation of aramid reinforcement into the laminated structure. The enhancement ratios were 63.4% for two-layer laminates with one aramid layer and 123.5% for three-layer laminates with two aramid layers. These findings indicate that aramid fiber reinforcement is an effective strategy for improving the mechanical performance of laminated wood composites.
- Researchpp 10460–10486Yang, C., Ling, Z., Li, Z., Qin, Z., and Shen, J. (2025). "Numerical modelling and theoretical analysis of timber-concrete glued-in threaded rod shear connectors with and without notches," BioResources 20(4), 10460–10486.AbstractArticlePDF
Timber-concrete composite (TCC) structures offer superior bending stiffness, load capacity, and environmental benefits, but shear connector performance—critical for timber-concrete integration—remains a challenge. This study investigated TCC structures using notched shear connectors and glued-in threaded rods (GiRs) via push-out tests, finite element (FE) modelling, and parametric analyses. Twenty-seven specimens were tested, and the validated FE model simulated material nonlinearities and contact. The results showed increased GiR diameter and embedment length enhance load capacity and stiffness (GL series), with diminishing returns beyond a certain embedment. A 100 mm notch size optimized stiffness and load capacity for notched connectors (RG series). Parametric studies highlighted the influence of notch size, GiR embedment length, and diameter on load capacity, stiffness, and ductility. The FE model accurately predicted structural behavior, and theoretical models for load capacity prediction showed 1 to 32% error. This study provides valuable insights for optimizing TCC shear connector design and enhancing structural performance.
- Researchpp 10487–10503Alammari, B. S. (2025). "Physiological and biochemical processes in the exogenous administration of selenium nanoparticles and selenium/copper oxide nanocomposite to reduce salt stress in Zea mays L.," BioResources 20(4), 10487–10503.AbstractArticlePDF
Research on nanoparticles (NPs) is gaining increasing popularity as a way to enhance abiotic stress tolerance and improve crop productivity. This study assessed the effects of foliar spray of selenium NPs (Se NPs) and selenium/copper oxide nanoparticles (Se/CuO NPs) at 50 and 100 ppm on the growth and biochemical characteristics of Zea mays L. plants grown under saline stress conditions (100 mM). Se NPs and Se/CuO NPs were analyzed by energy dispersive X-ray, transmission electron microscopy, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analyses. The Se NPs and Se/CuO NPs were found to have an average particle size of 135.2 and 75.1 nm using the ImageJ tool. Shoot and root lengths, chlorophyll levels, protein, phenols, and flavonoids were all investigated in this study. Plant growth and chlorophyll concentration dropped under salt stress but were improved with the application of Se and Se/CuO NPs. The enzymes catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione reductase exhibited the highest values at 100 ppm of Se/CuO NPs, of 74.4, 132.1, and 43.2 mmol/g, respectively. Se and Se/CuO NPs reduced stress and increased chlorophyll. ZnO-NPs improved maize plants’ resistance to the unfavorable effects of saline soils. Finally, plant metabolism and abiotic stress tolerance were improved by Se and Se/CuO NPs.
- Researchpp 10504–10520Al-Saif, A. M., Abdel-Aziz, H. F., Abd El-wahed , A. E.- wahed N., Khalifa, S. M., Elnaggar, I. A., El-Shershaby, S. S., Farouk, M. H., Abulmeaty, S. A., Hammad, E. M., and Hamdy, A. E. (2025). "Pre-harvest foliar spray of calcium, GA3, and salicylic acid to enhance apricot yield and fruit quality," BioResources 20(4), 10504–10520.AbstractArticlePDF
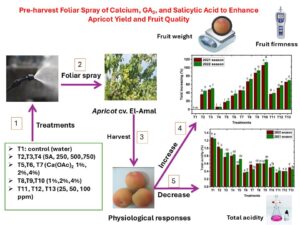
The impact of different pre-harvest foliar sprays was assessed relative to the yield and quality of apricot fruits (cv. El-Amal) under field conditions. Apricot trees were sprayed with various solutions, including salicylic acid (SA at 250 and 750 ppm), calcium acetate [Ca(OAc)₂ at 2% and 4%], calcium chloride (CaCl₂ at 2% and 4%), and gibberellic acid (GA₃ at 25 and 100 ppm) at the pit hardening growth stage before harvest. All foliar spray treatments positively affected fruit yield per tree compared to untreated plants. The most effective treatments were CaCl₂ at 4% and GA₃ at 100 ppm, followed by SA at 750 ppm and Ca(OAc)₂ at 4%. All treatments significantly increased fruit weight compared to the control group. GA₃ also significantly improved fruit firmness, outperforming all other treatments. Additionally, CaCl₂ at 2% and SA at 250 ppm resulted in higher firmness. SA at 750 ppm exhibited higher total soluble solid (TSS) content. While the foliar spray treatment without any solution resulted in the lowest fruit acidity, SA at 250 ppm had the highest acidity. In conclusion, pre-harvest foliar application of GA₃ (100 ppm), CaCl₂ (2%), and Ca(OAc)₂ (4%) can effectively enhance fruit yield and improve quality of apricots.
- Researchpp 10521–10531Kubojima, Y., Kato, H., Sonoda, S., and Nanko, K. (2025). "Estimation of wood density without weighing using bending vibration and static bending tests – Effect of span-to-height ratio on the estimation accuracy," BioResources 20(4), 10521–10531.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of the span-to-height ratio of wooden cantilevers on density estimation using bending vibration and static bending tests were examined. Bending vibration and static bending tests were performed for wooden cantilevers with various span-to-height ratios, and the densities of wooden cantilevers were estimated based on the measurements. The end condition of the cantilever was apart from the ideal condition for the smaller span-to-height ratios and approached to the ideal condition with the increase in the span-to-height ratio. The accuracy of the density without the correction decreased as the span-to-height ratio decreased. After correction based on the ideality of the end condition, the density could be accurately estimated without weighing the specimen.
