Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2906-2916Ahn, J., Lee, D., Youe, W., Lee, B., Lee, T., Seo, J., Kim, J., Wu, Q., Jeong, M., Sung, S., and Gwon, J. (2022). "Mechanical processing control in manufacturing nanofibrillated cellulose by interpreting its rheological properties," BioResources 17(2), 2906-2916.AbstractArticlePDF
Nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) has generated significant interest due to growing concerns about low carbon emission, environmental issues, and the guaranteed outstanding performance of applied products. Because of this trend, the importance of NFC production from an industrial angle has also been emphasized. In this study, ground pulps (at -300 μm clearance, 40 passes) were homogenized by using a pilot-scale microfluidizer (at 1,500 bar, up to 5 passes) to produce the NFC, and its characteristics were investigated. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images showed that the size and distribution of the NFC particles gradually decreased by up to three passes on account of the microfluidizer treatment and remained constant after that mechanical pass number. The viscoelastic properties (dynamic moduli) and viscosity of the NFC suspension steadily increased with three passes of the treatment, and the same trends as in the SEM images were observed after these passes. These results demonstrated that the NFC fluid behavior inside the equipment depends on the morphological properties of the manufactured NFC particles. Additionally, a good agreement between the morphological and rheological results implied that rheological analysis can be a reasonable approach to predicting the quality (size and distribution) of manufactured NFC particles.
- Researchpp 2917-2932Matan, N., and Songsamoe, S. (2022). "Controlled release of orange oil vapour to delay the ripening and mould growth of mangosteens (Garcinia mangostana) using rubberwood sawdust," BioResources 17(2), 2917-2932.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of rubberwood sawdust containing orange oil was evaluated relative to the quality of mangosteens after harvest, transportation, and storage. Orange oil emulsion (500 µl L−1) was added to the rubberwood sawdust as an adsorber and inserted into sachets in different amounts (0 g, 70 g, 140 g, 210 g, and 280 g). Then, each sachet was packed into a corrugated paper box (about 35 L) containing 15 kg of mangosteens, transported for 3 days by truck, and stored at 30 ± 2 °C for nine days. Results showed that the sachet containing 210 g of orange oil absorbent was able to delay the ripening of mangosteens by two stages of the ripening scale and inhibit mould growth. In addition, the overall quality of the treated fruit was good, especially in terms of loss of weight and firmness. Orange oil vapour from the sachet had a high antioxidant capacity that affected the pigment of mangosteen by preventing the degradation of chlorophyll and carotenoids. D-limonene was the main factor that inhibited mycelium growth on the fruit. This finding indicates that rubberwood sawdust containing orange oil in a paper box can be used to improve the quality of mangosteens in the fruit market.
- Researchpp 2933-2958Khadraoui, M., Khiari, R., Brosse, N., Bergaoui, L., and Mauret, E. (2022). "Combination of steam explosion and TEMPO-mediated oxidation as pretreatments to produce nanofibril of cellulose from Posidonia oceanica bleached fibres," BioResources 17(2), 2933-2958.AbstractArticlePDF
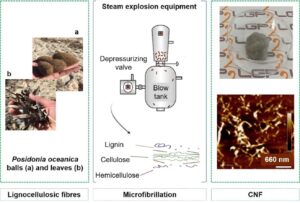
Posidonia oceanica is the dominant sea grass in the Mediterranean Sea. This biomass has great potential for use as a novel lignocellulosic material on an industrial scale. In this work, an innovative approach was applied to produce cellulose nanofibril (CNF) from Posidonia. First, fibres were isolated by a delignification-bleaching process, followed by refining and TEMPO-mediated oxidation to facilitate their further microfibrillation. Cellulose nanofibril suspensions were then produced by steam explosion or grinding (Masuko supermasscolloider). Next, CNF gel-like suspensions were characterized by several techniques such as morphological analysis (Morfi, optical microscopy, atomic force microscopy, transmission electron microscopy) and turbidity measurements. Nanopapers, prepared by filtration, were used to perform tensile tests. Finally, the efficiency of the combination of TEMPO-mediated oxidation and steam explosion was discussed. Obtained results show that the steam explosion process allows the production of CNF with a width between 4 and 10 nm and properties close to those obtained by the grinding process.
- Researchpp 2959-2976Liu, C., Cheng, S., Cao, S., Wang, P., and Cai, J. (2022). "Hygroscopic properties of six tree species with four tangential thicknesses," BioResources 17(2), 2959-2976.AbstractArticlePDF
The differences of hygroscopic property among six tree species with four thicknesses were examined. The density, chemical composition, crystallinity, equilibrium moisture content (EMC), and moisture absorption rate were measured by static saturated salt solution method, and the isothermal moisture absorption curve was fitted by the H-H model to analyze monolayer molecular adsorption and multilayer molecular adsorption. The results show that under the same relative humidity (RH), the EMC of Picea asperata and Populus deltoides were increased with increasing thickness, while that of Quercus spp. and Xanthostemon melanoxylon were decreased. The moisture absorption rate of P. asperata was the largest and that of X. melanoxylon was the smallest. When RH ranged from 0 to 97%, the monolayer molecular adsorption water amount of samples with different thicknesses of the six tree species gradually became close. With the increase of tree species density, the monolayer molecular adsorption water amount of the thinner sample is gradually greater than that of the thicker sample. The change of multi-layer molecular adsorption water content is consistent with that of EMC, Moisture absorption rate, monolayer molecular adsorption water, and multilayer molecular adsorption water are related to the chemical composition content, density, and thickness of tree species.
- Researchpp 2977-2996Tian, H., Shi, R., Wei, H., Lu, N., Sun, W., Ren, H., Zheng, Y., Li, J., and Wang, X. (2022). "Effects of rumen fluid as bioaugmentation additive on fungal diversity dynamics during sweet sorghum ensiling," BioResources 17(2), 2977-2996.AbstractArticlePDF
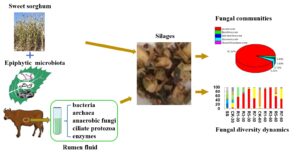
Fungi play a critical role in silage and rumen fluid, both of which share similar ecosystems. This study is designed to supplement sweet sorghum ensiling with the rumen fluid from beef heifers and evaluate the effect on fungal diversity dynamics and silage quality by high-throughput sequencing and chemical methods. Simultaneously, this study investigated the correlation between fungal communities and chemical compositions of silages. The results suggested that the addition of rumen fluid significantly affected the richness and diversity of fungi in silage. Alpha diversity of total fungi and the relative abundance of Pichia increased, while Schizophyllum and Penicillium decreased, following the supplementation of rumen fluid during 60 days ensiling. In addition, the silage quality was positively correlated with Pichia, but negatively correlated with Hannaella and Vishniacozyma. The findings reveal that the rumen fluid can improve the ensiling characteristics by effectively reducing the reproduction of adverse fungi. However, further research is required to verify the connection of specific pure fungal isolates with the fermentation performance of silage.
- Researchpp 2997-3013Zhu, G., Zhao, J., Chen, Q., Guo, Q., Cheng, D., Bijaya, G., and Li, W. (2022). "The comparative potential of four Compositae plants for phytoremediation of karst lead/zinc mine tailings contaminated soil," BioResources 17(2), 2997-3013.AbstractArticlePDF
A tailings concentration gradient experiment was done to demonstrate the comparative evaluation of phytoremediation for Cd, Pb, and Zn in karst lead/zinc mine tailings contaminated soil by four Compositae plants (Crassocephalum crepidioides, Bidens pilosa, Ageratum conyzoides, and Cosmos bipinnatus). The results indicated that the four species grown in the dose-gradient mine tailings were tolerant to these metals to varying degrees. C. crepidioides and B. pilosa were more tolerant to heavy metals, while C. bipinnatus was the most sensitive species. Despite the high concentrations of Pb and Zn in the culture substrate, there was only a small increase in the concentration of these elements in the plant organs compared to the control. However, all species were observed to be shoot accumulators for Cd. C. crepidioides accumulated a maximum of 132.1 and 159.1 mg·kg-1 of Cd in leaves and stems, respectively, and these results were higher than those in the roots (67.2 mg·kg-1) and soil (75.8 mg·kg-1). C. crepidioides can be regarded as a Cd-hyperaccumulator, with a Cd removal of 4.56% to 9.97% from the soil polluted by lead/zinc mine tailings after single season cultivation. The comprehensive analysis result indicated that C. crepidioides exhibited the highest tolerance, biomass production, and removal of heavy metals, indicating its ability in the phytoremediation of contaminated soil in Pb/Zn tailings affected area.
- Researchpp 3014-3024Lima, F. O., Lirya Silva, L. C., Ferreira, B. S., Morais, C. A, G., Bertolini, M. S., Barreiros, R. M., Azambuja, M. A., Caraschi, J. C., Favarim, H. R., and Campos, C. I. (2022). "Influence of the addition of Al2O3 nanoparticles and the duration of pressing on the physical properties of OSB panels," BioResources 17(2), 3014-3024.AbstractArticlePDF
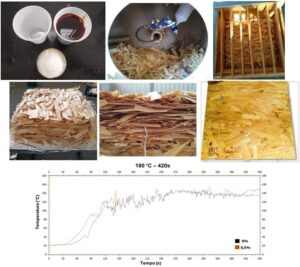
For greater durability, materials must withstand contact with water, making it difficult for biodegrading agents to attack. The present study produced and evaluated the heat transfer for two pressing times and the physical properties of OSB panels, produced with pinewood strands and Al2O3 nanoparticles addition. The nanoparticles were synthesized through the sol-gel-protein method and added to the resin in the proportion of 0.5%. During the pressing process, heat transfer and distribution in the central region of the particle mat were evaluated using a type K thermocouple. After its fabrication, the panels were characterized to evaluate density, moisture content, thickness swelling, and water absorption. The results obtained indicated that the nanoparticle addition caused a refractory effect in the central region of the mat, leading to a small reduction in the pressing temperature for the 600 s cycle. However, there was no compromise in resin cure, indicating good interaction of the panels with nanoparticles in water contact, for both pressing times. There was an improvement in the panel thickness swelling with the addition of 0.5% of Al2O3 nanoparticles, with all properties meeting the Class 1 indicators of the EN 300 (2006) standard.
- Researchpp 3025-3041Matin, P., Rahman, M. R., Huda, D., Bin Bakri, M. K., Uddin, J., Yurkin, Y., Burko, A., Kuok, K. K., and Matin, M. M. (2022). "Application of synthetic acyl glucopyranosides for white-rot and brown-rot fungal decay resistance in aspen and pine wood," BioResources 17(2), 3025-3041.AbstractArticlePDF
Due to its non-toxicity and environmentally friendly nature, carbohydrate-based fatty acid (CFA) esters are encouragingly used as antimicrobials and synthetic intermediates. They also are notably applied in food, surfactant, and pharmaceutical industries. In this respect, methyl 2,6-di-O-isopentanoyl-α-D-glucopyranoside (2), synthesized in a single step from methyl α-D-glucopyranoside (1), was converted into four other 3,4-di-O-acyl esters (3 – 6). All the newly synthesized CFA esters (2 – 6) were applied for the first time to study decay resistances of aspen (Populus tremula) and pine (Pinus sibirica) wood from decay caused by white-rot (Polyporous versicolor L.ex. Fr.) and brown-rot (Postia placenta (Fr). Cke.) fungi. Most of these CFA esters protected these woods from fungal attack, reduced deterioration, and preserved the weight percentage of woods at a certain point. It is noted that the CFA esters compounds reduced the deterioration and suppressed the weight percentage loss of wood at a certain point and from low to moderate decay resistances against the selected fungi.
- Researchpp 3042-3056Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Yahya, R., Alawlaqi, M. M., Fareid, M. A., Amin, B. H., and Abdelghany, T. M. (2022). "Copper oxide nanoparticles as fungistat to inhibit mycotoxins and hydrolytic enzyme production by Fusarium incarnatum isolated from garlic biomass," BioResources 17(2), 3042-3056.AbstractArticlePDF

Garlic (Allium sativum L.) being infected by mycotoxigenic fungi is one of the primary factors limiting its nutritional and medical value. Therefore, there is an urgent need to repress mycotoxigenic fungi utilizing safer treatments, possibly involving nanoparticles. Fusarium incarnatum was isolated from garlic (A. sativum L.) that showed fungal contamination and their identification was confirmed using amplified and sequenced internal transcribed spacer nuclear ribosomal DNA regions, which confirmed the isolation of F. incarnatum from all cultivars. Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) at different concentrations showed inhibitory activity against F. incarnatum growth and mycotoxins, particularly at 400 ppm. The production of F. incarnatum mycotoxins, i.e., beauvericins, fusarins, moniliformin, and enniatins, was inhibited to 62.8%, 45.4%, 58.1%, and 55.0%, respectively at 400 ppm of CuONPs compared to the control. Shrinkage of the F. incarnatum cell membrane and collapsing of the cell walls were recorded via transmission electron microscopy at 400 ppm, but negligible distortion appeared at 100 ppm of CuONPs. CuONPs at 100 ppm encouraged the activity of CMC-ase, zylanase, and amylase, while 200 and 400 ppm promoted less enzyme activity. The current findings suggest that CuONPs have a fungistatic effect on F. incarnatum and their mycotoxins.
- Researchpp 3057-3066Nazir, S., Asad, M. J., Saqlan Naqvi, S. M., Zainab, T., Malik, S. I., Mehmood, R. T., Khan, J., Sultana, T., Nasir, N., and Hassan, A. (2022). "An engineered Aspergillus fumigatus GH3 β-glucosidase with higher glucose tolerance," BioResources, 17(2), 3057-3066.AbstractArticlePDF
β-glucosidases (3.2.1.21) are present in all domains of living organisms, and their importance in a number of essential biological processes and industrial applications has been highlighted. They are interesting for biomass conversion because b-glucans are the world’s largest source of biomass. For this reason, several fungal β-glucosidases have been investigated. The β-glucosidase gene of Aspergillus fumigatus, as well as its mutants D262E and W263F, were cloned and expressed in Pichia pastoris in this study. Their optimum temperature, pH, glucose tolerance, metal ion effect, and Vmax, km, and kcat were determined. The optimal temperature for recombinant β-glucosidase was 65 °C. For mutant D262E, there is an improvement in pH stability ranging from 4 to 6. As compared to the D262E mutant and recombinant β-glucosidase, mutant W263F showed a higher glucose tolerance and kcat.
