Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3378-3397Hitka, M., Naď, M., Gejdoš, M., Joščák, P., Jurek, A., and Balážová, Ž. (2022). "The effect of body mass on designing the structural elements of wooden chairs," BioResources 17(2), 3378-3397.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of increased body mass of users on the structural loading of wooden chair elements following the changes in anthropometric parameters in the adult population of the Slovak Republic. Moreover, the functional parts of a wooden chair most affected by the weight gain of an adult population were defined. The strength analysis of the tested chair was conducted using the program ANSYS. In the software environment, the 3D volume model taking into consideration orthotropic properties of wood was created. The structural elements of chairs for the current adult population are designed for the weight of 110 kg. The results suggest that the weight necessary for designing the structural elements of chairs must be 150 kg (130 kg + 15%). Comfort, physical health, well-being, performance, and security can be increased by designing such a device and equipment meeting the needs of the human body in a long-term viewpoint. It is suggested to create the standard taking into account men with a weight of up to 150 kg. Based on the results of the strength analyses, a chair load with a user’s weight of 150 kg will require a change in the dimensions of the side rails and the cross-section of the legs. The new knowledge gained is helpful for a better design of chair wooden elements taking into account the anisotropic (directional) structure of natural wood.
- Researchpp 3398-3412Chaipetch, W., Khongnakorn, W., Yirong, C., Boonkan, J., Jaiyu, A., and Heran, M. (2022). "Performance of a high rate two-stage anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) for the treatment of palm oil mill effluent," BioResources 17(2), 3398-3412.AbstractArticlePDF
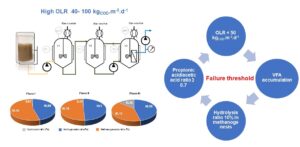
A two-stage submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor (2-sAnMBR) was operated to demonstrate the technology concept and to accelerate anaerobic biodegradation of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME). Then, the impact of different high organic loading rates (OLR) was investigated with a focus on water quality and biogas production. OLR higher than 50 kgCOD.m-3.d-1 induced an increase of volatile fatty acids (VFAs). As a consequence, the biogas production decreased from 19.8 to 11.0 L.d-1 and CH4 yield between 0.23 to 0.38 LCH4/gCODremoved. Nevertheless, the highest OLR (98 kgCOD.m-3.d-1) made it possible to reach a COD removal effectiveness of 70%, where the membrane contribution was around 23.9% to 34.7%. The ratio of propionic acid/acetic acid appeared to be a key indicator to prevent the AnMBR operation failure. Indeed, as soon as the value of 0.7 has been exceeded, several signs of AnMBR failure appeared. The methanogenic activity in AnMBR was inhibited by a hydrolysis ratio of 13% which transformed to VFA accumulation in system. The 250 mg.L-1 of Phenol concentration in POME was an inhibitory of the microbe in this system. Suspended solids concentration, proteins, polysaccharides, and volatile fatty acids were the substantial parameters that influenced the fouling rate.
- Researchpp 3413-3434Leggate, W., Outhwaite, A., McGavin, R. L., Gilbert, B. P., and Gunalan, S. (2022). "The effects of the addition of surfactants and the machining method on the adhesive bond quality of spotted gum glue-laminated beams," BioResources 17(2), 3413-3434.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of adding surfactants to polyurethane and resorcinol formaldehyde adhesives were tested relative to the gluability of spotted gum timber for structural glue-laminated beams (Glulam). While previous attempts to improve the bond performance of this very difficult to glue timber have focused primarily on timber surface preparations, this study concentrated on lowering the adhesive surface tension through added surfactants to improve the adhesive-timber surface wetting. Accordingly, 44 glulam samples were manufactured using polyurethane and resorcinol formaldehyde adhesives, with eight surfactant formulations and two different pre-gluing surface machining methods, i.e., face milling and planing. Although the surfactants were successful in drastically lowering the adhesive surface tension and improving adhesive spreading, none of the surfactant formulations tested were successful in improving the glulam adhesive bond qualities. Overall, the surfactant formulations produced considerably higher delamination, lower shear strength, and lower wood fibre failure compared to the control samples; therefore, they are not a viable solution to improve the gluing of spotted gum. The resorcinol formaldehyde adhesive and face milling produced considerably better results compared to the polyurethane adhesives and conventional planing.
- Researchpp 3435-3444Krajewsji, A., Jakiela, S., and Witomski, P. (2022). "Detection of old house borer larvae in wooden structures by acoustic emission method – Influence of larval size and sensor location," BioResources 17(2), 3435-3444.AbstractArticlePDF
The detection of old house borer larvae (Hylotrupes bajulus L.) in Scots pine wood (Pinus sylvestris L.) was performed using the acoustic emission (AE) method. Laboratory experiments (as preliminary) as well as real tests in full-sized building elements were performed. The sound energy of larvae with a mass of 0.011 g to 0.065 g placed in small samples of wood was calculated. A remarkable relationship was found between the calculated sound energy and larva mass. The AE measurement of an old house borer larva in construction element with a cross-section of 11.0 cm × 5.5 cm and a length of 203 cm was also performed. A remarkable drop in calculated sound energy was observed with increasing distance of the sensor from the larval presence. Similar measurements were also conducted in wood with a cross-section of 1.5 cm × 1.5 cm and a length of 203 cm. There was a smaller decline in the calculated energy of sound than in previous studies. For this reason, the AE method should be used in detecting wood-boring insects in furniture.
- Researchpp 3883-3905Voinov, N., Bogatkova, A., Zemtsov, D., Vititnev, A., and Marchenko, R. (2022). "Sedimentation of refined cellulosic pulp fines in the suspension during physical agglomeration," BioResources 17(3), 3883-3905.AbstractArticlePDF
A physical coagulator of fines was employed to separate suspensions comprising refined sulphate cellulose and waste paper, where no reagents were required. The physical coagulator was a porous cylinder with a rotating disk placed in its cavity. Using the MorFi Neo fibre analyser and the Hitachi SU 3500 digital microscope, a dispersed size distribution of well-developed fines in a suspension derived from softwood and hardwood pulp was obtained. The kinetics of fine sedimentation in the suspension was studied. The sedimentation rate of both individual agglomerates and a mass of them, as well as the magnitude of mass concentration in a cleared liquid, was determined. A relationship between the concentration of fines in the suspension and the structure of the pulp during their sedimentation was established. To intensify the fines sedimentation process, it was proposed to return a part of the sediment to the suspension passing into the physical coagulator. Process parameters for the sedimentation process and the construction of the sedimentation tank were obtained. The unit designed for collecting fines from the suspension is shown schematically. Use of this unit reduced the fibre sedimentation time, decreased the loads in wastewaters, and retained the consumer value of the pulp fibres.
- Researchpp 3906-3911Almeida, J. P. B., Rodrigues, E. F. C., Mascarenhas, F. J. R., Wolenski, A. R. V., Chahud, E., Branco, L. A. M. N., Pinheiro, R. V., Lahr, F. A. R., and Christoforo, A. L. (2022). "Influence of specimen dimensions in the determination of strength and modulus of elasticity in static bending of hardwoods," BioResources 17(3), 3906-3911.AbstractArticlePDF
In Brazil, standard ABNT NBR 7190 (1997) prescribes the determination of strength (fM) and modulus of elasticity (EM) in static bending from specimens measuring 5 cm × 5 cm × 115 cm. Thus, the relationship between the test span (L) and the specimen height (h) greater than or equal to 21 (L/h ≥ 21) is respected, ensuring that the effect of shear in the calculation of displacements is negligible (Euler Bernoulli Theory). Considering the expressive number of tree species cataloged in the Brazilian Amazon Forest, any procedure that aims to facilitate the realization of experimental tests is highly desirable because it provides the knowledge of unusual species. These wood species may potentially replace woods that have been traditionally used and historically exploited. Using five hardwood species, this research aimed to verify, while maintaining constant L/h ≥ 21 ratios, the influence of specimens dimensions in the determination of fM and EM. For all species studied, the statistical analysis found equivalence in the values of fM and EM determined as a function of the sample sizes. Therefore, respecting the ratio L/h ≥ 21, the size of the specimens does not influence the determination of strength and stiffness in static bending.
- Researchpp 3912-3928Zhou, C., Li, Z., Kaner, J., and Leng, C. (2022). "Development of a selection system for the colour of wardrobe furniture," BioResources 17(3), 3912-3928.AbstractArticlePDF

To solve the problem of pure perceptual and non-standardized selection of colour in furniture, a rational and reliable colour quantitative system was developed. This approach is beneficial to the upgrading and optimization of products by furniture manufacturing enterprises. The wardrobe colour selection system is based on the Munsell colour system, the colour harmony theory and the Birkhoff aesthetic colour selection system to construct a wardrobe colour selection system. It has three analytical parts, consisting of wardrobe colour selection and data analysis, which can provide a reference for the colour quantification used by furniture enterprises. Once the system was constructed, a company’s wardrobe colour selection and coated sheet sample was used as an example to test its efficacy. The wardrobe colour selection system was evaluated to optimize the design of the company’s original wardrobe product colour selection. The results showed that the wardrobe colour selection system improved consumers’ preference for the company’s wardrobe colour selection. The wardrobe colour selection system provides a reference for furniture companies, engineers and designers in product colour selection and optimization design, which is conducive to scientifically informed manufacture and a standard formulation of furniture colour.
- Researchpp 3929-3943Zhuang, B., Cloutier, A., and Koubaa, A. (2022). "Effects of strands geometry on the physical and mechanical properties of oriented strand boards (OSBs) made from black spruce and trembling aspen," BioResources 17(3), 3929-3943.AbstractArticlePDF
Black spruce is widely used for lumber production in Eastern Canada, and it has the potential to replace trembling aspen and paper birch for oriented strand board (OSB) manufacturing. This study evaluated the bending modulus of elasticity (MOE) and modulus of rupture (MOR), the internal bond (IB), and the thickness swelling (TS) of OSB panels made from black spruce and trembling aspen strands and how they were affected by strand geometry. All the panels met the CSA O437 (1993) standard for class O-2 properties except for the TS. The strand thickness had a significantly negative effect on the bending properties but a significantly positive effect on the IB and TS properties. The strand length had a significantly positive effect on the parallel bending properties but a significantly negative effect on the perpendicular bending properties and the IB, except for the TS. The OSB panels made from aspen obtained better bending properties, while the IB and TS properties were lower than those of the OSB black spruce panels. The results indicate that black spruce strands obtained from the Eastern Canadian softwood lumber industry are suitable for OSB production, but more work is required to reduce the TS.
- Researchpp 3944-3951Bispo, R. A., Trevisan, M. F., da Silva, S. A. M., Aquino, V. B. M., Saraiva, R. L. P., Arroyo, F. N., Molina, J. C., Chahud, E., Branco, L. A. M. N., Panzera, T. H., Lahr, F. A. R., and Christoforo, A. L. (2022). "Production and evaluation of particleboards made of coconut fibers, pine, and eucalyptus using bicomponent polyurethane-castor oil resin," BioResources 17(3), 3944-3951.AbstractArticlePDF
This research examined the influence of the compositions between coconut fiber (Cocos nucifera) and wood particles (Pinus taeda L. and Eucalyptus saligna) on physico-mechanical properties of homogeneous particleboards. The exploratory study was carried out under Tukey’s contrast test of means, at 5% significance level, with the following compositions: 100% coconut fiber (F100 P0 E0); 50% coconut fiber, 25% pine particles, and 25% eucalyptus particles (F50 P25 E25); and 50% of pine particles and 50% of eucalyptus particles (F0 P50 E50), with particle moisture content between 0% to 2% and 10%, in mass, of polyurethane-castor oil (PU-Castor) resin. Three panels were produced for each composition. The physico-mechanical properties such as density, moisture content, swelling in thickness after 24 h of immersion in water, perpendicular tensile strength, static bending strength, and modulus of elasticity were evaluated using standard methods. The results obtained indicated the potential for using coconut fiber for the production of homogeneous particleboards in view of the minimum criteria required by the normative documents, with emphasis on the physical property of swelling after 24 hours, which obtained a statistically equivalent average relative to the treatment that contained only wood particles.
- Researchpp 3952-3964Chen, B., Yu, X., and Hu, W. (2022). "Experimental and numerical studies on the cantilevered leg joint and its reinforced version commonly used in modern wood furniture," BioResources 17(3), 3952-3964.AbstractArticlePDF
The cantilevered leg joint commonly used in modern wood furniture was studied by numerical and experimental methods. A novel joint was proposed and compared with the typical joint commonly used in the cantilevered leg. Both of them were made of beech wood (Fagus orientalis Lipsky). The experimental results showed that the bending moment capacity of the novel joint was remarkably higher than the typical joints, which confirmed that the novel structure had a better mechanical performance. The numerical analysis was conducted according to GB/T 10357.3 standard, the results showed that the stresses of the typical joint were mainly concentrated on the wooden components, while the stresses of the novel joint were concentrated on the metal connectors. The stress concentration obtained by the finite element method (FEM) was consistent with the failure modes of the experimental tests, which provides a reliable method for evaluating and optimizing the novel furniture structure.
