Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2172-2186Abenghal, L., Lamoudan, H., and Brouillette, F. (2023). "Alkylated phosphorylated fibers: A new substitute for silicone in release paper manufacturing," BioResources 18(1), 2172-2186.AbstractArticlePDF
The production of release coatings has been increasing in recent years because of their use in various fields. However, commercially available release coatings are regarded as non-recyclable. As a consequence, the repulping of these residues is difficult, and their presence in the recycling stream represents an important source of contamination. One solution to this problem is to use new coating materials that can replace the siliconized backing, provided that these new materials are recyclable. As a solution to this problem, the authors propose the use of alkylated phosphorylated fibers to produce an environmentally friendly and inexpensive release paper. The results show that a surface application of hydrophobic phosphorylated fibers reduces the surface free energy of the paper support, as well as the peel strength, which facilitates the separation of the adhesive tape.
- Researchpp 2535-2550Teacă, C.-A. (2023). “Crystalline structure of cellulose in wood after chemical modification using cyclic acid anhydrides (maleic and succinic),” BioResources 18(2), 2535-2550.AbstractArticlePDF
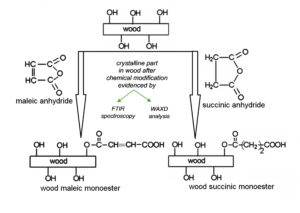
The chemical modification of wood can be directed to improve various properties, e.g., the dimensional stability, hardness properties, and/or durability properties, against weathering. In this study, a Romanian softwood species Abies alba L. was treated and chemically modified using two cyclic acid anhydrides, i.e., maleic and succinic, to improve its interfacial properties relative to unmodified wood. Structural changes, with focus on the evolution of crystalline part in wood after chemical modification, the water absorption, and the water repellent efficiency, were determined. Maleic anhydride exhibited a lower reactivity towards wood substrate than succinic anhydride, presumably because of their different chemical structure (maleic anhydride is very sensitive to the presence of water). It was found that the percentage of water absorption was diminished, primarily after the succinic anhydride treatment. The chemically modified wood was characterized via Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy and wide-angle X-ray diffraction methods. The crystalline part from wood structure was evidenced in relation to the employed anhydride in chemical modification approach.
- Researchpp 2551-2572Yer Çelik, E. N., Ayan, S., Özel, H. B., Turfan, N., Mehmet Yer, B., and Abdaloğlu, G. (2023). “Effects of melatonin applications on Anatolian black pine (Pinus nigra J. F. Arnold. subsp. pallasiana (Lamb.) Holmboe) afforestation performance in semi-arid areas,” BioResources 18(2), 2551-2572.AbstractArticlePDF

Melatonin, a substantial hormone, is a natural antioxidant agent that functions as a protector against the harmful effects of free radicals. Studies have found that “exogenous melatonin” applications have a positive effect on the growth and development of plants. This study investigated the adaptation of the seedlings that were transported from the nursery to the afforestation site for the process of planting. In 2019 the 2+0 aged bare-rooted Kastamonu/Taşköprü Anatolian Black pine seedlings, which are suitable for planting in semi-arid areas, were selected as research materials. Four different doses of “exogenous melatonin” (250, 500, 1000, and 1500 μM) were administered through two different methods (root-dipping and needle-spraying). Morphological seedling characteristics and bioactive chemical variables were measured for the control group and the seedlings treated with different doses of melatonin. Antioxidant enzyme activities were identified. When both the needle-spraying and root-dipping methods for melatonin application were evaluated in terms of morphological and biochemical variables, the best results were determined in low doses (250 to 500 μM). The results suggest that melatonin provides support to the metabolic process for the resistance of seedlings to low temperatures and semi-arid climatic conditions.
- Researchpp 2574-2588Liu, M., Zhu, X., Chen, Y., and Kong, Q. (2023). “Evaluation and design of dining room chair based on analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and fuzzy AHP,” BioResources 18(2), 2574-2588.AbstractArticlePDF
From the perspective of user needs, a design evaluation system for dining room chairs that can meet user needs was established. Based on the analytic hierarchy process (AHP), the user needs of a dining room chair were quantitatively analyzed by combining qualitative and quantitative methods. Moreover, the comprehensive weight ranking of 14 factors in the object hierarchy was obtained, which provided the design focus and quantitative indexes for designers in the early stage of dining room chair design. Then, in the later stage of dining room chair design, the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (FAHP) method was used to quantitatively evaluate the three design schemes and obtain the optimal design scheme. The experimental results showed that the user needs evaluation results were positively correlated with the “excellent” grade in the FAHP method. This indicated that the evaluation system realized a symmetry, reliability, and effectiveness between the user needs evaluation and FAHP. Therefore, it can be concluded that this evaluation system based on AHP and FAHP proposed in this study has reliability and validity, and it can be used for design evaluation to judge the popularity of products, enhance the competitiveness of products, and reduce product design costs.
- Researchpp 2589-2610Hassan, B., Fitzgerald, C., and Minett, R. (2023). “Toxicity, repellency, and horizontal transfer of foam insecticides for remedial control of an invasive drywood termite, Cryptotermes brevis (Blattodea: Kalotermitidae),” BioResources 18(2), 2589-2610.AbstractArticlePDF
Laboratory tests were conducted to compare imidacloprid and fipronil foams against various criteria to determine the effect of the deposit conditions, exposure method, and exposure time on the toxicity, repellency, and horizontal transfer of selected foam insecticides. Results of toxicity assays showed that imidacloprid and fipronil foams caused significantly higher mortality than control treatments; however, fipronil foam in fresh or old deposits killed Cryptotermes brevis pseudergates more quickly in the short and continuous exposure tests than foam containing imidacloprid. In brief exposure tests, imidacloprid failed to kill all termites when exposed to fresh deposits and delayed total mortality when exposed to dry residues. The mortality of C. brevis pseudergates was also significantly quicker when the fipronil foam was applied topically compared with the imidacloprid foam. In the repellency test, termites were not repelled from the surface treated with fipronil foam, but more than 90% repellency was observed after 24 h of exposure to imidacloprid-treated surfaces. Moreover, the non-repellent mortality of C. brevis with fipronil was significantly higher than imidacloprid in avoidance tests. Results showed that fipronil was effectively transferred to untreated termites from live or dead donors exposed via residual and topical spray.
- Researchpp 2611-2625Liu, W., Chen, M., Liu, H., Yi, B., Hu, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, D., and Li, C. (2023). “Isothermal drying characteristics and kinetic mechanism for tobacco with different water content,” BioResources 18(2), 2611-2625.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of drying temperature on the drying characteristics of tobacco was investigated with different water content. The isothermal drying characteristics and kinetics of three kinds of tobacco on the production line of a tobacco factory in Hubei were studied by halogen water analyzer. The drying characteristics of tobacco with different water content under isothermal conditions were evaluated by water loss characteristics, water diffusion coefficient, and activation energy. The results showed that the drying time of cut tobacco was reduced by increasing the drying temperature within a certain range. The water diffusion coefficient of cut tobacco decreased with the increase of temperature from 70 to 100 °C, and increased with the increase of initial water content. The activation energy of cut tobacco was related to the production process. The activation energy in the experiment was as follows: CT-2 > CT-3 > CT-1. Five drying models were used for non-linear fitting of the drying behavior of tobacco. The fitting degree of the Midilli model was the highest, reaching 0.9944. This data will be useful in the design of tobacco drying equipment.
- Researchpp 2626-2638Wang, L., Zhang, W., Chai, X., Zhou, Y., and He, C. (2023). “Effect of dry heat and polishing treatment on the germination rate and performance of seeds from Cassia obtusifolia L. as a turf filling material,” BioResources 18(2), 2626-2638.AbstractArticlePDF
Seeds from Cassia obtusifolia L., i.e. Semen cassiae (SC) were evaluated as environmentally friendly filler particles for artificial turf. The goal was to avoid unwanted germination problems of SC under wet conditions. This work evaluated the influence of different pretreatments on the germination rate and performance of SC. After the combination of polishing and dry heat (90 °C, 72 h) treatment, the germination rate of SC decreased to 0% and the activation energy increased to 216 kJ/mol. Compared with the untreated SC, the thermal stability of SC improved, with an initial degradation temperature of 214 °C and a pyrolysis residue of 31.9%. Additionally, the resilience and the water absorption of SC as a filler material increased to 4.13% and 169%, respectively. This study provides an effective pretreatment method for the solution of germination problem and the performance improvement of SC. This makes the pretreated SC a prospective candidate as an environmentally protective granular filling material.
- Researchpp 2639-2656Özyürek, Ö., and Çöpür, Y. (2023). “Integrated biorefinery for production of biodegradable film, bioethanol, and soda pulp from corn stalks,” BioResources 18(2), 2639-2656.AbstractArticlePDF
In traditional pulping, black liquor is burned in an alkali recovery system to produce energy. According to the integrated forest biorefinery (IFBR) concept, hemicellulose is partially pre-extracted prior to pulp production to generate value-added products. Corn stalks have a remarkable carbohydrate content (75% w/w), and thus were examined in this study in terms of the IFBR concept. The hemicelluloses were pre-extracted with hot water (90, 120, 135, and 150 °C), NaOH, and NaOH + NaBH4 (50, 70, and 90 °C) for 4 h. NaOH charges of 16.7, 26.7, and 33.3% were explored. The extracts were utilized to produce bioethanol and biodegradable films, and papermaking pulps were produced from the solid fractions. Differences among groups were identified via analysis of variance, and the Duncan’s test was applied to determine those differences that were significant. The results showed that the alkaline pre-extraction (26.7% NaOH at 50 °C) removed 35.6% of the xylose from the stalk structure. The liquid fraction collected from the hot water pre-extraction at 150 °C gave a 14.7% (g/100 g soluble material) yield of bioethanol. Moreover, the theoretical ethanol yield was calculated as 89.4%. The addition of gluten and nanocellulose to the xylan enabled the production of high-quality biodegradable films. Furthermore, the pulps produced from the hot water pre-extracted solid fractions were comparable in yield and pulp properties to the control soda pulp.
- Researchpp 2657-2669Valkonen, M. J., Cucharero, J., Lokki, T., Rautkari, L., and Hänninen, T. (2023). “Preparation of fully bio-based sound absorbers from waste wood and pulp fibers by foam forming,” BioResources 18(2), 2657-2669.AbstractArticlePDF
Building materials that are bio-based and produced from waste streams have a substantial effect on the carbon footprint of buildings. In this study, the authors prepared fully bio-based sound absorbers from waste wood and other cellulosic materials. Cutter shavings (CSs), softwood pulp, and cellulose powder (CP) were used as raw materials to prepare sound absorber samples using the foam-forming technique. The fully bio-based sound absorbers prepared were mechanically stable. However, an increase in CSs content decreased their mechanical properties, and samples with high CSs content became difficult to handle. The CP increased the mechanical properties, but it did not affect the sound absorption of the samples. The sound absorption properties of these fully bio-based materials could be tuned by carefully selecting CSs and fiber contents and adjusting the thickness of the material. Greater CSs content decreased the sound absorption properties of the materials. This decrease was mainly due to an increase in the average pore size, leading to poorer sound energy dissipation by visco-thermal effects.
- Researchpp 2670-2692Adutwum, J. O., Sakagami, H., Koga, S., and Matsumura, J. (2023). “Space-time analysis of the longitudinal variation in wood specific gravity of teak and its effect on tree growth and development,” BioResources 18(2), 2670-2692.AbstractArticlePDF
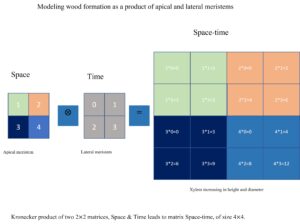
The space-time structure of a teak wood specific gravity (SG) dataset was analyzed using a mixed-effects model. Spatial correlation increased in space, a phenomenon attributable to the maturation of apical meristems, while the temporal correlation of vascular meristems decreased over time. The decay of temporal correlation over time was attributed to the diminishing crown effect on the later formed wood further away from the pith, morphogen gradient, and probably changing microenvironmental conditions. The Kronecker product was used to collect spatiotemporal data on the intricate dynamic process of the evolution of the apical and lateral meristems. The results showed that height and relative radial distance (RRD) (i.e., the flow of time with wood formation) were statistically significant factors, with their interaction showing no significance. The results confirm the usefulness of using the space-time approach to elucidate the interaction between the apical and lateral meristems, two major inherent biological systems that control tree growth and wood formation dynamics. To understand the origins of patterns that vary both temporally and spatially in the tree, future work should describe the variation of SG within the tree due to increasing height (space) and diameter (age) as a matrix; then the correlation function can be modelled.
