Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3279-3294Shi, S. Q., Cui, Z., Jin, Y., Smith, L., Wu, H. F., and Neogi, A. (2023). “Fiberboard made from scrap denim: Characterization of its properties by effective bulk modulus elastography,” BioResources 18(2), 3279-3294.AbstractArticlePDF
Fiberboards from scrap denim were fabricated using two different resins, melamine urea formaldehyde (MUF) and polymeric methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (pMDI). Resin content and MUF-pMDI weight ratio were studied. Physical and mechanical tests determined the modulus of elasticity (MOE), modulus of rupture (MOR), internal bond (IB), thickness swell (TS), and water absorption (WA). The resin content had significant impact on all properties. The MOE and IB were affected by the MUF-pMDI ratio. With 17 wt% more pMDI resin portion in the core layer of the denim boards, the IB for the denim fiberboard with a resin content of 15% was enhanced by 306%, while by 205% for the resin content of 25%. The increase in pMDI portion in the core layer of the boards improved both TS and WA of the scrap denim fiberboard. Effective bulk modulus elastography (EBME) was used to measure the acoustic reflection for the estimation of the strength properties of the denim fiberboard. The modulus results from EBME were correlated to the MOR, MOE, and IB of the denim fiberboard. A high correlation was found between the modulus from EBME and IB (R2 > 0.98). EBME can be a great technique to evaluate the bulk modulus distribution of the composites.
- Researchpp 3295-3307Guan, M., Bai, L., Fu, R., Han, Y., and Liang, H. (2023). “Effects of the type of lactic acid bacteria, hot-pressing temperature, and moisture content of fermented bamboo residue on the properties of self-bonding common particleboards,” BioResources 18(2), 3295-3307.AbstractArticlePDF
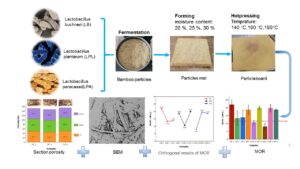
Self-bonding bamboo particleboards were prepared via hot pressing of bamboo residue fermented by lactic acid bacteria. An orthogonal experiment was designed to investigate the effects of three factors (type of lactic acid bacteria used for fermentation, moisture content (MC) of the fermented residue, and hot-pressing temperature) on the resulting self-bonding particleboards. The bending strength and internal bonding strength of the prepared self-bonding particleboards were tested. Fracture characterization was performed on the cross-section of the prepared self-bonding particleboards after bending breakage. The hot-pressing temperature, moisture content (MC), and type of lactic acid bacteria of the fermented residue had a significant effect on the mechanical strength of self-bonding particleboards, and with increased hot-pressing temperature, the strength of self-bonding particleboards increased. Analysis of the cross-sectional morphology and porosity confirmed the significant effect of hot-pressing temperature on the density distribution of self-bonding particleboards. The self-bonding particleboard produced at the hot-pressing temperature of 180 °C, MC of 30%, and that used Lactobacillus plantarum as a fermentation strain showed the best overall performance and reached Chinese standard requirements for common particleboards.
- Researchpp 3308-3318Kang, C.-W., Hashitsume, K., and Jang, E.-S. (2023). “Investigation of the sound-absorbing performances of pure coffee grounds,” BioResources 18(2), 3308-3318.AbstractArticlePDF
Various natural sound-absorbing materials such as rice by-products, coir fiber, date palm fiber, peanut husks, hardwood cross-sections, and forest by-products have been introduced to replace petroleum-based sound-absorbing materials in previous studies, and their sound-absorbing performance was significant. This study investigated the sound-absorbing performance of pure coffee grounds as an eco-friendly sound-absorbing material. After inserting coffee grounds into cylindrical holders with lengths of 20, 30, and 40 mm, the density of the coffee grounds was adjusted from 0.2 to 0.5 g/cm3. Then, the sound absorption coefficients were measured by an impedance tube. As the thickness and density increased, the sound absorption coefficient at low frequencies improved. However, the sound absorption coefficient at high frequencies decreased. The optimal noise reduction coefficient (NRC) of coffee grounds investigated in this study was 0.61 at a density of 0.3 g/cm3 and thickness of 50 mm. This result shows a sound-absorbing performance that is comparable to other natural sound-absorbing materials. This study concludes that coffee grounds have high use-value as an eco-friendly sound-absorbing material.
- Researchpp 3319-3327Khademibami, L., Shmulsky, R., Senalik, C. A., Seale, R. D., Ross, R. J., Mohammadabadi, M., Ward, K., and Williamson, T. (2023). “Flexural testing of structural insulated panels before and after creep testing,” BioResources 18(2), 3319-3327.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of duration of load testing on flexural properties of structural insulated panels was investigated herein. Structural insulated panels were manufactured by a member of the Structural Insulated Panel Association (SIPA) in accordance with International Code Council-Evaluation Service Report 4689. Two panel depths 16.5 cm and 31.1 cm (6.5 in. and 12.25 in.) were tested in short duration 1/3-point bending per American Society for Testing and Materials standards. All structural insulated panels had joints or discontinuities in the foam layer in a location that was subject to shear stress during the bending tests. Failure mode for all panels was horizontal shear within the foam layer. Within each panel depth, no statistically significant differences were detected between the maximum load values before and after creep testing. This finding indicates that the creep test loading was not detrimental to the strength of the structural insulated panels. While the results were not deemed to be statistically different for the Δymax (midspan deflection at Pmax) for the 31.1 cm depth class, they were statistically different from the 16.5 cm depth class. Overall, it appeared that there was minimal effect of the creep test loading on Δymax of the SIPs.
- Researchpp 3328-3341Lee, S.-H., Jo, H. M., and Lee, J. Y. (2023). “Manufacture and characterization of cationic nano-fibrillated cellulose from cotton pulp,” BioResources 18(2) 3328-3341.AbstractArticlePDF
The applicability of cotton-bleached soda pulp (C-BSP) was investigated as a raw material for manufacturing cationic nano-fibrillated cellulose (NFC) via quaternization of anionic NFC using glycidyl-trimethyl-ammonium chloride (GMA). The anionic NFC was prepared by beating and micro-grinding C-BSP, and quaternization was performed post treatment to induce a charge reversal in anionic NFC. The characteristics of cationic NFC manufactured using C-BSP and hardwood-bleached kraft pulp (Hw-BKP) as a control were analyzed. Relatively higher mechanical energy was required to prepare anionic NFC from C-BSP than that from Hw-BKP. Fourier transform infrared and zeta potential analyses results showed that quaternization by GMA post treatment electrostatically induced charge reversal in anionic NFC. However, GMA did not affect the fiber width and viscosity of the cationic NFCs. It was found that cationic NFC could be manufactured via quaternization of anionic NFC manufactured from C-BSP using less GMA than that for Hw-BKP.
- Researchpp 3342-3356Ünver, A. (2023). “Antioxidant properties, oxidative stability, and fatty acid profile of pitaya fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus and Hylocereus undatus) seeds cultivated in Turkey,” BioResources 18(2), 3342-3356.AbstractArticlePDF
Pitaya is a tropical fruit from a newly cultivated plant in Turkey that has increasing economic value. In this study, its seed properties were investigated. Pitaya fruit samples used in the research were obtained from local producers in the Gazipaşa/Antalya region. The dry matter, protein, oil, and ash content of H. polyrhizus and H. undatus pitaya seeds were 89.7% to 89.1%, 19.8% to 17.5%, 22.8% to 24.0%, and 2.8% to 4.09%, respectively. The oil and protein contents of the seeds were very high. The total phenolic content, α-tocopherol content, γ-tocopherol content, free radical scavenging activity, and induction time of H. polyrhizus and H. undatus pitaya seeds were 12.8 to 11.9 mg GAE/g dry sample, 3.67 to 2.75 g/kg oil, 1.29, 1.64 g/kg oil, 46.9% to 51.5%, and 5.37 to 5.07 h, respectively. Seeds contained significant amounts of phenolic compounds and tocopherols, which play an important role in increasing oxidative stability. The percent inhibition of DPPH indicated that pitaya seeds may be evaluated as an antioxidant source. Unsaturated fatty acids were high in seed oils of both pitaya species. Linoleic acid, a polyunsaturated fatty acid, was dominant in both pitaya species. The chemical properties of the seeds were similar to those of species grown in tropical countries. Future studies should investigate other pitaya species grown in Turkey.
- Researchpp 3357-3372Zhang, Z., Ma, Y., Qin, C., Liu, X., Li, X., Huang, H., and Yao, S. (2023). “Quantitative determination of petroleum hydrocarbons in oily sludge following efficient n-heptane separation,” BioResources 18(2), 3357-3372.AbstractArticlePDF
Accurate analysis of the main chemical components of oil-bearing sludge is an important prerequisite for effective soil remediation and resource reuse. However, precise analysis of the extract components is difficult to achieve because of the mutual interference of saturates, aromatics, and resins, collectively called SAR, and asphaltene that are introduced during chloroform extraction. In this study, SAR was efficiently extracted using n-heptane, while asphaltene components were retained in soil because of their insolubility in n-heptane. The maximum yield of SAR extraction was 27.0%, indicating an increase of 1.75% compared to chloroform extraction. The extracted SAR components were separated by chromatography and the main structural units and components were analyzed. The results show that saturates, aromatics, and resins have a single component, a high content of major components, and contain fewer impurities using n-heptane extraction. Moreover, the solubility of asphaltene was inhibited during the effective extraction of SAR components with n-heptane and did not influence the subsequent analysis of SAR component. Efficient SAR extraction, accurate SAR component analysis, and high efficiency asphaltene separation was achieved using n-heptane-extraction-assisted pyrolysis. This provides a new method for the component analysis of oily sludge and promotes its efficient separation.
- Researchpp 3373-3386Yang, X., Jiang, H., Ma, L., Yang, W., Zhao, X., Hu, C., and Ge, Z. (2023). “Micro image classification of 19 high-value hardwood species based on texture feature fusion,” BioResources 18(2), 3373-3386.AbstractArticlePDF
For classification of wood species with similar microstructure, 19 high-value hardwood species of Papilionaceae, Ebenaceae, and Caesalpiniaceae were used as experimental objects. Images of transverse sections, radial sections, and tangential sections were collected by Micro CT. Local binary patterns (LBP) are often used for feature extraction. LBP deformed forms such as uniform LBP, rotation-invariant LBP, and rotation-invariant uniform LBP were fused with Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix (GLCM) to form three fusion features. The fusion features were combined with support vector machine (SVM) or BP neural network to realize wood classification. The texture feature fusion method was found to be better than the single feature classification. Among them, the effect of uniform LBP and GLCM fusion was the best, and the classification accuracy combined with SVM was the highest. The evaluation of the classification of 19 kinds of hardwood mainly depended on transverse sections, and its accuracy was higher than that of the radial and tangential sections. Therefore, the classification results of transverse sections should be taken as the main evaluation basis for the classification of the 19 high-value hardwood species.
- Researchpp 3387-3399Hamdan, S., Said, K. A. M., Rahman, M. R., Sawawi, M., and Sinin, A. E. (2023). “Gambus Hadhramaut: The Malaysian malay lute tuning retrieval,” BioResources 18(2), 3387-3399.AbstractArticlePDF
This study identified elements in a simple homemade gambus from a local crafter using a scientific approach. The gambus was made from geronggang wood (Cratoxylum arborescens), a light Malaysian hardwood with pink sapwood, distinct from the heartwood with brick-red or deep pink. The sound was processed to generate fast Fourier transform (FFT) and time-frequency analysis (TFA) using PicoScope and Adobe Audition software, respectively. The gambus A 1st string (note C4#) displayed a harmonic overtone at the 1st and 2nd octave. The 2nd string (note A3) showed harmonic overtone at the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd octave. The 3rd string (note D3#) showed a significant fundamental peak and harmonic overtone at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th octave. The 4th string (note A2#) displayed consistent harmonic overtones at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th octave. The 5th string (note E2) had a harmonic overtone at the 5th octave. Gambus A showed an inconsistent signal in the 6th string (note D2#) with inharmonic overtone at 3.35th and 6.79th overtones. The gambus A 1st to 6th strings are C4#, A3, D3#, A2#, E2, and D2#, respectively. The gambus B 1st to 6th strings are C4, G3, D3, A3, E3, and B2, respectively.
- Researchpp 3400-3412Kang, L. H., Seo, Y. B., and Han, J. S. (2023). “Producing flexible calcium carbonate from waste paper and their use as fillers for high bulk paper,” BioResources 18(2), 3400-3412.AbstractArticlePDF
Microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) was prepared from post-consumer old corrugated container (OCC) material, which was first disintegrated in water, cleaned to remove impurities, and then fibrillated by grinding. Those processed MFCs were treated with in-situ formation of calcium carbonate by adding calcium oxide and injecting carbon dioxide into the mixture up to the ratio of 1:40 (MFC : calcium carbonate) by weight. The MFCs had a dark brown color initially but turned into high brightness materials similar to commercial ground calcium carbonate (GCC) after the in-situ formation process. The MFCs that had calcium carbonate attached on their surfaces, which were lengthy and flexible, were called flexible calcium carbonate from OCC (FCCO). Paper containing FCCO gave higher bulk, higher stiffness, and higher tensile index without lowering smoothness when compared to the paper containing commercial GCC. However, brightness was slightly lowered because of initial low brightness of the OCC. This study also demonstrated the feasibility to substitute wood fibers up to 5% with FCCO without lowering essential properties for printing paper. Benefits of the waste paper are savings of both wood resources and production cost.
