Volume 16 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 6781-6790Elbidi, M., Hewas, A., Asar, R., and Mohd Salleh, M. A. (2021). "Comparative study between activated carbon and biochar for phenol removal from aqueous solution," BioResources 16(4), 6781-6790.AbstractArticlePDF
Removal of phenol from wastewater using local biochar (BC) was investigated, while using activated carbon (AC) as a reference material. The main parameters affecting the sorption process were initial concentration, contact time, pH, and temperature. Statistical analysis of the results showed that the maximum removal percent when using AC and BC were 95% and 55%, respectively. Experimental data showed that the removal of phenol has fast kinetics and reached equilibrium within 5 minutes. The Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models were applied to fit the adsorption experimental data. Pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic models were employed.
- Researchpp 6791-6798Cavus, V. (2021). "Weathering performance of mulberry wood with UV varnish applied and its mechanical properties," BioResources 16(4), 6791-6798.AbstractArticlePDF
Mulberry wood is used in carpentry, fences, turnery, and garden architecture. In this study, various mechanical properties (modulus of rupture, modulus of elasticity, Janka hardness, and screw holding resistance) of mulberry (Morus alba) wood and its weathering performance after applying 3- and 5-layer UV system parquet varnishes with different surface applications were investigated. The varnished materials were aged using UV lamps for 252 h and 504 h, and the aged specimens were compared with non-aged specimens. The results of the variance analyses found that all tests were significant. According to the results, it was found that while the yellow color (b*) tone value, lightness, and glossiness (perpendicular (⊥) and parallel (║) direction at 20°, 60°, and 85° angles) values decreased for both varnish applications, the pendulum hardness value increased. The adhesion strength (pull-off) test (MPa) to the surface first decreased and then increased.
- Researchpp 6799-6813Wei, X., Xu, S., Sun, L., Tian, C., and Du, C. (2021). "Propagation velocity model and two-dimensional defect imaging of stress wave in larch (Larix gmelinii) wood," BioResources 16(4), 6799-6813.AbstractArticlePDF
The propagation law of stress wave in larch (Larix gmelinii) wood was studied in this work. External factors affecting the propagation velocity of stress wave in wood cross-section were studied using the orthogonal experiment method. The most influential factors were shown by the experimental results, and the parameters of the propagation velocity model of stress wave in larch wood were optimized. Based on the optimized propagation velocity model, combined with the traditional defect determination method, a twelve-directional stack imaging (TDSI) steps system was developed for larch wood internal defect detection. The analysis results showed that of the three external factors of temperature, moisture content, and illumination duration, temperature had the greatest influence on the propagation velocity model of stress wave in larch wood cross-section. Using TDSI to image the defective larch wood not only can locate the defective area, but also it can achieve a high imaging precision of 95.52%, and the imaging precision is unrelated to the location of the defect, which has a good quantitative defect detection effect.
- Researchpp 6814-6830Zhang, X., Li, L., Tian, J., Li, N., Zuo, L., Yan, L., He, J., and Du, X. (2021). "H2O2 bleaching of brown pulp with adsorbed xylan and its modifying effects on the mechanical properties of paper," BioResources 16(4), 6814-6830.AbstractArticlePDF
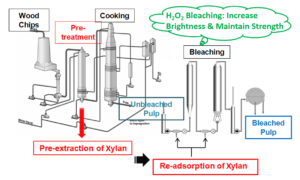
Xylan is the primary hemicellulose in most hardwood species, especially in birch. Research has highlighted the exploitation of xylans as a strength-enhancing additive to paper due to the current trend for the effective utilization of biomass. In this paper, a new pulping process was proposed, which involved the extraction of xylan prior to pulping, followed by the re-adsorption of the pulp after the final stage in the digester, followed by a suitable bleaching process. The aim of this work was to bleach hardwood kraft pulp (brown pulp) with adsorbed birch xylan via hydrogen peroxide and study the effect of the bleaching parameters on the paper properties. The results showed that the optical properties of paper decreased; however, the mechanical properties increased after the brown pulp adsorbed birch xylan. During the bleaching process, better mechanical properties were obtained with shorter bleaching times and lower bleaching temperatures, initial pHs, and MgSO4 dosages. However, the optical properties were improved as the bleaching time, temperature, initial pH, and MgSO4 dosage were increased. The adsorption of birch xylan could effectively modify the mechanical properties of paper made from brown pulp under various phases.
- Researchpp 6831-6849Liu, S., Hu, C., and Lu, K. (2021). "Manufacture of Mikania micrantha vinegar and investigation of its repellent activity for Forcipomyia taiwana," BioResources 16(4), 6831-6849.AbstractArticlePDF
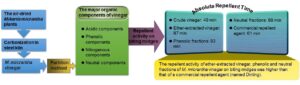
Crude vinegar was prepared from Mikania micrantha plants using a steel kiln. The ether-extracted vinegar and acidic, phenolic, and neutral fractions were obtained by the partition method. The fundamental properties of crude vinegar, including its fractions applied to repel biting midges (Forcipomyia taiwana), were investigated. Results indicated that the crude vinegar had a moisture content of 91%, Gardner color value of 11.2, a reddish-brown color, specific gravity of 1.0164, pH of 5.36, organic acid content of 2.50%, and soluble tar content of 0.78%. In ether-extracted vinegar of M. micrantha, the acidic component was the major ingredient, followed by the neutral, phenolic, and nitrogenous components. The main organic compounds of the acidic, phenolic, nitrogenous, and neutral components were acetic acid, phenol, 3-pyridinol, and 2-furanmethanol, respectively. The results also demonstrated that the crude vinegar, ether-extracted vinegar, and the phenolic and neutral fractions effectively repelled biting midges, with absolute repellent times of 49, 87, 83, and 99 min, respectively. The repellent activity of ether-extracted vinegar and the phenolic and neutral fractions of M. micrantha vinegar on biting midges was higher than that of a commercial repellent agent (named Dinling) with absolute repellent time of 61 min.
- Researchpp 6850-6869Kazeem, M., Ajijolakewu, K., and Abdul Rahman, N. (2021). "Cellulase production by co-culture of Bacillus licheniformis and B. paralicheniformis over monocultures on microcrystalline cellulose and chicken manure-supplemented rice bran media," BioResources 16(4), 6850-6869.AbstractArticlePDF
Single cultures and co-cultures of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus paralicheniformis isolated from compost were evaluated for their carboxymethyl cellulase (CMCase) and filter paperase (FPase) production potential. Using a medium supplemented with microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), in the co-culture, CMCase and FPase activities increased 8.87- and 2.28-fold and 10.15- and 3.20-fold over B. licheniformis and B. paralicheniformis monocultures, respectively. The synergistic behavior of the two isolates might be due to the consumption of hydrolysis product (glucose, cellobiose) by one or both of the isolates, which improved their metabolic performance for cellulase secretion. Optimal conditions for cellulase production by this co-culture were a temperature of 45 °C, and pH 7 at 180 rpm in a medium containing rice bran at 1% (w/v) and chicken manure as nitrogen supplement at 2% (w/v). The maximum CMCase and FPase produced under the above conditions were 79.8 U/mL and 12.5 U/mL, respectively. This corresponds to 257.4- and 59.5-fold enhancement in CMCase and FPase activity, respectively, over B. licheniformis monoculture, and 306.9- and 83.3-fold increase with respect to the B. paralicheniformis monoculture. These results indicate that improved cellulase production can be achieved through co-culture and chicken manure nitrogen-supplement.
- Researchpp 6870-6890Wang, H., Wu, J., and Chen, Z. (2021). "Carbon footprint accounting and low-carbon path optimization for imported timber-based wooden furniture supply chains," BioResources 16(4), 6870-6890.AbstractArticlePDF
Using an imported timber-based solid wood box bed (2000 mm × 1800 mm) as the functional unit, the ILCD 2011 midpoint assessment method was used to measure the life cycle carbon emissions of the product. Using this assessment, the Dijkstra algorithm was adopted to determine the shortest supply chain path and to obtain the minimum carbon footprint of the supply chain. Results showed that the total carbon footprint of the wood bed was 464 kg for the control case. For experimental cases, the carbon footprint ranged from 456 kg to 517 kg CO2-eq. The upstream process was identified as the primary contributor to the carbon footprint, accounting for 74.6% to 80.7% of the total carbon footprint, followed by the downstream and the core-stream processes. Configuration of a timber harvesting system with lower fuel consumption, purchasing timber from areas within shorter transportation distance, and reducing the proportion of incineration for waste treatment were feasible solutions to reduce the carbon footprint of the product. A case study optimizing the low-carbon path for the wooden furniture supply chain determined the shortest path for the participants in each link, such that the minimum total carbon footprint of the supply chain was 463 kg CO2-eq.
- Researchpp 6891-6909Han, X., Dai, J., Qian, W., Zhu, Z., and Li, B. (2021). "Effects of dowels on the mechanical properties of wooden composite beams in ancient timber structures," BioResources 16(4), 6891-6909.AbstractArticlePDF
In order to provide more accurate suggestions for the restoration of ancient timber buildings, five types of specimens were designed for static loading tests. The tree species used for the specimens was larch. The wooden composite beams were composed of purlins, tie plates, and fangs. The study analyzed the effects of the number and position of dowels on the mechanical behaviors of wooden composite beams in ancient timber buildings. The bending moment, slippage, strain of the wooden composite beams under the deflection of the beam allowed according to code, and the ultimate bearing capacity of the wooden column composite beams under failure conditions were examined. The test results showed that the dowels could improve the bending capacity of the wooden composite beams. The even distribution of the dowels was beneficial in reducing the sliding effect of the wooden composite beams. Under the amount of deflection allowed by the code, the mid-span section strain along the height of the wooden composite beam approximately conformed to the plane section assumption. The wooden composite beam still had bending capacity after each member failed. The results of this study illustrated that dowels improved the overall mechanical properties of the wooden composite beams.
- Researchpp 6910-6920Yan, F., Tian, S., Du, K., and Wang, X. (2021). "Effects of steam explosion pretreatment on the extraction of xylooligosaccharide from rice husk," BioResources 16(4), 6910-6920.AbstractArticlePDF
Rice husk, which contains hemicellulose, can be used as a renewable resource to produce xylooligosaccharide (XOS). However, it is difficult to destroy the lignin structure of rice husk. Steam explosion (SE) is an effective method in destroying the lignin structure to enhance the release of hemicellulose and cellulose. In this study, SE pretreatment was used at different high pressures. The results showed that the lignin structure of rice husk could be collapsed by SE pretreatment, and the chemical structures of rice husk were evaluated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The SE pretreatment resulted in the significant increase of XOS content and antioxidant activities. In summary, SE pretreatment under 2.5 MPa was chosen as a good option for the production of XOS from rice husk.
- Researchpp 6921-6932Sinković, T., Jambreković, B., and Sedlar, T. (2021). "Interpreting research results for the physical and mechanical properties of wood: An approach not dependent on a juvenile/mature wood boundary," BioResources 16(4), 6921-6932.AbstractArticlePDF
The interpretation and presentation of research on the physical and mechanical properties of wood in the radial direction is important for the estimation of technological properties in primary wood processing. It is common practice to define the boundary between the juvenile and mature wood zone of tree growth because of the differences in wood properties in these two zones. The juvenile and mature wood zones can be determined statistically based on the significance of the difference in the properties in a particular zone. This paper presents the insufficiency in the statistical determination of the boundary between juvenile and adult wood. Such limitations detract from the potential value and technological exploitation of wood as raw material. Statistical tests yielded zones that were too wide for the transition of juvenile wood to mature wood. Representations of the distribution of properties in the radial direction also complement the knowledge for assessing the technological properties based on the researched use of the presentation of polynomials of the second degree and the display of the Tukey HSD test in the form of comparison tables. The graphical representations by groups of the tested annual rings of fir wood also help to assess the technological properties.
