Volume 17 Issue 1
Latest articles
 Award Winner: 2023 BioResources Early Career Investigator Award
Award Winner: 2023 BioResources Early Career Investigator Award
Baral, N. R., Banerjee, D., Mukhopadhyay, A., Simmons, B. A., Singer, S. W., and Scown, C. D. (2024). “Integration of genome-scale metabolic model with biorefinery process model reveals market-competitive carbon-negative sustainable aviation fuel utilizing microbial cell mass lipids and biogenic CO2,” BioResources 19(3), 4056-4086.Hubbe, M. A. (2024). “Artists, papermakers, and the future,” BioResources 19(3), 4053-4055.- Researchpp 1090-1105Siam, N., Lipeh, S., Uyup, M., Ahmad Juhari, M., Talip, N., Che Amri, C., and Abdullah, N. (2022). "Anatomical and physical properties of three lesser-known timber species from Malaysia," BioResources 17(1), 1090-1105.AbstractArticlePDF
The purpose of this study was to determine the anatomical and physical properties of three lesser-known Malaysian timber species, i.e., mahang (Macaranga hosei), medang (Litsea costalis), and terap (Artocarpus scortechinii). Correlation factors that influenced the density and shrinkage were also discussed. From the results obtained, terap wood had the longest fibre (1421 µm), followed by medang (1309 µm), and mahang (1161 µm). Terap, medang, and mahang were categorized as having very thin fibres. The density of terap, medang, and mahang had average values of 504 kg/m3, 485 kg/m3, and 474 kg/m3, respectively. In addition, terap wood also showed the highest tangential shrinkage (3.8%), followed by mahang (2.2%) and medang (1.5%) wood. This present study showed that the density was significantly influenced by the fibre length, fibre wall thickness, vessel diameter, and number of vessels. In addition, the shrinkage was highly correlated with the density. Based on the conducted research, mahang, medang, and terap show potential as alternative raw material to fulfill demand in wood-based industries.
- Researchpp 1106-1119Fernández-Serrano, Á., and Villasante, A. (2022). "Modulus of rupture prediction in Pinus sylvestris with multivariate models constructed with resonance, ultrasound, and wood heterogeneity variables," BioResources 17(1), 1106-1119.AbstractArticlePDF
Multivariate models with multiple linear regression (MLR), artificial neural network (ANN), and k-nearest neighbors (KNN) were developed to predict the modulus of rupture of Pinus sylvestris structural timber. The aim of this study was to develop and compare these models obtained from resonance and ultrasound tests, static modulus of elasticity tests, and different measured wood feature. Resonance tests were performed in the three vibration modes (edgewise, flatwise, and longitudinal) to obtain the fundamental resonant frequencies. To compare the goodness-of-fit of the different models, the 10-fold cross-validation method was used, which proved to be an adequate strategy to avoid overfitting. The variable with the best predictive capacity of the modulus of rupture was knottiness. The error was notably lower in the multivariate than the univariate models. The ANN and KNN algorithms showed no improvement over the MLR. The most suitable MLR for prediction of the modulus of rupture was the model with four variables: knottiness, edgewise dynamic modulus of elasticity, velocity of ultrasounds, and longitudinal resonant frequency.
- Researchpp 1120-1135Jo, H. M., Lee, Y. H., and Lee, J. Y. (2022). "Fabrication of eco-friendly time indicator using cellulose-based materials," BioResources 17(1), 1120-1135.AbstractArticlePDF
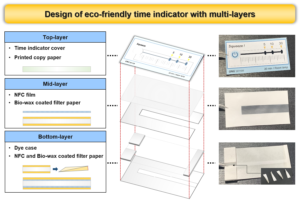
An eco-friendly time indicator (TI) was developed using cellulose-based materials. The TI comprises a dye, copy paper, nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) film, and filter papers coated with NFC slurry and/or paraffin-free biowax. A suitable dye and its conditions were determined by observing the dye solutions and the migration pattern at the different concentrations. Commercial filter papers were prepared, and the dye migration rate, depending on physical properties, was evaluated. NFC was coated to control the dye migration rate of filter paper. In addition, biowax was used to impart hydrophobicity to filter papers used for supporting NFC films, storing the dye, and allowing the migration of dye. Finally, a TI was fabricated using those components. Methylene blue was selected as a dye for the TI due to its deep color and high solubility. The results showed that the key property of filter paper affecting the dye migration rate was the pore size. The migration rate could be reduced when NFC was coated on both sides of the filter paper. Since biowax modified the hydrophobicity of filter paper surface, it was used to make the NFC film-supporting paper, location for dye storage, and bottom-layer. In conclusion, a multilayered TI could be assembled using cellulose-based materials.
- Researchpp 1136-1143Kobayashi, H., and Kurata, Y. (2022). "Relationship between photomorphogenesis and tree growth in Cryptomeria japonica assessed using light emitting diodes," BioResources 17(1), 1136-1143.AbstractArticlePDF
Recently, there has been considerable interest in establishing tree-rearing methods for breeding nursery trees, which are similar to the methods employed in plant factories to produce vegetables. Studies have shown that the efficiency of tree cultivation can be improved by changing the wavelength of the lighting that is used to raise young plants and that light emitting diodes (LEDs) are effective for this purpose. In this study, the effect of blue (450 nm), red (660 nm), and white (combination of blue and yellow (525 nm) LED lights was investigated for rearing Cryptomeria japonica saplings. 7 saplings with each LED were prepared and reared for 52 weeks in a constant environment chamber (Temperature: 23 ± 2 °C, relative humidity 50% ± 10%), and their growth rates and root system morphology were compared. After 52 weeks of breeding, red light induced slightly more stem growth than white light. Blue light was nearly three times more effective in stem growth than white light. Furthermore, the wavelength of light affected the root system morphology. Many root branches were observed in saplings reared under red light, while marked taproot growth was observed in saplings reared under blue light. There was a possibility that saplings could be produced more efficiently by using LED.
- Researchpp 1144-1160Mahathaninwong, N., Wandee, S., Totwaree, N., and Romyen, P. (2022). "Aerobic composting and vermicomposting of durian shell and citrus peel wastes," BioResources 17(1), 1144-1160.AbstractArticlePDF
Aerobic composting and vermicomposting processes were compared in the co-composting of durian shells and citrus peels. For decomposers, the microorganism catalyst from the Land Development Department, i.e., the LDD1 catalyst, and earthworms were used. The moisture contents of the durian shells and citrus peels were 84.6% and 77.3%, respectively, and the pH of the shells and peels were relatively low, as these are sources of potassium. The experiments utilized four different reactors: durian shells (100%) in reactor 1; durian shells and citrus peels (50% to 50% ratio) in reactors 2 through 4; with the LDD1 catalysts in reactor 3 and the earthworms in reactor 4. The temperature, pH, moisture content, electrical conductivity, NaCl, organic matter, organic carbon, C to N ratio, nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium), germination index, and size of the compost were analyzed according to the standards of the Land Development department (2013). Throughout the composting process, the pH tended to increase, although citrus peels, with a low pH of 3.95, were used as a raw material. At the end of the composting process, reactor 4, which used earthworms as decomposers, passed the standard criteria, yielding a germination index of 90%.
- Researchpp 1161-1172Koyuncu, M. (2022). "Experimental investigation of epoxy matrix and pine sawdust reinforced wood-polymer composite materials," BioResources 17(1), 1161-1172.AbstractArticlePDF
Mechanical, thermal, and water absorption properties of the composites have been studied as a function of sawdust content, using different weight percentage. The characteristics properties of the composites were studied using differential scanning calorimetry and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Field emission scanning electron microscopy was used to understand the interfacial bonding. The obtained results showed that the 15 wt% composites exhibited the highest tensile strength (7.5 MPa) and flexural strength (8.9 MPa) compared with the 5 wt%, 30 wt%, 40 wt%, and 50 wt% composites. A good interfacial combination was formed between 15 wt% of sawdust and epoxy resin. In terms of the tensile and flexural strength, the differential scanning calorimetry analysis confirmed that matrix modification could improve the mechanical properties and thermal stability of the composites compared to neat resin. The Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy spectrum showed the presence of functional groups pertaining to composites. The absorption data of the composite showed that the water uptake increased as the amount of sawdust in the composite increased. The 5 wt%, 15 wt%, 30 wt%, and 40 wt% sawdust composites also displayed less water absorption behavior (1.534%, 1.871%, 2.492%, and 4.127%, respectively) compared to the 50 wt% composite.
- Researchpp 1173-1186Li, R., Cao, J., Cai, L., Wang, P., Qu, H., Chen, M., Fu, J., and Chen, Y. (2022). "Effects of combined membrane-covered systems on aerobic composting of strawberry vine and chicken manure," BioResources 17(1), 1173-1186.AbstractArticlePDF
A combination of semipermeable membrane-covered composting systems and greenhouses was used to investigate the effects of different insulation systems on the aerobic fermentation of mixed raw materials and changes in the characteristics of fermentation feedstock. The combination of semipermeable membrane-covered and greenhouse systems increased the peak temperature by 6.53 °C, the average fermentation temperature by 28.2%, and extended the duration of the effective high-temperature stage of fermentation (temperature ≥ 50 °C) by 14 days. The decomposition percentage of solid organic matter in the enhanced group was 11.8% higher than that in the normal group, and the fermentation cycle was shortened by 5 days. The duplication provided by using both the semipermeable membrane-covered and greenhouse systems was conducive to the harmless treatment of raw materials, promoted the maturity and efficiency of composting, and reduced the content of biologically toxic substances. This study provides a theoretical basis for improving the efficiency of aerobic fermentation and the safe treatment of solid waste.
- Researchpp 1187-1204Cao, S., Zhou, S., Liu, J., Liu, X., and Zhou, Y. (2022). "Wood classification study based on thermal physical parameters with intelligent method of artificial neural networks," BioResources 17(1), 1187-1204.AbstractArticlePDF
In this study, 65 kinds of wood samples were classified by using artificial neural networks based on the measured value of wood thermal physical parameters. First, the thermal conductivities and the thermal diffusion coefficients of the wood samples were measured. The transient temperature rise curve of wood samples during the test process was recorded, and the characteristic values of the transient temperature rise curve were extracted by logarithmic curve fitting. The emissivity spectrum representing the thermal physical properties of wood surface was measured, and the characteristic spectral data were selected according to the principal component analysis. An artificial neural network model was established based on the extracted feature values and characteristic spectral data to classify the wood species. The experimental results showed that the comprehensive correct classification rate of the proposed wood classification method was 99.85%. In addition, the proposed wood classification method was compared with a wood classification method based on laser induced breakdown spectrum and near infrared spectrum, which indicates the feasibility of wood classification based on the values of wood thermal physical properties.
- Researchpp 1205-1231Zhang, Q., Lu, L., Liang, M., Wang, D., Huang, D., and Zhu, Y. (2022). "Efficient treatment of lead-containing wastewater using bagasse biochar modified via hydroxylapatite," BioResources 17(1), 1205-1231.AbstractArticlePDF
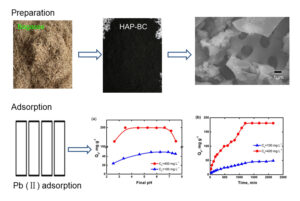
A hydroxylapatite bagasse biochar composite was prepared via the hydrothermal chemical precipitation method with bagasse as the primary raw material. The adsorption capacity of hydroxylapatite bagasse biochar composite for Pb(II) was determined using a series of batch adsorption experiments. The results showed that the point of zero charge value was near neutral pH, and the optimal pH ranged from 4.0 to 7.0. Langmuir isotherms were suitable for fitting the isothermal adsorption process of Pb(II) by the hydroxylapatite bagasse biochar composite. The maximum adsorption capacity of hydroxylapatite bagasse biochar composite in terms of Pb(II) was 210 mg·g-1 at 25 °C. Fourier transform infrared spectrometry analysis indicated that oxygen-containing functional groups were abundant on the external and internal surfaces of the composite sample, which provided numerous chemical sorption sites and resulted in an increase in the adsorption capacity of the composite sample. The Pb(II) removal mechanism of the hydroxylapatite bagasse biochar composite primarily utilized surface diffusion, electrostatic attraction, surface complexation, ion exchange, and a dissolving-coprecipitation reaction. The composite sample was suitable for the treatment of lead-contaminated water (containing zinc, arsenic, cadmium, etc.), which was a promising environmentally friendly material.
- Researchpp 1232-1240Jancikova, V., and Jablonsky, M. (2022). "Delignification of hemp stalk using a low transition temperature mixture composed of choline chloride and lactic acid," BioResources 17(1), 1232-1240.AbstractArticlePDF

This work used a literature search to select the most suitable system for the delignification process of annual plants. This process was evaluated in terms of lignin removal from plant biomass. Based on previous experiments, a low transition temperature mixture (LTTM) was used, which was a mixture of choline chloride and lactic acid in a molar ratio of 1:2. Samples of hemp fibers were examined. The delignification of biomass was monitored by changing the content of the main components. After application of the solvent at a temperature of 100, 120, or 140 °C and a delignification time of 2 or 4 h, the lignin content expressed by Kappa number decreased to the level of 22 to 13.7. Yields of hemp fibers sown after LTTM application ranged from 72.5 to 90.6%. The results confirmed that the use of LTTM (choline chloride/lactic acid) is a suitable system for the extraction of lignin from biomass. The findings showed that LTTM was an effective delignifying agent for hemp, as a relatively low Kappa number of 13.7 and a yield of 75.9% were achieved after only 2 h and at 140 °C.
