Volume 17 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 4116-4135Li, Y., Yao, L., Guo, Y., Liu, R., Wu, Y., Jia, H., Yu, X., Wang, C., Hu, Z., and Chen, C. (2022). "Comparative analysis on the mechanical properties of mortise-tenon joints in heritage timber buildings with and without a ‘Que-Ti’ component," BioResources 17(3), 4116-4135.AbstractArticlePDF
Three kinds of typical Chinese traditional mortise-tenon joints were tested. The effects of sparging on the deformation, hysteretic behavior, strength and stiffness degradation, and energy dissipation of the mortise-tenon joints were studied via low-cycle reversed loading tests with and without a ‘Que-Ti’ component. The results showed the following: the bearing capacity of the straight-tenon joint was the strongest, and the hysteretic loop of the through-tenon joint and half-tenon joint were asymmetric due to the asymmetry of the tenon form. The half-tenon joint was most likely to pull out the tenon, and the tenon pulling condition of the half-tenon joint can be effectively alleviated by adding a ‘Que-Ti’ component. From the perspective of energy consumption, it was found that the energy consumption capacity of the mortise-tenon joints after adding a ‘Que-Ti’ component was stronger than the joints without a ‘Que-Ti’ component. This shows that the ‘Que-Ti’ can be used as an effective component in terms of enhancing the mechanical properties of the mortise-tenon joints.
- Researchpp 4136-4150Qin, Y., Jiang, G., Xu, Q., Li, P., Wei, S., and Liu, J. (2022). "Preparation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxy-valerate) (PHBV)-based composites using poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) and bagasse," BioResources 17(3), 4136-4150.AbstractArticlePDF
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) matrix composites were prepared by powder blending and a hot-pressing process with poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) as a toughening agent and bagasse as a reinforcing agent. The effects of different contents of PBAT and bagasse on the mechanical properties, the thermal properties, and the section morphology of the composites were studied. By comparing the powder blending process with the conventional twin-screw melt extrusion blending process, it was found that the composites prepared by the powder blending process had better appearance and mechanical properties. With the increase of the PBAT content, the mechanical strength and modulus of the PHBV/PBAT composites decreased, but the flexibility increased. The addition of PBAT also caused the crystallinity of the composites to decrease and the thermal stability to increase. Based on the mass ratio of 60% PHBV and 40% PBAT, different contents of bagasse were added. It was found that the mechanical strengths of the composites were lower than that of the composites without bagasse, but the modulus was greatly improved. The crystallization properties of the composites improved, and the thermal stability decreased. This indicated that the addition of bagasse could reduce the material cost and improve the properties of PHBV.
- Researchpp 4151-4166Ma, J., Quan, G., Yan, J., Ippolito, J. A., Cui, L., Wang, H., Qiu, T., and Sun, Y. (2022). "Biochar extract compounds alter germination and growth of crop seed," BioResources 17(3), 4151-4166.AbstractArticlePDF
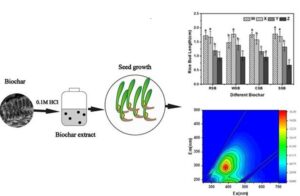
Positive or negative plant growth effects due to soluble organic biochar compounds are not well understood. Increasing quantities (0 g, 0.5 g, 2.5 g, and 5 g) of four different biochars were extracted with 0.1 M HCl, which were separated and marked as W, X, Y, and Z. Corn and rice seeds were treated with biochar extract solution. The rice straw Y and Z solutions positively affected corn germination, while the cotton straw Z solution negatively affected it. When differences were present, the biochar extract solutions always caused reduction in rice seed germination. The rice straw and cotton straw solutions tended to increase, the wheat straw Y and Z solutions tended to decrease, while little differences were evident in terms of the effects of the Spartina alterniflora solution on corn bud and root length when compared to the control. Increasing the biochar solution extract treatments reduced the rice bud and root length when compared to the control, especially with solution Z. Organic compounds, e.g., triethyl phosphate, 2,4-bisphenol, were present in the solutions, which likely promoted seed growth at lower concentrations. Determining the presence of biochar organic moieties helped with designing biochars for enhanced seed germination, growth, and crop productivity.
- Researchpp 4167-4185Feng, Y., Liu, G., Sun, H., Xu, C., Wu, B., Huang, C., and Lei, B. (2022). "A novel strategy to intensify the dissolution of cellulose in deep eutectic solvents by partial chemical bonding," BioResources 17(3), 4167-4185.AbstractArticlePDF
The relatively low solubility of cellulose in choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents (DESs) restricts their practical application in the production industry. Here, cellulose was slightly oxidized into dialdehyde cellulose (DAC) at first, and then partial chemical bonding was introduced to intensify the dissolution process of cellulose in (choline chloride-resorcinol) DES. In this process, the solubility of cellulose in DES increased 10-fold, and the crystallinity of cellulose decreased over 24% while the oxidation level was lower than 20%. An intensified hydrogen bond network was revealed, which implied that cellulose components mainly acted as hydrogen bond donor after dissolution. A new class of DES containing cellulose was thus preliminarily established. The cellulose chains and the intensive hydrogen bond network also resulted in an increased viscosity and a conversion from Newtonian behavior to non-Newtonian behavior of dissolved samples. The phase transition behaviors of dissolved samples were gradually converted from crystallization to cool crystallization. The proposed and performed strategy is novel and scalable and will open a fresh perspective to achieve higher efficient dissolution of cellulose in DES and establish a new partially derivatized cellulose/DES system.
- Researchpp 4186-4195Sun, G. R., He, Y. R., and Wu, Z. H. (2022). "Effects of thermal treatment on the dimensional stability and chemical constituents of new and aged camphorwood," BioResources 17(3), 4186-4195.AbstractArticlePDF
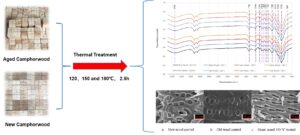
Green and naturally aged camphorwood (Cinnamomum camphora) samples were thermally treated at 120, 150, or 180 °C for 2.5 h to investigate how various thermal treatments affected dimensional stability and hygroscopity. As a result, mass loss showed an increasing trend after treatment from 0.88% to 2.44%, whereas equilibrium moisture content exhibited a decreasing trend (in the range of 10.88% to 7.96%) after treatment at 180 °C. Additionally, thermal treatment improved the dimensional stability of camphorwood samples. Fourier-transform infrared spectra for wood after thermal treatment revealed that treatment led to hemicellulose deacetylation.
- Researchpp 4196-4205Xu, S., Xu, P., Zhao, P., and Du, Y. (2022). "Effect of different size ratio and filling method on the characteristics of calcium silicate-filled paper," BioResources 17(3), 4196-4205.AbstractArticlePDF
Process conditions were investigated relative to the use of the fly ash pre-desilication-alkali lime sintering method to extract calcium silicate, which is a by-product of alumina co-production technology, for use as paper filler. The ratio of different fiber raw materials, filler filling ratio, and filling method were studied, and papermaking experiments were conducted. The results showed that calcium silicate filler at a higher proportion (40%) paper can still maintain high mechanical properties. Under the same filling ratio and filling method of calcium silicate filler, the comprehensive performance of softwood pulp and hardwood pulp papermaking paper was found to be better than that of deinked pulp paper.
- Researchpp 4206-4225Morais, F. P., and Curto, J. M. R. (2022). "3D computational simulation and experimental validation of structured materials: Case studies of tissue papers," BioResources 17(3), 4206-4225.AbstractArticlePDF
The development and optimization of structured materials, such as tissue paper materials, benefit from modeling strategies that take into consideration its structural hierarchy at the fiber and the paper levels. The use of an innovative three-dimensional voxel approach to model both the fiber and the 3D paper structure were validated by comparison of the computational structures with the laboratory-made structures. The main goal of this work was to model tissue structures and obtain a computational implementation adapted for tissue products. The fibers were modeled in 3D according to their dimensions, and the structures produced by them were characterized using the Representative Elementary Volume (REV) and image analysis computational tools. This methodology made it possible to model the fibers according to their morphology, flexibility, and collapse, resulting in a tissue structure with thickness, porosity, relative bonding area, coverage, among other properties. The experimental design plan included the production and characterization of isotropic laboratory structures with basis weights of 20, 40, and 60 g/m2 with different eucalyptus fibers and beating degrees. With the aid of these advanced computational tools, mathematic models with predictive capacity for tissue properties such as softness, strength, and absorption can be developed.
- Researchpp 4226-4240Shen, Z., Liu, Y., Wei, X., Zhang, L., Zeng, L., Wang, S., and Min, D. (2022). "Structural characteristics of eucalyptus lignin regulated through alkali cooking process," BioResources 17(3), 4226-4240.AbstractArticlePDF
Understanding the basic chemical structure of lignin macromolecules can facilitate the development of lignin-based materials. In this study, the lignin structure was regulated through different alkali cooking conditions. The acid precipitated lignin from the spent cooking liquor was purified and fractionated with different organic solvents. The lignin samples with different structures were obtained by regulating the cooking time. The structural characteristics of the lignin preparations were systematically investigated. The results revealed that the structure of lignin was regulated by the heating time and the residence time during the cooking process. Non-condensed lignin was achieved after a specific cooking condition; it had higher molecular weight (9686 g/mol), more β-O-4 linkages (25.3/100Ar), but lower phenolic hydroxyl content (1.51 mmol/g) than the counterpart pulping with longer time duration. The non-condensed lignin also had excellent thermal stability. Compared with industrial lignin, the lignin with non-condensed structure can be modified to obtain phenolic resin materials with better performance. The non-condensed structure with the specific characteristics can broaden the valorization of lignin for producing biochemical and biomaterials.
- Researchpp 4241-4261Liu, R., Yan, J., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Tian, C., Fu, P., Li, X., and Zhou, L. (2022). "Research on the upgrading of bio-oil based on low-carbon alcohol solvents and ultrasonic-emulsification," BioResources 17(3), 4241-4261.AbstractArticlePDF
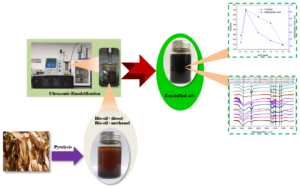
Effects of the emulsifier type, hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) value, bio-oil ratio, ultrasonic power density, and ultrasonic time were tested relative to the physicochemical properties and stability of emulsified oils to broaden the use of bio-oil and overcome its defects. The results showed that the turbidity and stabilization times of the emulsified oils reached the maximum values of 184 NTU and 84 min (Span 80 and Tween 80), 191 NTU and 92 min (HLB value of 5), 280 NTU and 92 min (bio-oil ratio of 5%), 191 NTU and 81 min (ultrasonic power density of 0.96 w/mL), 273 NTU and 97 min (ultrasonic time of 20 min), respectively. When the bio-oil to methanol ratio was 1:1, the turbidity value of the emulsified oil reached a maximum value of 664 NTU and the stability time was greater than 24 h. The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analysis indicated that the emulsified oil did not delaminate after 30 d, and the uniformity and stability of the emulsified oil were improved.
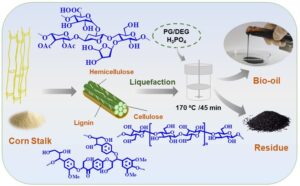
- Researchpp 4262-4279Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Zhao, H., Liu, Z., Huang, J., Yang, Y., and Chen, Y. (2022). "Characterization of liquefied products from corn stalk in the presence of polyhydric alcohols with acid catalysis," BioResources 17(3), 4262-4279.AbstractArticlePDF
Atmospheric liquefaction technology has been used widely and is an effective way of biomass component utilization. In this paper, the liquefied products obtained from corn stalk using polyhydric alcohols 1,2-propanediol (PG) mixed diethylene glycol (DEG) through acid catalysis under atmosphere pressure were characterized by various analytical technologies. The results indicated that 39 kinds of organic compounds were present in bio-oil, among which alcohols were the most, phenols were the second, and their relative contents were 70.7% and 25.6%, respectively. There were also some organic acids, ethers, esters, and ketones. More than 80% of these compounds had a carbon number less than 25. Carbon nuclear magnetic resonance spectra (13C-NMR) showed that different chemical shifts (ppm) corresponded to various carbon types. The chemical composition of the residue from liquefaction was complex and contained a certain amount of large molecular substances that were difficult to degrade. It required more severe pyrolysis conditions than those of corn stalk. Results from X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) indicated the destruction of crystalline structure of carbohydrates and the cellulose molecules were cracked, indicating that the cellulose was degraded and the degree of liquefaction was high.