Volume 18 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 1384-1397Erdinler, E. S., Seker, S., Hazır, E., and Koc, K. H. (2023). "Evaluation of the factors affecting opening-closing performance of wooden cabinet doors," BioResources 18(1), 1384-1397.AbstractArticlePDF
This study determined the deflection performance of wooden cabinet doors during opening and closing by using different material types, opening-closing angle, and load force. The independent variables consisted of material type, opening-closing angle, and load force, and the dependent variable was determined as deflection value. Medium density fiberboard (MDF) and particleboard (PB), both melamine faced, were used as two different material types. Opening and closing angles and directions of forces were performed as directed in BS EN 16122 (2012) and TSE EN 9215 (2005) and the doors were loaded by forces of 300N, 375N and 450N. The factors affecting deflection value and the interaction between them were investigated by multivariate analysis of variance. The results showed that the material type, angle, load force, and the mean between the material type and load force was significant. As the loading force increased, the deflection value increased. As the moisture increased, the deflection value increased, and as the material density increased, deflection value decreased. The adequacy of models was evaluated by the R-square (R²) and Adjusted R-square (Adj-R2) values. The results for these values were 88.23 % and 86.58 %, respectively.
- Researchpp 1398-1419Koponen, A., Cecchini, J., Heiskanen, S., Selenius, M., and Jäsberg, A. (2023). "Vacuum-assisted water removal from highly refined furnishes," BioResources 18(1), 1398-1419.AbstractArticlePDF
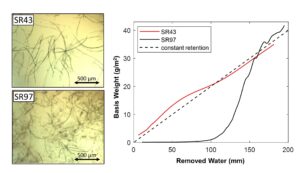
A vacuum-assisted sheet former was used for analyzing water removal from refined bleached hardwood kraft pulp furnishes. The Schopper Riegler (SR) values of the studied furnishes ranged from 43 to 97. Water removal time increased significantly with increasing SR value; the water removal time for SR97 furnish was two orders of magnitude longer than for SR43. Retention behaved differently with different SR levels. Retention was approximately constant for SR43 and SR72, for SR85 retention was initially slightly lower, and for SR97 retention was initially very low. The clogging of the wire due to the fines was very strong for SR97. A simple model of flow resistance of the filtered sheet worked very well for SR43 and SR72, and the model worked reasonably well for SR85. However, for higher SR levels, a retention model is needed to predict accurately the water removal in real-life applications.
- Researchpp 1420-1435Jansuwan, K., Jumrat, S., Punvichai, T., Karrila, S., Sirikitputtisak, T., Songthongkaew, N., and Pianroj, Y. (2023). "Properties of bio-oil and bio-char from high-intensity microwave-assisted pyrolysis of oil palm shell waste," BioResources 18(1), 1420-1435.AbstractArticlePDF
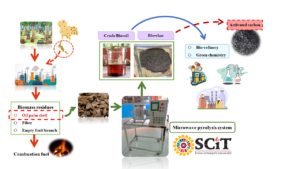
Microwave-assisted pyrolysis was applied using four magnetrons to implement a high intensity at a power density of 0.3 107 W/m3 with 800 g specimen size. The 23 full factorial experimental design manipulated the factors temperature, mixture ratio, and pyrolysis time, seeking to maximize %yield at minimum cost of crude bio-oil. The optimum according to model fit had a temperature of 611 °C with a 70:30 sample mixture ratio of oil palm shell (OPS) to activated carbon (AC), and time 39.6 min for a yield of 15.3% and 8.48 Thai-Baht/cc cost. The coefficients of determination were R2 = 93.99% and 94.00% for the respective models. In the aqueous phase of crude bio-oil, acetic acid was the dominant chemical component at 55.2%, whereas phenol was dominant in the bio-oil phase at 44.2%, from 400 °C pyrolysis temperature. The assessed properties of bio-char were proximate composition, heating value, specific surface, and pore volume, and these were improved compared to the raw OPS. However, these properties must be improved further to match commercial-grade activated carbon.
- Researchpp 1436-1453Ratnasingam, J., Ab Latib, H., Choon Liat, L., Jegatheswaran, N., Othman, K., and Amir, M. A. (2023). "Environmental, social, and governance adoption in the Malaysian wood products and furniture industries: Awareness, adoption, and challenges," BioResources 18(1), 1436-1453.AbstractArticlePDF
As the world intensifies efforts to mitigate the effect of global climate change, an on-line survey was carried out involving 1,081 wood products and furniture manufacturers in Malaysia. The main objective was to evaluate the level of awareness, extent of adoption, and challenges faced by these manufacturers in adopting environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. The survey found that large-sized companies were more receptive to adopting ESG practices, as opposed to the medium-, small-, and micro-sized companies. Respondents were apparently more responsive to environmental requirements, followed by governance, and finally the social factors. Within the environmental sphere, compliance with using certified and legal wood and wood products, waste management, and conformance to emission standards were well received among respondents. The survey revealed that market forces and legislative requirements were the two most important factors that enticed respondents to comply with the ESG practices; among those respondents who did not comply with ESG requirements, the primary deterrent factors include lack of awareness, no direct benefit from adopting ESG, and the high cost involved. The ESG compliance may transform the wood products and furniture industries into a more sustainable industry, offering equitable wages and green jobs while producing high value-added products.
- Researchpp 1454-1464Jang, E.-S., and Kang, C.-W. (2023). "Effect of steam explosion treatment on impregnation of three species of softwoods: North American spruce, Korean pine, and Japanese larch," BioResources 18(1), 1454-1464.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of steam explosion were investigated relative to impregnation of wood. Three types of softwoods [North American spruce (Picea orientalis), Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis), and Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi)] were prepared and subjected to steam explosion treatment. The cross-sectional surfaces of the samples were observed with SEM, and their open-pore and closed-pore porosities were determined using a gas pycnometer. The softwoods were vacuum impregnated using ACQ-2 (Alkaline Copper Quaternary), a commercial preservative. After steam explosion treatment, the impregnation amount increased by 42.9% in the spruce and 155% in the Korean pine. However, there was no significant difference in the Japanese larch. The results from this study indicated that the steam explosion treatment helped to improve open-pore porosity by generating micro-cracks in the cell walls of softwoods, which improved the impregnation process. However, the degree of improvement in impregnation process differed by the species type.
- Researchpp 1465-1481Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., and Abdel Ghany, T. M. (2023). "Nanoemulsions of some edible oils and their antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-hemolytic activities," BioResources 18(1), 1465-1481.AbstractArticlePDF
Plant oils have been applied for numerous purposes. Developing the composition of oils through nanotechnology has become a requirement, whether from a medical or industrial point of view. In this study, nanoemulsions (NEs) of olive and peanut oils were evaluated. GC-MS was used to determine the saturated and unsaturated fatty acids contents in both oils. Based on the area %, cis-8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid (54.0%), myristic acid (30.7%), and arachidonic acid (23.1%) were the greatest constituents in peanut oil, while arachidonic acid (23.2%), cis-11,14,17-eicosatrienoic acid (22.7%), and cis-11-eicosenoic acid (11.4%) were the greatest constituents in olive oil. TEM examination indicated that the diameter of peanut oil NEs (14.6 nm) was less than that of olive oil NEs (24.5 nm). Olive oil and its NEs exhibited more antioxidant activity than peanut oil and its NEs had IC50 values of 158.6, 102.5, 435.1, and 291.5 µg/mL, respectively. Negligible hemolysis was observed using olive oil, unlike peanut oil, while hemolysis based olive oil NEs was increased compared with hemolysis based peanut oil NEs, particularly at high concentrations of 600 to 1000 µg/mL. Molecular docking investigation offered the structure–activity correlation and binding modes of cis-8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid with Salmonella typhi (5ZXM) enzymes.
- Researchpp 1482-1492Tanaka, Y., Fukuda, N., Ranaivoarimanana, N. J., Hatakeyama, M., and Kitaoka, T. (2023). "Preparation of spherical microparticles composed of cellulose nanofiber and cellulose diacetate via Pickering emulsion templating," BioResources 18(1), 1482-1492.AbstractArticlePDF
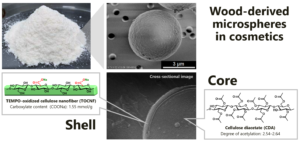
Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) derived from woody bioresources is a fascinating natural nanomaterial. In this work, spherical microparticles were fabricated by using TEMPO-oxidized CNF (TOCNF) and cellulose diacetate (CDA) via Pickering emulsion templating. The CDA-dissolved organic solvents were emulsified stably with TOCNF, followed by removing the solvents to form microspheres with core-shell structures, where the CDA cores were covered with the TOCNF shells. The prepared spherical microparticles possessed an average diameter and sphericity index of 6.4 μm and 0.96, respectively. The zeta-potential value was approximately -48 mV, indicating the stable colloidal system in water. The CDA/TOCNF microparticles were stained with toluidine blue dye for negatively-charged TOCNF. Besides, furry nanofiber-like morphology was observed on the particle surface by scanning electron microscopy. Wood-derived CDA/TOCNF microspheres are a promising alternative to fossil resource-derived, non-biodegradable microbeads in cosmetic applications.
- Researchpp 1493-1507Zou, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Y., and Shen, Z. (2023). "Cantilever plate mid-span patch method for dynamically testing the in-plane Poisson's ratio of oriented strand board," BioResources 18(1), 1493-1507.AbstractArticlePDF
A cantilever plate span-to-span patch method was proposed and demonstrated for dynamic testing of OSB Poisson’s ratio with high testing accuracy, simplicity, ease of implementation, and effectiveness. It is based on the patch method with zero transverse stress equal to the cantilever plate. Its effectiveness was verified by the four-point bending method and the patch strain gauge method with zero transverse stress. The simulation and theoretical analysis showed that the relative errors of OSB longitudinal and transverse Poisson’s ratios dynamically tested by the span-in patch method and the patch method with zero transverse stress were within ±3.8%. The OSB longitudinal and transverse Poisson’s ratios dynamically tested by the span-in patch method were in good agreement with those tested by the four-point bending method. Thus, the method is applicable to the cantilever plates with l/b= 5 to 6, b/h = 4 to 10, and l/b = 4, b/h = 7 to 10 for cantilevered plates, etc.
- Researchpp 1508-1524Indarti, E., Abdul Rahman, K. H., Ibrahim, M., and Wan Daud, W. R. (2023). "Enhancing strength properties of recycled paper with TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose," BioResources 18(1), 1508-1524.AbstractArticlePDF
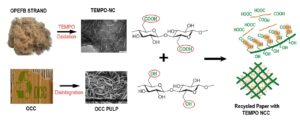
Recycled fibers used in the manufacturing of paper and board are associated with strength deficiencies. This study investigated the use of TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose from oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB-TEMPO) for reinforcing papers made from such fibers. Strength properties of tensile and tear were enhanced with the addition of OPEFB-TEMPO, with strong correlations, as indicated by the R2 values. The reinforcement capability was supported by the scattering coefficient-percent relationship. The only drawback of the nanocellulose addition is that it reduces pulp drainability, which can be minimized by adding drainage aids. Because only a relatively small amount is required, OPEFB-TEMPO has the potential to be used as paper strengthening agent, particularly in the production of low grammage papers.
- Researchpp 1525-1544Ahmad Sobri, N. S., Shuhaida, H., Jamaliah, M. J., Masdar, M. S., Takriff, M., Mohammad, A. W., and Manaf, M. A. (2023). "Green production of prebiotic xylooligosaccharides via enzymatic hydrolysis from xylan black liquor of oil palm frond," BioResources 18(1), 1525-1544.AbstractArticlePDF
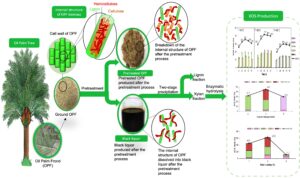
The black liquor generated from the alkaline pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass is usually disposed of into wastewater, which could lead to environmental pollution. Alkaline black liquor (ALBL) contains a large amount of xylan with a small fraction of lignin, making it a promising raw material for the production of xylooligosaccharides (XOS). In this study, xylan was extracted from the ALBL generated upon treating the oil palm frond (OPF) with sodium hydroxide via two-stage precipitation for the separation of lignin and recovery of xylan. As a result, approximately 84.0% of xylan retrieved from the ALBL was recovered. Subsequently, enzymatic hydrolysis was optimized to recover the maximum amount of XOS from xylan. The results showed that enzymatic hydrolysis produced the highest XOS (62.5%) under optimal conditions of 50 °C, 4 U/mL xylanase, and 3% xylan loading for 48 h. The study provides insight for maximizing utilization of ALBL of OPF for future biorefinery economy.
