Volume 18 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 255-271Ma, H., Wang, A., Ji, J., Liu, Y., and Gong, M. (2023). “Experimental study of the behavior of box floor with orthogonal ribbed beams by poplar LVL,” BioResources 18(1), 255-271.AbstractArticlePDF
Considering the unidirectional layout of ribbed beams and simple structure in traditional wooden floors, it is not suitable for large-span wooden buildings. Six groups of floor ribbed beams with plane size of 4.8 m×3.6 m were designed and manufactured by using poplar laminated veneer lumber (LVL), among which five floor specimens were orthogonal ribbed beams and the other one was traditional. A bending performance test was carried out to analyze the influence of different ribbed beam spacing and high span ratio on the mechanical performance of poplar LVL orthogonal ribbed beams, and its results were compared with that of the traditional floor with ribbed beams. The results showed that the box floors with orthogonal ribbed beams had good integrity during the bending process. Moreover, the change of the high span ratio had an important influence on the bending performance of the box floors with orthogonal ribbed beams, and the change of the spacing of the ribbed beams had a relatively small influence on the flexural performance of the box floors with orthogonal ribbed beams. Under the same conditions, the bending performance of the box floors with orthogonal ribbed beams was better than that of traditional floor.
- Researchpp 272-290Zou, Y., Zhang, W., Chen, H., and Cheng, H. (2023). "Investigating the moisture absorption behavior of bamboo fiber-reinforced epoxy composites by modelling," BioResources 18(1), 272-290.AbstractArticlePDF
The aim of this research was to investigate the moisture absorption of bamboo fibers (BFs) and their composites manufactured using different methods. The hygroscopic properties of BFs, jute fibers (JFs), glass fibers (GFs), and epoxy (EP) were compared and analyzed using dynamic vapor sorption (DVS), as well as the hygroscopic properties of the BF-Naval Ordnance Laboratory (BF-NOL), JF-NOL, GF-NOL, and bamboo fiber-reinforced epoxy composites manufactured via filament winding (FW), hot pressing (HP), and resin transfer molding (RTM). The results were analyzed using the Guggenheim-Anderson-deBoer (GAB), parallel exponential kinetics (PEK), and DoseResp models. The results indicated that BFs conformed to type II. The moisture adsorption isotherms of BF-NOL, JF-NOL, GF-NOL, and BF composites prepared by different molding processes exhibited a typical V-shape. The GAB and DoseResp models provided good fits to the changes in adsorption and desorption processes. The final equilibrium moisture content (EMC) of BFs and BF-NOL were 27.1% and 3.95%, respectively, the final EMC of BF composites prepared by RTM was 2.34%.
- Researchpp 291-301Chen, X., and Mao, Z. (2023). "Dissolution and reaction catalysis strategy using alkaline solvent for mild fabrication of chitin composite hydrogel for dye adsorption," BioResources 18(1), 291-301.AbstractArticlePDF
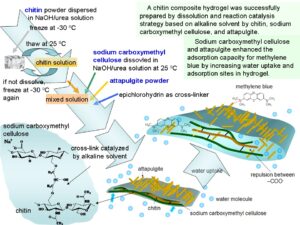
As the most abundant natural amino polysaccharide, chitin remains among the least exploited polymers due to its poor solubility, which restricts its research and utilization. In this study, a new chitin composite hydrogel was prepared by a mild process at 25 °C within a short time. To enhance the adsorption capacity, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and attapulgite were introduced into the structure of a hydrogel by chemical reaction and physical interaction, respectively. Alkaline solution was used as a solvent to dissolve chitin and used as a catalyst to accelerate the cross-linking reaction between chitin and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. This solvent (8 wt% NaOH/6 wt% urea solution) has dual functions: to dissolve chitin and to accelerate the cross-linking reaction of chitin with carboxymethyl cellulose by epichlorohydrin. The cross-linking reaction occurred at room temperature (25 °C) within a short time (4 h). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) indicated that chitin and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose has been successfully cross-linked. X-ray diffraction results showed that the cross-linked structure was amorphous and that attapulgite kept its crystal structure in the hydrogel. Scanning electron microscopy showed the coarse surface of composite hydrogel with attapulgite. The adsorption capacity for methylene blue reached 167 mg g-1.
- Researchpp 302-316Budakçı, M., Korkmaz, M., and Karal, I. (2023). “Antifungal effects of staining process on wood: Hardness, gloss, and color change,” BioResources 18(1), 302-316.AbstractArticlePDF
This study determined the effects of wood staining on wood-destroying fungi. To achieve this goal, different types of wood samples were used, including Scotch pine (Pinus sylvestris L.), Eastern beech (Fagus orientalis Lipsky), sessile oak (Quercus petraea Liebl.), and mahogany (Entandrophragma cylindricum). Aniline (C6H2NH2), chemical (tannin (C14H10O9) + potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7)), and Van Dyke brown stains (Fe2O3MnO2 + K2Cr2O7 + H2O) were applied to the samples, because a walnut color (brown) is preferred by customers. The stained samples were exposed to Fomitopsis palustris and Coriolus versicolor, and mycelium growing on wood was observed for 3 months. Hardness, gloss, and total color change tests were applied to the samples to determine the antifungal effects. The results showed that staining increased the total color change values of the wood, while decreasing in the gloss and hardness values. The chemical stain showed antifungal effects against both fungi.
- Researchpp 317-336Dziugan, P., Romanowska-Duda, Z., Piotrowski, K., Cieciura-Wloch, W., Antolak, H., Smigielski, K., Binczarski, M., Witonska, I., and Domański, J. (2023). “Improving biorefinery sustainability and profitability by cultivating aquatic plants on ozonized distillery effluents,” BioResources 18(1), 317-336.AbstractArticlePDF
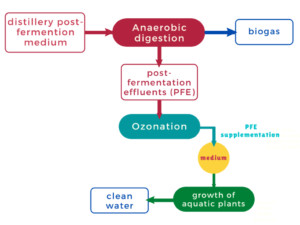
Industrial production of biogas offers a way to manage distillery leachate. The waste is usually subjected to anaerobic digestion for producing biogas. However, the effluent from anaerobic processes has high chemical oxygen demand (COD) and is harmful to the environment. An effective method of lowering COD is ozonation. Effluent from biogas plants after ozonation has the potential for use in breeding grounds for plants of the Lemnaceae family. Thus, they can provide a valuable additional source of biomass for the production of bioethanol. Lemna minor L. and Spirodela polyrhiza cultures were grown in media with the addition of 2.5% PFE, which had been treated by ozonation for between 6 and 50 min. Using ozonated effluent was an effective cultivation technique in all variants. The analyzed parameters were plant growth, chlorophyll index, fresh plant weight and photosynthetic traits (net photosynthesis, stomatal conductance, transpiration and concentration of intercellular CO2). The best growth of Lemna minor L. was observed in the media with PFE treated for 12 min. Similar effects were obtained for S. polyrhiza, with ozone treatment for 12 and 25 min. The results show the potential of using ozone-treated post-fermentation leachate as a supplement in culture media.
- Researchpp 337-356Li, H., Luo, L., Qiao, J., Li, X., Tu, J., Wang, Q., and Chen, Z. (2023). "The influence of rosin, blowing agent, and mould type on the sound insulation of paper-based foams," BioResources 18(1), 337-356.AbstractArticlePDF
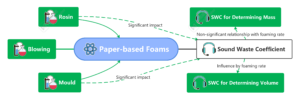
Wooden foams have been extensively researched in recent years because of their special structure and green features. At the same time, noise pollution is increasing, prompting sound insulation to become another research focus. In this study, a three-factor, five-level orthogonal experiment was designed, and 25 sets of specimens were produced for testing and analysis in 19 frequency bands. To measure the sound insulation, two criteria were used: the material sound loss rate (for determining mass) and the material sound loss rate (for determining volume sound). After measuring, these two values were compared. It was found that the material was highly isolated from high frequency noise. The amount of adhesive used and the choice of mould had a considerable effect on the sound insulation of the specimens as the foaming rate was varied. Good sound insulation can be achieved when the foaming rate is very low and when the foaming rate is very high.
- Researchpp 357-366Pipiska, T., Paschová, Z., Král, P., Nociar, M., Červenka, J., Meyer, M., and Wimmer, R. (2023). "Alternative particleboards based on treated and untreated hay," BioResources 18(1), 357-366.AbstractArticlePDF
Agricultural resources have a great potential to be a supplement or replacement for wood, especially in countries lacking wood resources, or during times of economic turmoil of wood markets, for manufacturing panel products. Previous research has focused on various sources including wheat straw, rice straw, rapeseed, or oil palm stems, but so far hay was not considered. Hay consists of cut and dried grasses, legumes, or other herbaceous plants. It has similar structure to wheat straw with a typical waxy surface layer and poor bondability. Soaking in NaOH was employed to improve the bondability of used full-length hay, or hay particles for urea formaldehyde (UF) resin. A comparison of the physical and mechanical properties was assessed. The vertical density profile of hay panels made from treated hay reached smaller differences between surface and core density. Full-length hay panels reached the higher average values of the equilibrium moisture content (EMC), due to the structure. The bending properties of panels made of treated hay particles showed improvement, with modulus of rupture being 3.5 times higher, and modulus of elasticity 2.6 times higher than that of the untreated hay particles. Thickness swelling after 48 hours decreased for the NaOH-pretreated hay panels.
- Researchpp 367-381Zhang, S., Huang, Z., Wu, Y., and Zhu, Y. (2023). "Effect of thermal bridge in light-frame wood wall," BioResources 18(1), 367-381.AbstractArticlePDF
The presence of thermal bridges in a wall increases local heat conduction of the building envelope, resulting in a decrease in the wall’s average thermal resistance. Simultaneously, the internal surface temperature of thermal bridge is lower than that of the surrounding areas and shows a tendency of condensation. Therefore, it is necessary to employ thermal bridges in the stage of construction design. In the research, a two-dimensional steady-state numerical simulation was performed targeting thermal bridges with light-frame wood wall. Meanwhile, the heat bridge effect was simulated under different circumstances by changing the types of insulation and cladding materials, the number of the studs, and the framing factor. The results showed that the linear heat transfer coefficient increased linearly as the studs and framing factor rose. After the test was validated, the relative error rate between the simulated correction coefficients and the experimentally derived correction coefficients was 11.4%, indicating that the correction coefficients can be simulated.
- Researchpp 382-399Mohammadi Nematabad, S., Pourmousa, S., Tajdini, A., Jahan Latibari, A., and Lashgari, A. (2023). "Identifying and ranking components of manufacturing sustainability in the Iranian papermaking industry," BioResources 18(1), 382-399.AbstractArticlePDF
Factors of manufacturing sustainability in the papermaking industry were identified and ranked using qualitative analysis and nonparametric tests. Based on a review of the literature on sustainable development and production, seven main factors of economic, environmental, technological, social, human, material and product, and regulations were identified to underpin the manufacturing sustainability in the papermaking industry, as well as some sub-factors. Then, a self-designed questionnaire was developed to take a poll among papermaking managers and experts regarding the effectiveness of the factors and sub-factors in manufacturing sustainability and their status. The factors affecting manufacturing sustainability in the papermaking industry were confirmed by the standard and significance coefficients in the structural equations and the predictive criterion. The cross-validated redundancy index showed that the data were valid enough for prediction. The research factors were ranked by the ordinal average affecting sustainability, current status, and distance to sustainability. The materials and product, environmental, technological, and economic factors had the greatest influence on manufacturing sustainability, and the regulation and human factors had the highest distance to sustainability. To achieve manufacturing sustainability in the papermaking industry, regulations and human factors need to be further studied. Their improvement has potential to achieve manufacturing sustainability.
- Researchpp 400-416Li, J., Lu, Y., Peng, X., Jiang, P., Zhang, B., Zhang, L., Meng, H., Kan, Z., and Wang, X. (2022). "Discrete element method for simulation and calibration of cotton stalk contact parameters," BioResources 18(1), 400-416.AbstractArticlePDF
To improve the accuracy of the discrete element research, physical and simulation experiments were used to calibrate the cotton stalk contact parameters. Based on the stalk-stalk and stalk-steel contact mechanics, the parameters were measured in physical experiments, and the discrete element simulation software was used to build the stalk model. In the simulation process, the Plackett-Burman experiment was used to screen three significant factors from six initial factors. The steepest Plackett-Burman experiment was used to determine the optimal interval of the significant factors. A second-order regression model of the significant factors and the angle of repose was established according to the Central Composite design experiment. The best parameter combination of the significant factors was then obtained: the coefficient of static friction on stalk-steel contact was 0.31, the coefficient of static friction on stalk-stalk contact was 0.62, and the coefficient of rolling friction on stalk-stalk contact was 0.02. The relative error between the physical angle of repose and the simulated angle was 3.27%, indicating that it is feasible to apply the simulation experiment instead of the physical one. It offers insights into cotton stalk contact parameter settings and film-stalk separation in the simulation.
