Volume 18 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5635-5654Pařil, P., Baar, J., and Rousek, R. (2023). “Innovative, low-cost eco-composite boards produced from high-energy milled wood, plastic waste, and bio-polymer,” BioResources 18(3), 5635-5654.AbstractArticlePDF
Currently, there is a big issue with waste, its processing and subsequent use. While there are many initiatives to replace materials that are poorly biodegradable, it is necessary to process and ideally use the waste that is already produced. In this study, the properties of composite boards made of waste materials and biodegradable polymer were investigated. The composite boards were made from wood and plastic waste using high-energy milling technology. This technology for material preparation is promising, as it includes controlling the morphology of particles, homogenizing the mixture, and drying the material during the milling process. The results showed higher flexural strength of high-density fiberboard (HDF) boards compared with tested composites with one exception. Wood/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) [PHBV] composite exhibited 30% higher modulus of elasticity (MOE) than HDF due to the higher modulus of PHBV. The lowest thickness swelling (3%) and water absorption (12%) were measured for wood/recycled high density polythene (rHDPE) composite. The HDF boards recorded the lowest dimensional stability. The highest water absorption of tested composites was measured for wood/PHBV composite. The resistance to wood-rotting fungi was greatest for wood/PHBV composite containing marble powder, which corresponded to the results of scanning electron microscopy.
- Researchpp 5655-5664Li, Y., Ma, Y., Yang, X., Du, H., Meng, F., and Xuan, C. (2023). “Effects of moisture and particle size on alfalfa’s thermal conductance, diffusivity, and heat capacity,” BioResources 18(3), 5655-5664.AbstractArticlePDF
Researching the thermal characteristic parameters of alfalfa is of fundamental importance for accurately measuring heat transfer and distribution during the compression process. Therefore, the thermal characteristic parameters were measured using the transient plane heat source method. Additionally, the study examined the impact of moisture content and particle size on the thermal characteristic parameters of alfalfa. The experimental results indicated that the thermal conductivity of alfalfa increased with higher moisture content, and it decreased with the increase of particle size. Similarly, the specific heat capacity increased with higher water content, while the particle size had little effect on specific heat capacity. The thermal diffusion coefficient initially decreased and then stabilized with higher water content. Moreover, the influence of particle size on thermal diffusion coefficient was not significant. The obtained thermal characteristic parameters are valuable for investigating temperature changes during the densification process of alfalfa.
- Researchpp 5665-5682Li, Q., Sang, T., Li, Y., Li, M., and Sun, Q. (2023). “Intangible cultural heritage complexes in China: Representation and restoration of pigmented reliefs in Kaiping Diaolou,” BioResources 18(3), 5665-5682.AbstractArticlePDF
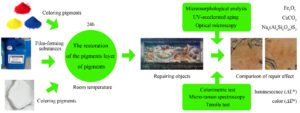
Restoration techniques were explored for the patterns, materials, and surface pigments of the pigments decoration art of Kaiping Diaolou and Villages, a world cultural heritage site in southern China. Field investigation was supplemented by scanning electron microscopy, microscopic Raman spectroscopy characterization, colorimetric tests, and tensile tests. Materials and concepts for the restoration of the Kaiping Diaolou pigments were analyzed. Raman spectroscopy was used to characterize the surface pigments display of pigments decorative patterns. The main colors of restoration included green, red, white, and blue. The green color was a mixture of colored copper arsenate minerals. The red color was made of hematite (Fe2O3). White was calcite, and blue was lapis lazuli or synthetic ultramarine. SEM revealed both pigments show similar flake flocculent section morphologies. UV accelerated aging experiments showed that the Ultraviolet absorber and antioxidants effectively inhibited the degradation of the interface matrix. The interface was less prone to cracking. The tension test showed that the bond stress reached a maximum value of 0.193 MPa at a curing temperature of 20 °C under 95% ambient humidity. The results provide strong evidence for pigment restoration in Kaiping Diaolou. This study also provides a scientific reference for the pigment conservation of other architectural decorations from the same historical period.
- Researchpp 5683-5702Pei, P., Zou, R., Wang, X., Liu, J., Liu, L., Deng, X., Li, X., Yu, M., Tan, J., and Li, S. (2023). “Biocomposite optimization with NaOH-modified bagasse fiber, polybutylene succinate, and poly(lactic acid) using RSM approach,” BioResources 18(3), 5683-5702.AbstractArticlePDF
Alkali-treated bagasse fiber was used as a process variable for optimization of the properties of polybutylene succinate/poly(lactic acid)-based biocomposites using Box-Behnken design (BBD) and response surface methodology (RSM). The optimum conditions for three factors, i.e., NaOH-treated bagasse fiber (0.55 to 1.65 g), polybutylene succinate (1.1 to 2.3 g), and poly(lactic acid) (2.2 to 3.4 g) on the bending strength of biocomposite were investigated. The optimum combination was 0.91 g of NaOH-treated bagasse fiber, 1.14 g of polybutylene succinate, and 3.10 g of poly(lactic acid). The bending strength for NaOH-treated bagasse fiber/polybutylene succinate/ poly(lactic acid) composite was 27.0 MPa, which was 26.0% higher than native bagasse fiber-based composite. The composites were also characterized by thermogravimetric analysis, mechanical testing, Fourier transform infrared, scanning electron microscopy, water absorption, and contact angle tests. Results demonstrated that the bending strength, impact strength, and tensile strength of alkali treated bagasse fiber-based biocomposite increased by 26.0%, 15.5%, and 23.3%, separately, compared with native bagasse-based composite after sequential homogenization, compounding, and hot pressing. The hydrophobicity for alkali-treated bagasse fiber/PBS/PLA was also improved. Thus, NaOH-treated biomass materials/biodegradable polymer was judged to be suitable for preparing green composite materials.
- Researchpp 5703-5723Arango-Agudelo, E., Rendón-Muñóz, Y., Cadena-Chamorro, E., Santa, J. F., and Buitrago-Sierra, R. (2023). “Evaluation of Colombian coffee waste to produce antioxidant extracts,” BioResources 18(3), 5703-5723.AbstractArticlePDF
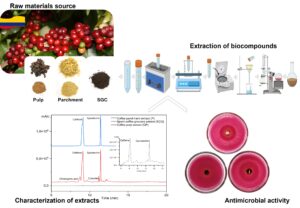
During coffee production, several types of waste such as pulp, mucilage, husk, parchment, coffee silver skin, and spent coffee grounds are generated. The amount of coffee waste and their environmental issues require effective valorization. Those wastes can be used as a source of bioactive compounds. In this work, solid-liquid extraction was used to obtain different solutions, and their phenolic contents, antioxidant capacities, fatty acid profiles, and antimicrobial activities were evaluated. Characterization of the waste materials showed that the highest yield (18.8%) was obtained for spent-coffee grounds. The highest total phenolic contents, caffeine and epicatechin, was observed for coffee pulp extract. Catechin was only observed for parchment. The lipid fraction in the coffee by-products extracts indicated that the spent coffee ground had a higher amount of total lipids, followed by the pulp, and finally the parchment. The most predominant fatty acids in all the extracts were palmitic, stearic, linoleic, oleic, arachidic, and behenic. However, parchment and coffee pulp extracts exhibited an inhibition halo against E. coli bacteria growth.
- Researchpp 5724-5749Deaconu, I., Porojan, M., Timar, M. C., Bedelean, B., and Campean, M. (2023). “Comparative research on the structure, chemistry, and physical properties of Turkey oak and sessile oak wood,” BioResources 18(3), 5724-5749.AbstractArticlePDF
The objective of this research was to establish comparatively some relevant features of Turkey oak and sessile oak wood, in order to better understand the drying behavior of these species. The analyzed samples were obtained from freshly harvested trees of the same age, originating from the Southern Sub-Carpathians. The microscopic analysis revealed that Turkey oak has larger earlywood pores than sessile oak. In heartwood, they are partly filled with tyloses for both species. The macroscopic analysis showed that Turkey oak wood has a much lower proportion of heartwood (only 50%) compared to sessile oak (90%). The comparative FTIR analysis of the two species showed similar qualitative chemical composition, but also some differences between sapwood and heartwood regarding the relative proportion of the main constituents, and very likely in the structure of lignin. High amounts of extractives were found in Turkey oak sapwood (5.34% in cold water, 7.77% in hot water, and 21.60% in NaOH 1%), close to the values obtained in sessile oak heartwood. The research also revealed that the Turkey oak sapwood and heartwood have statistically similar values of oven-dry density, shrinkage coefficient, fiber saturation point, while in sessile oak, the values are clearly higher in the heartwood.
- Researchpp 5750-5764Zhang, W., Zhou, C., Yu, M., Huang, T., and Kaner, J. (2023). “Interface design for the mobile terminal for furniture shopping in the post-epidemic era: An empirical evidence of user demand collection,” BioResources 18(3), 5750-5764.AbstractArticlePDF
The Internet economy is flourishing, and the form of consumption has shifted from offline brick-and-mortar shopping to online consumption. At the same time, COVID-19 led to many offline stores being constrained in many ways, accelerating the conversion of shopping. The purpose of the study is to enable users to effectively use mobile products and optimize their service experience during furniture consumption. This study compares the relevant theories and the current state of research. Through qualitative and quantitative methods, user needs are investigated and data analysis is conducted to summarize interface improvement suggestions. The high-fidelity prototype design was conducted, and the interactive prototype was delivered to users for testing to verify the effect and feasibility of interface optimization and to propose improvement suggestions for the mobile terminal of furnishings.
- Researchpp 5765-5776Wang, Y., Ma, J., Zheng, Q., Ma, Y., Jia, S., and Li, X. (2023). “Heterogeneous phosphotungstate catalyst mediated efficient alcoholysis of furfuryl alcohol into long-chain levulinates,” BioResources 18(3), 5765-5776.AbstractArticlePDF
The synthesis of alternative fuels from biomass has emerged to be a vital strategy to maintain sustainable development. Long-chain levulinate esters (LEs) are a class of good biofuel candidates because they have similar structures to biodiesels and superior heating values. The synthesis of long-chain LEs with effective heterogeneous catalysts has always been challenging. In this work, a few heterogeneous phosphotungstate catalysts were facilely prepared, among which the V3+ exchanged phosphotungstic acid catalyst (VPW) was the most active for the alcoholysis of furfuryl alcohol (FA) and 1-hexanol into 1-hexyl levulinate (HL). A maximum HL yield of 63% was achieved at 180 °C. The VPW catalyst could be reused without obvious decrement of activity. The system was also applicable to the alcoholysis of FA with other hexanols and 1-octanol into various long-chain LEs.
- Researchpp 5777-5797Chen, D., Yin, D., Liu, W., Lan, W., and Wang, Y. (2023). “Anaerobic co-digestion scheme of biogas engineering based on feedstock and temperature,” BioResources 18(3), 5777-5797.AbstractArticlePDF
This article investigates the current status and distribution of the feedstock of biogas engineering in China, evaluates the temperature conditions for anaerobic co-digestion (AcoD), and assesses the biogas production potential of feedstock in AcoD, including six feedstocks, namely, maize straw (M), wheat straw (W), rice straw (R), pig manure (P), cow manure (C), and sheep manure (S). The total amount of M, W, and R was 3.89 × 108, 2.10 × 108, and 1.50 × 108 tons, respectively, and that of P, C, and S was 8.46 × 108, 1.31 × 109, and 4.95 × 108 tons, respectively. However, the spatial distributions and amount of those resources were found to be uneven in China. Heilongjiang has abundant maize straw, and Henan has abundant wheat resources. Sichuan is rich in cow manure, while Inner Mongolia is rich in sheep manure. The analysis of total biogas production (TBP) by mono-digestion and co-digestion (using two feedstocks at ratio of 1:9, 3:7, 5:5, 7:3 and 9:1) showed that co-digestion outperforms mono-digestion under 15 and 25 °C. Thus, it is necessary to study anaerobic co-digestion scheme (AcoDS), which will provide a reference for biogas engineering in different regions to promote the biogas yield based on their actual situation.
- Researchpp 5798-5812Zhang, Z., and Zhou, H. (2023). “Dielectric characteristics of poplar powder under high-frequency electric field,” BioResources 18(3), 5798-5812.AbstractArticlePDF
Dielectric properties of poplar tree powder were measured at frequencies from 5 to 30 MHz. The effects of moisture content, frequency, and bulk density on the dielectric constant and dielectric loss factor were analyzed. The polar groups of wood powder were characterized by infrared spectroscopy to reveal the response mechanism of wood powder in the high-frequency electric field. The results showed that, in general, wood powder’s dielectric constant and dielectric loss factor increased with increasing bulk density and moisture content. In the moisture content range from 0 to 24%, the dielectric constant ε’ of wood powder decreased with the frequency increase with 5 MHz as the maximum value of ε’. When the moisture content was 0 ≤ w < 20%, wood powder’s dielectric loss factor ε” varied as a quadratic function with increasing frequency, corresponding to a maximum value of ε” at 13.4 to 17.7 MHz. When the moisture content was >20%, the dielectric loss factor ε” of wood powder decreased linearly with increasing frequency, and the maximum value of ε” was 5 MHz. The infrared spectrum showed that the polar groups in the wood powder were mainly -OH, C=O, C-O, and -CH, with the highest percentage of -OH.
