Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 4954-4963Chen, Y., and Gu, F. (2023). “Quantitative analysis of traditional Chinese color,” BioResources 18(3), 4954-4963.AbstractArticlePDF
Chinese traditional colors are an important component of traditional culture, containing profound national culture and unique aesthetic ideas. Analyzing and applying the color characteristics of traditional Chinese colors can integrate traditional color design concepts into contemporary design, implying a design path from tradition to the present, and meeting the diversified and personalized consumer needs of the market. This study examined consumers’ psychological perception of traditional colors using the Natural Color System and Likert scale. Factor analysis and association tests revealed color attributes and image cognitive traits. The results reveal that blackness often degrades color image judgement. Saturation influenced Tang and Qing color perception. Red, green, and blue are the ideal hues for the Tang, Song, and Qing Dynasties, respectively. Song Dynasty culture and emotions are perfectly reflected in the green color. The Ming Dynasty’s visual traits are blue, and its culture and feeling are yellow. The red color best reflects the Qing Dynasty’s cultural and emotional traits, and the blue hue best matches its aesthetic traits. The study attempts to quantify customised furniture color design and improve product color design’s cultural meaning and aesthetic effect.
- Researchpp 4964-4976Chen, W., Liu, J., Fang, Y., and Zhao, J. (2023). “Timber knot detector with low false-positive results by integrating an overlapping bounding box filter with faster R-CNN algorithm,” BioResources 18(3), 4964-4976.AbstractArticlePDF
Knot detection is an important aspect of timber grading. Reducing the false-positive frequency of knot detection will improve the accuracy of the predicted grade, as well as the utilization of the graded timber. In this study, a framework for timber knot detection was proposed. Faster R-CNN, a state-of-the-art defect identification algorithm, was first employed to detect timber knots because of its high true-positive frequency. Then, an overlapping bounding box filter was proposed to lower the false positive frequency achieved by Faster R-CNN, where a single knot is sometimes marked several times. The filter merges the overlapping bounding boxes for one actual knot into one box and ensures that each knot is marked only once. The main advantage of this framework is that it reduces the false positive frequency with a small computational cost and a small impact on the true positive frequency. The experimental results showed that the detection precision improved from 90.9% to 97.5% by filtering the overlapping bounding box. The framework proposed in this study is competitive and has potential applications for detecting timber knots for timber grading.
- Researchpp 4977-4993Armenta, E. E., Coronado, M. A., Ayala, J. R., León, J. A., and Montes, D. (2023). “Essential oil extraction for all: A flexible and modular system for citrus biomass waste,” BioResources 18(3), 4977-4993.AbstractArticlePDF
The essential oil industry is a growing sector that generates 5.41 billion USD annually worldwide. Essential oils are widely used in medicine, agriculture, and perfumery. Although there are available systems in the market for domestic essential oil extraction, replacing the entire equipment in case of repair or malfunction can be costly. To address this problem, a pilot-scale essential oil extractor system was developed that operates through hydrodistillation. This system was used to process various citrus wastes such as green and yellow lemons, oranges, grapefruits, and Eucalyptus globulus. A factorial design was performed, and the best conditions were used to extract other biomass residues. GC-MS analysis revealed that the primary compound for orange, grapefruit, and green lemon essential oils is D-imonene, with 95.4%, 95.5%, and 49.2%, respectively. For yellow lemon the primary compound appeared to be D-limonene with 73.0% content, though the GC/MS data were less clear, and for eucalyptus, it is eucalyptol with 71.0%. The estimated production costs were 0.01 USD/mL, 0.04 USD/mL, 0.06 USD/mL, 0.07 USD/mL, and 0.15 USD/mL for orange, grapefruit, green lemon, yellow lemon, and eucalyptus essential oils, respectively. Therefore, the developed system is a competitive option for pilot-scale essential oil extraction.
- Researchpp 4994-5012Lei, J., Ren, D., Liu, Z., Wang, S., Lei, D., Luo, J., and Lei, M. (2023). “Discrete element contact parameters measurement and calibration of sugarcane leaves based on RSM-PSO,” BioResources 18(3), 4994-5012.AbstractArticlePDF
In response to the lack of accurate and reliable parameters in the discrete element simulation analysis of the sugarcane leaf crushing and return device, in this work, the actual and simulated errors of two stacking angles α and β of sugarcane leaves were used as indicators to calibrate the discrete element parameters. The second-order regression models between the important parameters and the indicators were obtained by Plackett-Burman test, steepest climb test, and Box-Behnken optimization test, and the analysis of variance and interaction factors were performed. The response surface method and particle swarm optimization algorithm were used to find the best significance parameters, and the best combination of significance parameters was obtained: the static friction coefficient between sugarcane leaves was 0.306, the rolling friction coefficient between sugarcane leaves was 0.198, and the recovery coefficient of sugarcane leaf-plate collision was 0.102. The relative errors of the simulation results and the physical test stacking angle α and stacking angle β were 0.609% and 1.643%, respectively. The calibration parameters can provide a theoretical reference for the design and research of sugarcane leaf crushing and returning machines, as well as the calibration of discrete element model parameters for leaf crops with high water content.
- Researchpp 5013-5027Ahmad, M. H., Amini, M. H. M., Sobri, S. A., Sakagami, H., and Hermawan, A. (2023). “Effect of radial growth rate on wood properties variation of Sentang (Azadirachta excelsa) tree planted in Kelantan, Malaysia,” BioResources 18(3), 5013-5027.AbstractArticlePDF
Properties of Sentang wood planted in Kelantan, Malaysia, were studied, focusing on the effect of radial growth rate on variation in the fiber and vessel element dimensions, moisture content, density, shrinkage, bending, and compression strength at the breast height of the tree. The trees were categorized into slow-, average-, and fast-growth categories, based on their breast height diameter and standard deviation. The variations in properties were then examined from the pith to the bark. The fiber length and diameter tend to decrease until a certain distance from the pith, followed by an increase toward the bark. Contrastingly, the vessel element length and diameter tend to increase until a maximum size is reached and then exhibit a relatively constant size toward the bark. The fast-growing trees tended to have longer and larger fibers, while the slow-growing trees tended to have longer and larger vessel elements. In addition, the fast-growing trees tended to have a higher green moisture content and shrinkage, lower density, lower modulus of rupture (MOR), and lower compression strength. The results revealed that growth rate seems to influence the modulus of elasticity (MOE) less than the MOR and compression strength.
- Researchpp 5028-5040Gao, Q., You, J., Liao, X., and Wang, Z. (2023). “Identification and analysis of ancient ship wood excavated at Nantong hydraulic site,” BioResources 18(3), 5028-5040.AbstractArticlePDF
The Nantong Ancient Ship refers to an ancient Chinese wooden ship of the late Ming Dynasty excavated in Nantong city in December 2022. This paper identifies the wood and discusses its related analysis. Wood samples extracted from the Nantong Ancient Ship were studied from the viewpoints of anatomy, physics, and chemistry. Microscopic identification results concluded that willow and Chinese fir were the main wood species used to make this ship. The content of holocellulose in the ancient wood was only 37.9 to 38.9%, while the content of lignin was 55.2 to 56.4%. The cellulose crystallinity of ancient wood was 39 to 42% lower than that of healthy recent wood. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra revealed that the deterioration of ancient wood caused cellulose and hemicellulose degradation, but no apparent lignin alteration. The results could provide a basis for drawing up a conservation plan for the Nantong Ancient Ship. They could also provide a reference for the research and conservation of other archaeological shipwrecks in China.
- Researchpp 5041-5056Wang, Y., Ji, Q., and Li, H. (2023). “Preparation, characterization of chitin-based activated carbon for Orange II removal,” BioResources 18(3), 5041-5056.AbstractArticlePDF
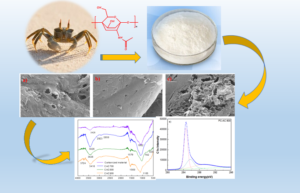
Chitin-based activated carbon (CAC) was prepared by a two-step process of carbonization and potassium carbonate chemical activation. The CAC was characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), N2 adsorption/ desorption, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The adsorption performance of CAC for Orange II (O II) was evaluated in terms of contact time, adsorption temperature, initial concentration, adsorption kinetics, adsorption isotherms, and thermodynamics. The CAC had a surface area of 1320 m2 g-1 and a total pore volume of 1.10 cm3 g-1. The maximum monolayer adsorption capacity was 1010 mg g-1 at 318.2 K for O II, respectively. Equilibrium isotherms showed that the Langmuir model had a higher coefficient of determination than the Freundlich model. The thermodynamic results indicated that the adsorption process of O II onto CAC 800 was spontaneous and endothermic. Given the results of this work, CAC can be used as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of dyes from wastewater.
- Researchpp 5057-5072Tanifuji, K., Sakurai, K., Miyamoto, T., and Okayasu, Y. (2023). “Effect of chemical composition on thermal decomposition behavior of herbaceous plants for production of plant-based biochar for storing carbon in soils,” BioResources 18(3), 5057-5072.AbstractArticlePDF
In order to use plant biomass as biochar for storing carbon in soils, the relationship between the chemical composition of plants and biochar yield obtained by thermogravimetric (TG) analysis was studied. The extractive content of herbaceous plants such as dokudami (Houttuynia cordata), halcyon (Erigeron philadelphicus), and mugwort (Artemisia Spp.) was higher than that of Japanese cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa), and the yields at 250 and 300 °C tended to decrease with increasing extractive content of plants. This indicated the possibility that thermal decomposition of herbaceous plants can be conducted at low temperatures (below 350 °C). In addition, the content of crystalline carbohydrates (remaining upon treatment with 5% sulfuric acid) of herbaceous plants was lower than that of Japanese cypress, and the yield at 400 °C tended to decrease with increasing crystalline carbohydrate content of plants. This indicated the possibility that herbaceous plants can be used to obtain biochar with higher yield at 400 °C than woody plants. Therefore, herbaceous plants are considered to be feasible resources as raw materials for biochar production for storing carbon in soils.
- Researchpp 5073-5084Hartono, R., Sutiawan, J., Hermawan, D., Wibowo, S., and Zulfiana, D. (2023). “Termite and decay resistances of Sumatran elephant dung-based particleboard modified with wood shavings and bamboo layering,” BioResources 18(3), 5073-5084.AbstractArticlePDF
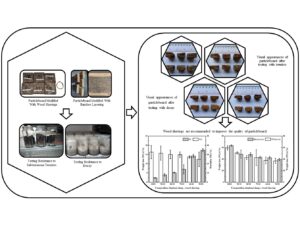
Elephant dung (ED) particleboard (PB) still has subpar physical and mechanical qualities. In earlier research, adding wood shavings and bamboo layers to ED-derived PB successfully enhanced its physical and mechanical qualities. However, the resistance to termites and decay of this PB is still unknown. Therefore, this study examines the resistances to termites and decay of the PBs from ED fiber-modified with wood shavings and bamboo layering. ED and wood shavings were distributed throughout the PB in ratios of 100/0, 90/10, 80/20, 70/30, 60/40, and 50/50 (w/w %). Meanwhile, tali bamboo (Gigantochloa apus), talang bamboo (Schizostachyum brachycladum), kuning bamboo (Bambusa vulgaris), belangke bamboo (Gigantochloa pruriens), and betung bamboo (Dendrocalamus asper) were the materials used in this study. These findings demonstrated that adding wood shavings could improve PB’s resistance to termite and decay attacks. However, in this investigation, the layering of bamboo diminishes the PB’s resistance to termite and decay attack. A 50/50 ratio between ED and wood shavings achieved slightly higher termite mortality and lower weight loss than others. Meanwhile, kuning bamboo had lower termite mortality and higher weight loss than others.
- Researchpp 5085-5095Zamaninasab, S., Lashgari, A., Roohnia, M., Jahan-Latibari, A., and Tajdini, A. (2023). “Fermentation pretreatment and extraction’s effect on the acoustic properties of walnut wood (Juglans regia),” BioResources 18(3), 5085-5095.AbstractArticlePDF
Despite the progress in synthetic polymer industries, wood is one of the main materials in making musical instruments because of its unique characteristics. Many instrument makers try to improve the acoustic properties of wood by traditional treatments. In this study, the changes in the acoustic properties of walnut wood during the processes of fermentation pretreatment, water washing, and organic solvent washings were evaluated. For this, the samples were divided into two groups of 20. For the first group, de-extraction was started with fermentation pretreatment, while the second group samples directly underwent stepwise extraction, using hot water and ethanol-acetone solvents. The results showed a decrease in density, dynamic modulus of elasticity, and damping factor due to the soaking process. But the elastic stiffness did not change. The values of the acoustic coefficient and the acoustic conversion efficiency increased due to the soaking process. The values of density, dynamic modulus of elasticity, elastic stiffness, and damping factor decreased due to ethanol-acetone washing, while the acoustic coefficient and acoustic conversion efficiency showed a significant increase. In general, soaking process and ethanol-acetone washing with fermentation pretreatment improved the acoustic properties of walnut wood.
