Volume 17 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5178-5189Li, X., Fu, J., and Jiang, L. (2022). "Erosion wear behavior of bamboo fiber-reinforced high-density polyethylene composites with nano silicon dioxide filler subjected to rotary water jet," BioResources 17(3), 5178-5189.AbstractArticlePDF
The erosion wear behavior of bamboo fiber-reinforced high-density polyethylene (HDPE) composites with silicon dioxide (SiO2) nanoparticles filler was investigated based on the sand-carrying water (a mixture of water and garnet sand) jets (SCWJ). The composites consisted of varying weight percentage of SiO2 fillers were prepared through press molding technology. Based on the rotating water jet technique, the erosion wear performance of composites was considered with varying erosion times and shooting distances. The results showed that composites filled with SiO2 possessed better resistance to SCWJ erosion. The erosion resistance of the composites highly corresponds to their impact strength. The maximum erosion rate occurred at a shooting distance of 0.5 cm and an erosion duration of 180 s. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis further demonstrated that the erosive wear mechanisms mainly included the pulverization of bamboo fibers, brittle fracture of HDPE matrix, and increase in oxygen content.
- Researchpp 5190-5206Komariah, R. N., Krishanti, N. P. R. A., Yoshimura, T., and Umemura, K. (2022). "Characterization of particleboard using the inner part of oil palm trunk (OPT) with a bio-based adhesive of sucrose and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP)," BioResources 17(3), 5190-5206.AbstractArticlePDF
The effective utilization of the inner part of oil palm trunk (OPT), generally considered a waste product, is desired. In this study, particleboards were manufactured using the inner part of OPT with a bio-based adhesive made of sucrose and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP). The mixture ratio of sucrose to ADP and the resin content were changed to investigate the optimum condition of the adhesive. The pressing condition was set at 180 °C for 10 min, and the target density was 0.8 g/cm3. The optimum mixture ratio of sucrose to ADP was 80:20, and the optimum resin content was 20 wt%. The manufactured boards had modulus of rupture (MOR) and modulus of elasticity (MOE) in bending values of 16.4 MPa and 4.3 GPa, respectively. The internal bond strength (IB) was 1.85 MPa, and the thickness swelling (TS) was 9.6%. This indicated that the constructed particleboard was comparable to the 13 types of JIS A 5908 standard (2003). In addition, the particleboard had good termite and decay resistance, similar to those of OPT particleboards made with synthetic adhesives. It was clarified that excellent particleboard could be manufactured from the inner part of OPT and a bio-based adhesive made of sucrose and ADP.
- Researchpp 5207-5214Menezes, I. S., Fraga, I. F., Mascarenhas, F. J. R., Moraes, M. H. M., Cavalheiro, R. S., Aquino, V. B. M., Santos, H. F., Molina, J. C., Lahr, F. A. R., and Christoforo, A. L. (2022). "Comparative dimensioning of plane timber truss by ABNT NBR 7190:1997 method and ABNT NBR 7190-1:2022 method," BioResources 17(3), 5207-5214.AbstractArticlePDF
Wood, a renewable source and a material with excellent mechanical properties, is one of the oldest materials used in civil construction. In Brazil, its use is widespread in roof structures in the form of plane trusses. Given the Brazilian context of the growing presence of wood in structural systems, in addition to the normative updating processes, this study presents a comparison between calculation methods and possible increases in material consumption of wood for roof structure. The design methods compared are according to the recently published standard ABNT NBR 7190-1 (2022) and its previous version ABNT NBR 7190 (1997). The results were obtained via iTruss software, which includes linear-elastic structural analysis by the finite element method (FEM). It was concluded that the ABNT NBR 7190-1 (2022) presents a conservative dimensioning in relation to the previous version of 1997, favoring safety. However, there were no significant increases in wood consumption, demonstrating the efficiency of the revised version.
- Researchpp 5215-5233
Ehman, N., Ponce de León, A., Felissia, F. E., and Area, M. C. (2022). "Towards biodegradable barrier packaging: Production of films for single-use primary food liquid packaging," BioResources 17(3), 5215-5233. AbstractArticlePDF Award Winner: 2021 BioResources Early Career Investigator Award
Award Winner: 2021 BioResources Early Career Investigator Award
This research aimed to obtain bio-degradable microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) films from a pine sawdust pulp for use as liquid containers. The films were combined with food-grade polyols (sorbitol, glycerol, and mannitol) to improve the hydrophobicity and provide barrier properties. Pine sawdust (a by-product of primary wood industrialization, highly available, and inexpensive) was treated with soda-ethanol and a 2-stage oxygen sequence. The resulting pulps were mechanically fibrillated to produce MFC with a disk refiner. The polyols were added to improve crosslinking and achieve a plasticizing effect. The films were dried at 25, 50, and 60 °C. The mechanical and barrier properties (tensile strength, elongation, vapor permeability, and water absorption), the crystallinity, and the transparency of the films were evaluated. Total migration tests were carried out to verify the compliance of the films with current regulations. Finally, the film’s biodegradation properties in soil under normal climatic conditions were evaluated.
- Researchpp 5234-5242Jang, E.-S., and Kang, C.-W. (2022). "Change in sound absorption capability on thermally modified transverse and radial planes of Indonesian Homalium foetidum," BioResources 17(3), 5234-5242.AbstractArticlePDF
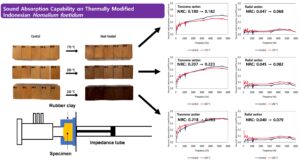
This study investigated the difference in sound-absorbing capabilities by thermally modified wood with respect to temperature and anatomical direction. Indonesian Homalium foetidum was used as testing material. After the samples were thermally modified at 170, 200, and 230 °C for 8 h, sound absorbing capability in the transverse and radial planes was investigated. As the treatment temperature was increased, the noise reduction coefficient (NRC) of the radial plane increased by 26.4%, and that of the transverse section increased by 7.3%. However, at 230 °C, the maximum NRC of the radial plane was 0.097 (SD: 0.015), and that of the transverse section was 0.263 (SD: 0.016). As a consequence, the sound absorption effect of the radial plane was negligible. Therefore, thermally modified Indonesian Homalium foetidum could be expected to absorb sound when used as a transverse section.
- Researchpp 5243-5254Li, G., Li, Z., Yin, T., Ren, J., Wang, Y., Jiao, Y., and He, C. (2022). "Drying biomass using waste heat from biomass ash by means of heat carrier," BioResources 17(3), 5243-5254.AbstractArticlePDF
Agricultural and forestry biomass direct-fired power generation represents an important technology to promote low-carbon energy transition and sustainable development. To solve the problems of boiler output fluctuation caused by unstable combustion of high moisture content biomass and insufficient recovery of ash waste heat after combustion, steel heat carriers (HC) were used to absorb high-temperature ash (HTA) waste heat, and then HC was directly mixed with high moisture biomass for dewatering and drying. The thermal efficiency of waste heat recovery decreased with the increase of ash temperature, and the highest thermal efficiency of waste heat recovery was 77.4% at a heat-carrying spheres temperature (THC) of 600 °C and a mixing mass ratio of 3. Through the optimization of waste heat recovery and mixed drying process, at a biomass ash temperature of 800°C, 1 kg of ash was able to dry 0.75 kg of high moisture content biomass, resulting in a reduction in fuel moisture by about 10%.
- Researchpp 5255-5267Guo, W., Hu, F., De, X., Hou, Z., Wang, Z., and Jiang, X. (2022). "Description of the instantaneous stress drop behavior of a cornstraw-potato residue mixture based on stress relaxation models," BioResources 17(3), 5255-5267.AbstractArticlePDF
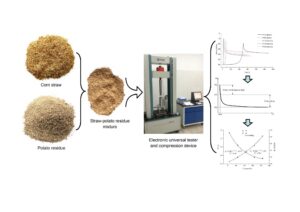
Studying the stress relaxation characteristics can provide important process parameters for the granulation and briquetting of biomass materials. In this study, a generalized Maxwell model and fractional model were established to describe and analyze the stress instantaneous drop behavior of a cornstraw-potato residue mixture during the stress relaxation process. Stress relaxation characteristic parameters, e.g., the stress instantaneous drop time, were obtained. Using this information, the influence of the compression speed on the stress instantaneous drop time, stress relaxation time ratio, and other parameters were analyzed. In addition, the regression model of the compression frequency and compression speed was established, which provided a method for determining the appropriate compression frequency of the molding equipment according to the compression speed.
- Researchpp 5268-5284Salahfard, M.-H., and Hosseinihashemi, S. K. (2022). "Effects of various treatment methods on decay resistance and dimensional stability of nano-silver-treated Persian/Shiraz inlay (Khatam)," BioResources 17(3), 5268-5284.AbstractArticlePDF
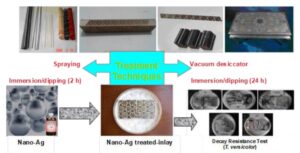
Four types of Shiraz inlay (Khatam) samples were impregnated with nano-silver solution via spraying (S), a vacuum desiccator (VD), and immersion/dipping (I/D) for 2 h and 24 h techniques. The decay resistance and dimensional stability were evaluated after each treatment. The impregnated specimens were exposed to white-rot fungus for 10 weeks by the agar-plate method, and the weight loss was determined to assess decay. The dimensional stability of samples after 2 and 24 h soaking in water were measured. According to the results, the highest weight loss (13.1%) was observed in the Shesh-Pareh Khatam (SPK)-untreated samples and the lowest weight loss (1.5%) occurred in the Ostokhani Khatam (OK)-VD-treated samples. The highest volumetric shrinkage (39.0%) was observed in the Haft Shamseh Alam-Zar Khatam (HSAZK)-untreated samples after 24 h soaking, and the lowest volumetric shrinkage (3.8%) was noted in the OK-S-treated samples after 2 h soaking. The highest volumetric swelling (64.1%) was observed in the HSAZK-untreated samples after 24 h soaking, and the lowest volumetric swelling (4%) was found in the OK-S-treated samples after 2 h soaking in water. Generally, the highest anti-shrinkage-efficiency (111.0%) and anti-swelling-efficiency (145.4%) after 24 h soaking in water were observed in the OK-S-treated and SPK-VD-treated samples, respectively.
- Researchpp 5285-5299Mangurai, S. U. N. M., Hermawan, D., Hadi, Y. S., Sulastiningsih, I. M., Arsyad, W. O. M., Abdillah, I. B., Purusatama, B. D., Kim, J. H., Febrianto, F., Park, S. Y., and Kim, N. H. (2022). "Resistance of the inner part of oil palm trunk impregnated with aqueous polymer-isocyanate to subterranean termite attack," BioResources 17(3), 5285-5299.AbstractArticlePDF
Isocyanate impregnation was studied relative to the subterranean termite (Coptotermes curvignathus Holmgren) resistance of the inner part of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) trunk. Unproductive oil palm trunk was harvested and divided into top and bottom parts. Samples were isolated from the inner part of the trunk with a size of 2.5 cm x 2.5 cm x 0.5 cm. The samples were impregnated with 10% and 20% aqueous polymer-isocyanate and then heated at 60 °C for 48 h. The specimens were fed to subterranean termites under laboratory conditions. The weight percent gain values were 15.3% to 21.0% and 9.2% to 14.7% for the top and bottom parts, respectively. A higher isocyanate concentration decreased the moisture content and increased the density of inner part of the oil palm trunk. Impregnation with aqueous polymer-isocyanate increased termite mortality at the bottom part and decreased the feeding rate and weight percent loss. Impregnation with 10% and 20% aqueous polymer-isocyanate enhanced the resistance class of the bottom part of the inner part of the oil palm trunk from very poorly resistant (V) to poorly resistant (IV) and moderately resistant (III), respectively, based on the standard adopted.
- Researchpp 5300-5318Fioreze, M., Labotić, L., Eleto Torres, C. M. M., and Silva, C. M. (2022). "Effects of pretreatments on the solubilization and theoretical methane production of waste activated sludge from a Brazilian eucalyptus kraft pulp mill," BioResources 17(3), 5300-5318.AbstractArticlePDF
Waste activated sludge (WAS) originating from kraft pulp mill effluent treatment plants represents an important environmental challenge for this industry. Anaerobic digestion is a promising option for WAS treatment, with the added benefit of biogas production. This paper presents the application of thermal, thermal-alkaline, and mechanical pretreatment methods in order to promote the solubilization of organic matter to enhance the anaerobic digestion of the WAS from a Brazilian Eucalyptus bleached kraft pulp mill. A total of 16 pretreatment operating conditions were compared. Chemical analyses showed an improvement in organic matter solubilization, with an increase greater than 7-fold for soluble chemical oxygen demand and 4-fold for biochemical oxygen demand. Nutrient solubilization showed an increase greater than 10-fold for total Kjeldahl nitrogen and 3-fold for total phosphorus. Theoretical biochemical methane potential was improved from 211 mLCH4/gVS for raw sludge to 333-343 mLCH4/gVS after mechanical pretreatment, 314-360 mLCH4/gVS after thermal pretreatment, and 373-378 mLCH4/gVS after thermal-alkaline pretreatment. In general, thermal-alkaline pretreatment showed the best results for all the evaluated parameters, with the advantage of requiring lower temperature and retention time when compared to thermal conditions.
