Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 384-399Zhou, J., Gao, G., Li, Y., Wang, D., Hu, J., Song, Y., and Chen, P. (2022). "A method of hydrophobically modifying paper with a trace reagent," BioResources 17(1), 384-399.AbstractArticlePDF
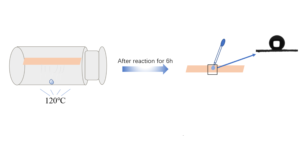
It is of great importance to protect paper cultural relics, especially in terms of making them waterproof. One of the important ways to protect paper cultural relics is by hydrophobic modification treatment. However, most of the existing hydrophobic modification methods rely on a great deal of organic solvents, which poses greater risks to safety and pollution. In this work, a simple, green, and effective method for paper hydrophobic treatment was proposed and evaluated. The vapor of a fluorinated triethoxysilane was reacted with the active hydroxyl group on the paper in a closed space, which realized the hydrophobic modification of the paper in one step. The contact angle of the hydrophobic paper prepared by this method was 148.4° under optimal experimental conditions. In addition, this method did not damage the paper, based on the results of the scanning electron microscopy of the paper before and after hydrophobic treatment. The generality of this method was verified by using other substrates and hydrophobic reagents. This method is simple to operate and does not require the usage of a large amount of organic reagent. It is expected to receive widespread attention in the field of the protection of paper and wooden cultural relics.
- Researchpp 400-410Liu, P., Zhou, Q., and Tian, J. (2022). "A two-variable model for predicting the effects of moisture content and density on the mechanical properties of Phyllostachys edulis bamboo," BioResources 17(1), 400-410.AbstractArticlePDF
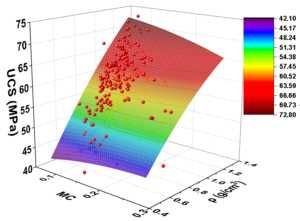
Phyllostachys edulis bamboo is one of the most valuable bamboo species in the world. It has the following advantages: high strength, light weight, and green, renewable character. In addition, it has a broad application prospect under the background of developing green buildings all over the world. The moisture content and density are the key factors affecting the mechanical properties of bamboos. However, there is no two-variable model of the mechanical properties with respect to the moisture content and density of P. edulis bamboo. In this paper, analysis of the compression parallel to the grain, bending, tensile parallel to the grain, and shear parallel to the grain of P. edulis bamboo were performed. The relationship between the mechanical properties and the moisture content and density was fitted by a two-variable model. The results show that the two-variable model has good fitting effect. As such, the two-variable model can be used to predict the mechanical properties of P. edulis bamboo according to its moisture content and density.
- Researchpp 411-428Lee, C.-G., Kim, M.-J., and Eom, C.-D. (2022). "Kinetic study of torrefied woody biomass via TGA using a single heating rate and the model-fitting method," BioResources 17(1), 411-428.AbstractArticlePDF
A model-fitting method at a single heating rate (10 °C·min-1) was used to investigate the thermal kinetic characteristics of torrefied woody biomass. The kinetic parameters were examined for pine, oak, and bamboo samples with the order of the reaction set ranging from 0.1 to 0.5 and 1.0. Based on the thermogravimetric, derivative thermogravimetric, and derivative2 thermogravimetric curves obtained, the ranges at which substantial hemicellulose and cellulose pyrolysis occurs were set as the analysis range, and the kinetic parameters of each species were analyzed. The activation energy and pre-exponential factor were obtained at these analytical ranges using two differential methods (Friedman and Chatterjee-Conard) and an integral method (Coats-Redfern). Although there were numerical differences between the results of the differential and integral methods, the thermal properties of each sample exhibited a consistent trend. Softwood was found to have the highest reactivity and intermolecular collisions per unit weight during thermal decomposition. In the case of the torrefied oak and torrefied bamboo, considering that the carbon content and fixed carbon content were approximately 24% to 25% higher than the softwood, it is appropriate to consider the thermal characteristics of each species for producing a solid fuel based on the application.
- Researchpp 429-444Guo, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, M., Chen, X., and Tian, X. (2022). "Kinetics of delignification and carbohydrate degradation during the ozone bleaching of low-consistency hardwood pulps," BioResources 17(1), 429-444.AbstractArticlePDF
With rising concern for environmental protection, the use of ozone has been increasingly studied in the pulp and paper industry. Feasible models for efficient quality prediction and process control are in high industrial demand. In this study, the reaction kinetics of delignification and viscosity during the ozone bleaching process (OBP) of low-consistency hardwood pulp (LCHP) are explored using exponential and zero-order response models, respectively. The effects of ozone dose, reaction temperature, reaction time, and pH on the changes in residual lignin content and pulp viscosity were analyzed. The corresponding kinetic parameters, such as the reaction order, rate constant (k), and activation energy (E), were also obtained. The models suggest that temperature should be one of the most significant factors affecting the effectiveness of the OBP system. The strategy to improve the OBP selectivity is based on reducing the reaction temperature while increasing the ozone concentration and pH in the reaction system.
- Researchpp 445-459Cheng, L., Zhao, P., Di, Y., Dai, J., Wang, Z., Guo, X., and Wang, W. (2022). "Predictive model of the modulus of elasticity in static bending (MOE) of larch wood based on gray relation analysis (GRA) and gene expression programming (GEP)," BioResources 17(1), 445-459.AbstractArticlePDF
To accurately evaluate the modulus of elasticity in static bending (MOE) of wooden components in ancient timberwork buildings under the “minimum intervention principle,” the nondestructive testing of physical and mechanical properties were conducted on larch. Using moisture content (MC), density (ρ), the stress wave propagation velocity ( ), the modulus of elasticity in dynamic bending (Ed), the rotational resistance value of the drilling needle (fdrill), and the resistance value of the feeding needle (ffeed) as the main parameters, the correlation between several parameters and MOE was firstly calculated using the Gray Relation Analysis (GRA) and ranked according to the strength of the correlation. Six combinations were selected according to the ranking, and the Gene Expression Programming algorithm (GEP) was used to build models for predicting MOE. The results showed that the correlation between several parameters and MOE was good (between 0.5 and 0.8), and the prediction model established with combination 6 was the best, which indicated that the prediction model established based on GRA-GEP algorithm had a certain feasibility and effectiveness, and the combined effect of the six parameters to evaluate the MOE of wooden components of ancient buildings was better in the field inspection.
- Researchpp 460-468Özyurt, H., and Özdemir, F. (2022). "Laminated wood composite design with improved acoustic properties," BioResources 17(1), 460-468.AbstractArticlePDF
Next-generation laminated wood composites were produced using waste poplar (Populus deltoides) veneer and polyvinyl acetate adhesive. Four experimental groups and one control group were created. Ten-layer laminated wood veneer samples were reinforced with natural rubber (Group A), linoleum (Group B), felt (Group C), and elastomeric sponge (Group D); these materials were used in the fifth adhesive layer (middle layer). The sound absorption coefficients of the control and experimental groups were tested via the impedance tube method, according to ASTM standard E1050 (2006). Attention was paid to the acoustic behavior at low frequencies (63 Hz to 250 Hz), mid frequencies (250 Hz to 2000 Hz), and high frequencies (2000 Hz to 6300 Hz). It was determined that the sound absorption coefficient of the experimental groups considerably increased. It can be suggested that the experimental groups be used as sound absorbing acoustic panels and the control group as sound reflective acoustic panels.
- Researchpp 469-491Abd Latif, N., Brosse, N., Ziegler-Devin, I., Chrusiel, L., Hashim, R., and Hussin, M. (2022). "A comparison of alkaline and organosolv lignin extraction methods from coconut husks as an alternative material for green applications," BioResources 17(1), 469-491.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of alkaline (kraft and soda) and organosolv pulping were evaluated relative to the structural properties of lignin isolated from coconut husk (CH) biomass. The various types of functional groups within the isolated lignin samples were characterized and compared using a variety of complementary analyses including Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, gel permeation chromatography (GPC), and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). All isolated CH lignin samples contained a significant quantity of non-condensed guaiacyl-type (G) and syringyl-type (S) units but a lesser amount of p-hydroxyphenyl (H) units, as demonstrated and supported by previous research. The alkaline CH lignin produced lignin with higher molecular weight (Mw SL: 959 g mol-1 > Mw KL: 769 g mol-1) than the organosolv lignin (Mw OL: 606 g mol-1) sample, resulting in smaller fragments and a higher degree of solubility in water or other solvents. Because of significant differences in the physicochemical characteristics of the various lignin polymers, their properties and structure were improved with respect to alternative approaches in lignin-based applications.
- Researchpp 492-503Costa Vieira, J., Costa Vieira, A., de Oliveira Mendes, A., Carta, A. M., Fiadeiro, P. T., and Costa, A. P. (2022). "Toilet paper perforation efficiency," BioResources 17(1), 492-503.AbstractArticlePDF
Today, the toilet paper market offers product types with varying number of plies, providing better mechanical strength and liquid absorption. Several tissue paper perforation systems exist, and the best commonly applied is a top-cutting mechanism that includes an oblique blade, a combined oblique blade, or a simple spiral blade. The perforation efficiency must be high to have an easy sheet separation from the roll of the toilet paper, which does not always occur. Hence, consumer satisfaction can depend on the perforation performance. To study this, a laboratory perforation system was used to perforate different commercial toilet papers (in brands and number of plies) and evaluate their perforation efficiency. A finite element method (FEM) was used to simulate the curve of the progression of perforation efficiency as a function of the cut distance. The main findings were a stabilization of the perforation efficiency from a cut distance of 6 mm and a 15% increase in the cut distance for the laboratory blade to match the industrial perforation efficiency. The FEM analysis confirmed the behavior of the evolution of perforation efficiency with the increase of the cut distance.
- Researchpp 504-518Zhang, Y., Yu, S., and Luo, W. (2022). "Preparation and characterization of nanocellulose coating modified by titanium dioxide," BioResources 17(1), 504-518.AbstractArticlePDF
The hydrophilic character of cellulose nanowhiskers (CNWs) coating was changed by the use of TiO2 to modify CNWs, thus preparing TiO2/CNWs coating by a two-step method. Meanwhile, the effect of the additive amount and particle size of TiO2 on the surface structure and water contact angle (WCA) of the coatings was studied. The solid contents of the suspension were characterized by Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The TiO2/CNWs coating was characterized via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Moreover, their wettability by water was revealed by the contact angle analyzer. The AFM and WCA analyses showed different additive amount and particle size of TiO2 have different effects on the surface structure and the WCA of the coatings. When the additive amount of TiO2 was 0.2 wt% and the particle size of TiO2 was 30 nm, the WCA and surface roughness (Rq) of the obtained TiO2/CNWs coating reached maximum values of 86.2° and 135nm, respectively. The TiO2 was relatively evenly distributed in the coating and the addition of TiO2 increased the crystallinity of CNWs from 79.67% to 84.89%. In addition, the FTIR and XPS analyses showed that TiO2 only physically dispersed in CNWs instead of having significant chemical reaction with CNWs.
- Researchpp 519-526Almeida, A. D. S., Criscuolo, G., Arroyo, F. N., Aquino, V. B. M., Silva, D. A. L., Molina, J. C., Chahud, E., Branco, L. A. M. N., Christoforo, A. L., and Lahr, F. A. R. (2022). "Estimation of compression and shrinkage properties of Brazilian tropical timber through porosimetry analysis by mercury intrusion," BioResources 17(1), 519-526.AbstractArticlePDF
Wood is a natural material with properties that are strongly influenced by anatomical characteristics, so studies that aim to correlate properties through empirical equations in search of simplification to obtain the values of their characteristics are essential. In this context, this work aims to generate multiple regression models to estimate the properties of shrinkage and compression parallel and normal to the grain of Brazilian tropical woods as a function of the values of porosity, density, and for both properties, with porosity being obtained by mercury intrusion porosimetry. As a result, the radial (RRT) and total tangential (RTT) shrinkage could be estimated through porosity. However, it was not possible to estimate them considering only density as an independent variable. All the models that were used were able to accurately estimate the modulus of resistance and modulus of elasticity values (fc,0, Ec,0, fc,90, and Ec,90).
