Volume 17 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3345-3354Korpela, A., Jaiswal, A. K., Tanaka, A., and Asikainen, J. (2022). "Wet tensile strength development of PAE wet-strengthened NBSK handsheets by AKD internal sizing," BioResources 17(2), 3345-3354.AbstractArticlePDF
Polyamide-epichlorohydrin (PAE) is used in papermaking to increase the paper’s wet strength. High levels of PAE can make repulping of paper more difficult. PAE deposits can also impair paper machine performance by plugging the paper machine felts. The results of a preceding study indicated that the wet strength of paper containing a moderate amount of PAE (added amount 0.3 wt%) can be increased by utilizing internal alkylketene dimer (AKD) sizing. In the present study, the effects of an added amount of PAE and AKD on the wet strength of handsheets made from Nordic bleached softwood pulp (NBSK) were examined. The wet strength was measured after soaking the sheets in ion-exchanged water for up to 1 month. The improving effect of AKD sizing on the wet strength was long-lasting and it was apparent especially with a low and moderate added amount of PAE (0.15 and 0.45 wt%) resulting in higher wet strength than the highest added amount of PAE (1.35 wt%) alone. No clear sign of worsened repulpability was observed at low to moderate treatment levels. The results suggest that use of small or moderate amounts of PAE with AKD can be a viable option for paper mills facing problems related to the high usage of PAE.
- Researchpp 3355-3377Pakdil, N. B., and Balaban, S. (2022). "Assessment of non-pressurized electro dewatering of waste activated sludge with graphite electrodes," BioResources 17(2), 3355-3377.AbstractArticlePDF
Changes of physical and chemical characteristics of sludge were investigated with respect to the pH, process time, and applied voltage by means of the electric field treatments. A model reactor with the desired speed was used to generate an electric field to separate water from the sludge without applying pressure. All electrodes mounted on the reactor were produced from graphite. Two different distances between anode and cathode (2.3 cm and 4.3 cm) were used to examine the effects on dewatering capacity of sludge. Differentiations of dependent variables inferred from the experimental processes were also surveyed by Box-Behnken experimental design. The water in the sludge was separated effectively when the samples were exposed to an electric field. The total solid increased from 1.07% to 6.60% at pH 6.5 when sludge was exposed to 25 V for 60 min. Furthermore, the optimum distance between electrodes was 2.3 cm for dewatering of sludge samples, where the capillary suction time of influent sludge was observed to decrease by approximately 85.5% at raw sludge pH. Similarly, the viscosity parameters decreased by approximately 99%. There was an increase in the soluble chemical oxygen demand, PO4-P, and NH4-N concentrations of water discharged from the model reactor.
- Researchpp 3378-3397Hitka, M., Naď, M., Gejdoš, M., Joščák, P., Jurek, A., and Balážová, Ž. (2022). "The effect of body mass on designing the structural elements of wooden chairs," BioResources 17(2), 3378-3397.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of increased body mass of users on the structural loading of wooden chair elements following the changes in anthropometric parameters in the adult population of the Slovak Republic. Moreover, the functional parts of a wooden chair most affected by the weight gain of an adult population were defined. The strength analysis of the tested chair was conducted using the program ANSYS. In the software environment, the 3D volume model taking into consideration orthotropic properties of wood was created. The structural elements of chairs for the current adult population are designed for the weight of 110 kg. The results suggest that the weight necessary for designing the structural elements of chairs must be 150 kg (130 kg + 15%). Comfort, physical health, well-being, performance, and security can be increased by designing such a device and equipment meeting the needs of the human body in a long-term viewpoint. It is suggested to create the standard taking into account men with a weight of up to 150 kg. Based on the results of the strength analyses, a chair load with a user’s weight of 150 kg will require a change in the dimensions of the side rails and the cross-section of the legs. The new knowledge gained is helpful for a better design of chair wooden elements taking into account the anisotropic (directional) structure of natural wood.
- Researchpp 3398-3412Chaipetch, W., Khongnakorn, W., Yirong, C., Boonkan, J., Jaiyu, A., and Heran, M. (2022). "Performance of a high rate two-stage anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) for the treatment of palm oil mill effluent," BioResources 17(2), 3398-3412.AbstractArticlePDF
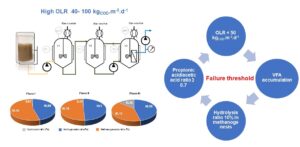
A two-stage submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor (2-sAnMBR) was operated to demonstrate the technology concept and to accelerate anaerobic biodegradation of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME). Then, the impact of different high organic loading rates (OLR) was investigated with a focus on water quality and biogas production. OLR higher than 50 kgCOD.m-3.d-1 induced an increase of volatile fatty acids (VFAs). As a consequence, the biogas production decreased from 19.8 to 11.0 L.d-1 and CH4 yield between 0.23 to 0.38 LCH4/gCODremoved. Nevertheless, the highest OLR (98 kgCOD.m-3.d-1) made it possible to reach a COD removal effectiveness of 70%, where the membrane contribution was around 23.9% to 34.7%. The ratio of propionic acid/acetic acid appeared to be a key indicator to prevent the AnMBR operation failure. Indeed, as soon as the value of 0.7 has been exceeded, several signs of AnMBR failure appeared. The methanogenic activity in AnMBR was inhibited by a hydrolysis ratio of 13% which transformed to VFA accumulation in system. The 250 mg.L-1 of Phenol concentration in POME was an inhibitory of the microbe in this system. Suspended solids concentration, proteins, polysaccharides, and volatile fatty acids were the substantial parameters that influenced the fouling rate.
- Researchpp 3413-3434Leggate, W., Outhwaite, A., McGavin, R. L., Gilbert, B. P., and Gunalan, S. (2022). "The effects of the addition of surfactants and the machining method on the adhesive bond quality of spotted gum glue-laminated beams," BioResources 17(2), 3413-3434.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of adding surfactants to polyurethane and resorcinol formaldehyde adhesives were tested relative to the gluability of spotted gum timber for structural glue-laminated beams (Glulam). While previous attempts to improve the bond performance of this very difficult to glue timber have focused primarily on timber surface preparations, this study concentrated on lowering the adhesive surface tension through added surfactants to improve the adhesive-timber surface wetting. Accordingly, 44 glulam samples were manufactured using polyurethane and resorcinol formaldehyde adhesives, with eight surfactant formulations and two different pre-gluing surface machining methods, i.e., face milling and planing. Although the surfactants were successful in drastically lowering the adhesive surface tension and improving adhesive spreading, none of the surfactant formulations tested were successful in improving the glulam adhesive bond qualities. Overall, the surfactant formulations produced considerably higher delamination, lower shear strength, and lower wood fibre failure compared to the control samples; therefore, they are not a viable solution to improve the gluing of spotted gum. The resorcinol formaldehyde adhesive and face milling produced considerably better results compared to the polyurethane adhesives and conventional planing.
- Researchpp 3435-3444Krajewsji, A., Jakiela, S., and Witomski, P. (2022). "Detection of old house borer larvae in wooden structures by acoustic emission method – Influence of larval size and sensor location," BioResources 17(2), 3435-3444.AbstractArticlePDF
The detection of old house borer larvae (Hylotrupes bajulus L.) in Scots pine wood (Pinus sylvestris L.) was performed using the acoustic emission (AE) method. Laboratory experiments (as preliminary) as well as real tests in full-sized building elements were performed. The sound energy of larvae with a mass of 0.011 g to 0.065 g placed in small samples of wood was calculated. A remarkable relationship was found between the calculated sound energy and larva mass. The AE measurement of an old house borer larva in construction element with a cross-section of 11.0 cm × 5.5 cm and a length of 203 cm was also performed. A remarkable drop in calculated sound energy was observed with increasing distance of the sensor from the larval presence. Similar measurements were also conducted in wood with a cross-section of 1.5 cm × 1.5 cm and a length of 203 cm. There was a smaller decline in the calculated energy of sound than in previous studies. For this reason, the AE method should be used in detecting wood-boring insects in furniture.
- Reviewpp 3445-3488Gaynor, J. G., Szlek, D. B., Kwon, S., Tiller, P. S., Byington, M. S., and Argyropoulos, D. S. (2022). "Lignin use in nonwovens: A review," BioResources 17(2), 3445-3488.AbstractArticlePDF
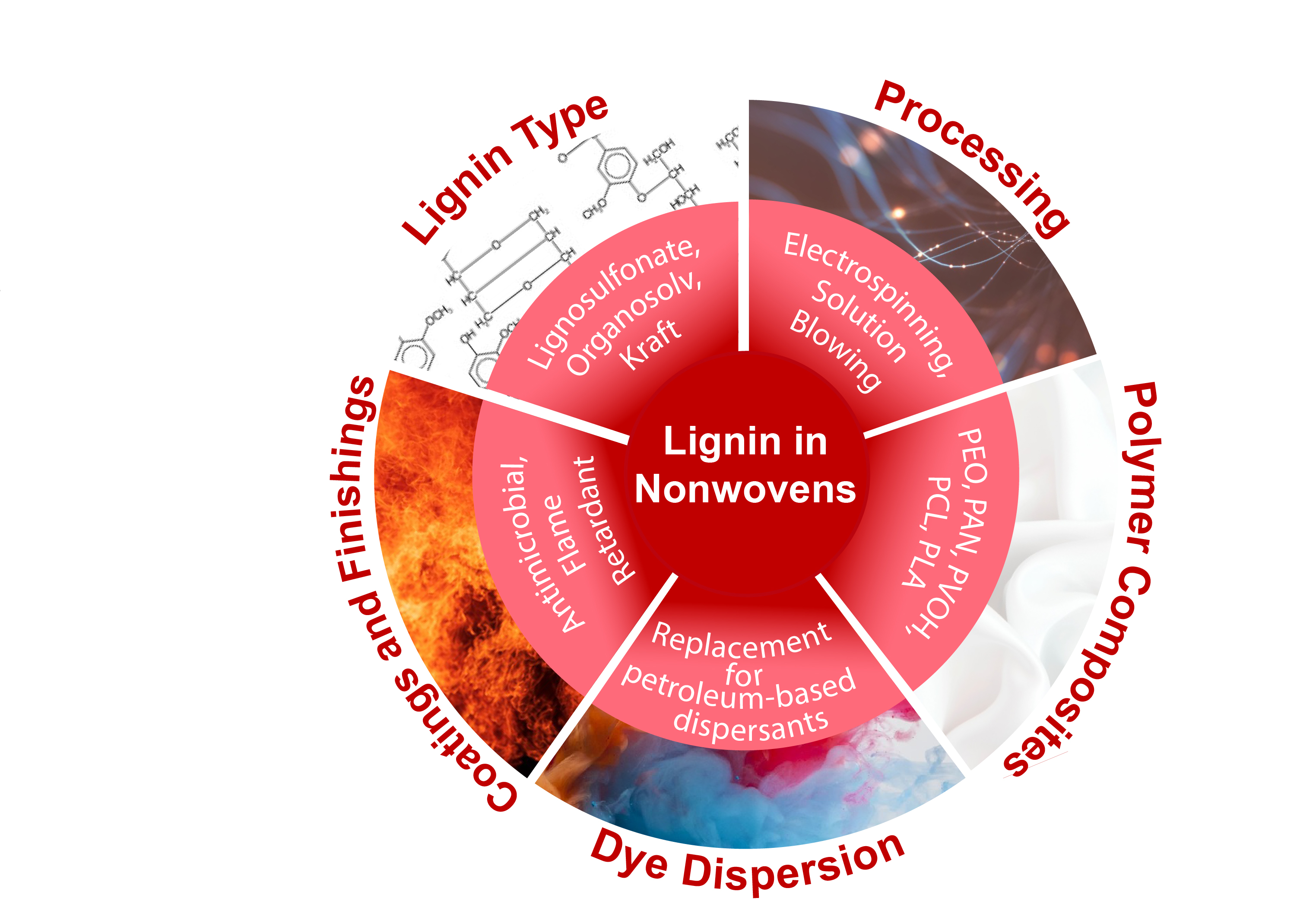
While lignin has been gaining wide research interest for a variety of applications across many industries, relatively little work has been published on its applications in nonwovens. Consequently, this article offers an overview of the underlying principles and both the present and future applications of lignin within the nonwoven industry. Due to the distinct structure of lignin, processing, fiber production, composites with polymers, dye dispersant, and fire-retardant applications are all unique opportunities for lignin application in nonwovens discussed in this review. Conventional nonwoven processing techniques, such as electrospinning, have been reported to successfully produce lignin-based nonwovens, specifically lignin/polymer composite nonwovens. This account points to pivotal polymer matrix/lignin composite compatibility issues that define various processing technologies. However, lignin use is not limited to incorporation within nonwoven fibers mats and is currently used in dye dispersion with the potential of phase out petroleum-based dye dispersants. Finally, the high phenolic content of lignin endows it with fire-retardant and antimicrobial properties, among others, that present additional opportunities for lignin in the nonwoven industry. Throughout this review, an effort is made to outline the advantages and challenges of using lignin as a green and sustainable ingredient for the production of nonwoven materials.
- Reviewpp 3489-3508Zhou, Q., Le, Q. V., Yang, H., Gu, H., Yang, Y., Sonne, C., Tabatabaei, M., Lam, S. S., Li, C., Chen, X., and Peng, W. (2022). "Sustainable conversion of agricultural biomass into renewable energy products: A Discussion," BioResources 17(2), 3489-3508.AbstractArticlePDF
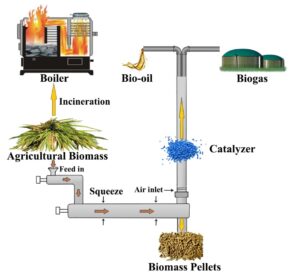
This paper discusses the use of agricultural biomass as a promising resource for renewable energy production, e.g., bio-oil and biogas via pyrolysis and catalysis, among other technologies. In order to prevent the accumulation of agricultural biomass, most countries still use traditional disposal or processing methods, e.g., burning in the field, which not only has a low energy conversion rate, but also releases harmful gases, e.g., CO2, CO, and NH3. These traditional methods are regarded as inefficient with respect to the low utilization of waste; they also pose a threat to human health. The energy conversion of agricultural biomass makes full use of resources and accelerates the development of green energy. In particular, agricultural biomass can lead to the production of high-quality renewable fuels and chemical raw materials through catalytic pyrolysis technologies. The fuel produced using catalytic pyrolysis has a low sulfur and alkali metal contents and techno-economic analysis shows that catalytic pyrolysis greatly reduces the production cost and improves the utilization rate of agricultural biomass. The production of bio-oil and gas via catalytic pyrolysis and agricultural biomass are environmentally friendly and economically feasible for clean energy production. Therefore, additional research is needed to enable the upscaling of renewable energy products.
- Reviewpp 3509-3550Pawlak, J. J., Frazier, R., Vera, R. E., Wang, Y., and Gonzalez, R. (2022). "Review: The softness of hygiene tissue," BioResources 17(2), 3509-3550.AbstractArticlePDF
The hygiene tissue industry has an extensive global market that is quickly growing. Market research has indicated that softness is one of consumers’ most highly desired properties. For certain hygiene tissue products (specifically bath tissue), this property can influence prices. A better understanding of the science of softness would allow companies to engineer soft tissue more economically and efficiently. Softness is a subjective perception related to physical aspects that make it challenging to express and measure. Human handfeel panel testing, which ranks the specimens through physical tests, has been recognized as the most reliable method to measure tissue softness. Much effort has been expanded in correlating the panel test results with some measurable properties. In this regard, equipment has been recently developed by combining several different mechanical, surface, and acoustic properties to characterize softness. In comparison with panel tests, these instruments (e.g., tissue softness analyzer) have been found to give equivalent softness metrics. A combination of materials selection and manufacturing operations are used to create softer tissue sheets. This paper reviews the sensation of softness as perceived by the human touch, techniques for measuring softness, the influence of fiber on softness, manufacturing techniques, and additives used for softness enhancement.
- Reviewpp 3551-3673Szlek, D. B., Reynolds, A. M., and Hubbe, M. A. (2022). "Hydrophobic molecular treatments of cellulose-based or other polysaccharide barrier layers for sustainable food packaging: A Review," BioResources 17(2), 3551-3673.AbstractArticlePDF
Paper, nanocellulose, and other polysaccharide-based materials can be excellent candidates for food packaging barrier layers, except that they tend to be vulnerable to moisture. This article reviews published research describing various chemical treatments having the potential to render hydrophobic character to such layers. Emphasis is placed on systems in which hydrophobic monomers are used to treat either particles or sheets comprised largely of polysaccharides. A goal of this review is to identify combinations of materials and procedures having promise for scale-up to industrial production, while providing effective resistance to moisture. The idea is to protect the underlying polysaccharide-based barrier layers such that they can continue to impede the transfer of such permeants as oxygen, greases, flavor compounds, and water vapor. A further goal is to minimize any adverse environmental impacts associated with the treatments. Based on the research articles considered in this review, promising hydrophobic treatments can be achieved involving silanes, ester formation, other covalent interactions, plasma treatments, and to some extent by various treatments that do not require formation of covalent bonds. The article is designed such that readers can skip ahead to items of particular interest to them.
