Volume 17 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2372-2389Sun, X., Zou, X., Liu, Y., Gong, M., and Song, Y. (2022). "Lateral loading behavior of the poplar LVL light wood shear wall," BioResources 17(2), 2372-2389.AbstractArticlePDF
Poplar laminated veneer lumber (poplar LVL) is made of fast-growing poplar veneer and structural adhesive, which can well meet the developing requirement of the modern wood structures. This paper mainly focuses on the lateral loading behavior of the poplar LVL shear wall. For this purpose, six shear wall specimens with different opening types were fabricated and tested under the action of monotonic and cyclic loading. Performances were analyzed on the failure pattern, the load-displacement curve, the shear strength, the ultimate displacement, the elastic lateral stiffness, and the energy dissipation. To strengthen the corner joint, an innovative custom-designed hold-down was adopted, and the mechanical performance was also considered. The results showed that the failure of the specimen was mainly due to the yield of the nails and the separation between the stud and the base plate, while the hold-down can greatly improve the shear strength, the ultimate displacement, and the energy dissipation performance of the poplar LVL shear wall without openings. At last, the evaluation formula of the bearing capacity for the light wood shear wall is proposed so as to promote the theoretical basis for the application of poplar LVL in the light wood frame construction.
- Researchpp 2390-2402Sun, Y., Xu, A., Chen, C., Luo, C., and Bao, L. (2022). "Effect of alkali and silane treatments on properties of green composites based on ramie fibers and cellulose acetate resin," BioResources 17(2), 2390-2402.AbstractArticlePDF
Green composites based on ramie fiber yarn and cellulose acetate resin were prepared via hot pressing. The ramie fiber yarns were treated with NaOH and 3-glycidoxypropyltriethoxysilane. The effect of surface treatment on the fiber adhesion to the resin surface and the mechanical properties of the green composites were studied. The chemical properties of the modified ramie fiber yarn were studied via Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The adhesion performance between the fiber and resin was evaluated. The tensile strength of the composites was measured through tensile testing. A single-fiber tensile experiment was used to determine the influence of the tensile strength of the single fibers after surface-treatment. The surface morphology changes were observed via scanning electron microscopy. The results showed fiber–resin adhesion was improved by the surface treatments. However, the surface treatments negatively affected the single-fiber mechanical properties, with the alkali treatment causing greater damage than the silane treatment.
- Researchpp 2403-2427Lenske, A., Müller, T., Ludat, N., Hauptmann, M., and Majschak, J.-P. (2022). "A new method to evaluate the in-plane compression behavior of paperboard for the deep drawing process," BioResources 17(2), 2403-2427.AbstractArticlePDF
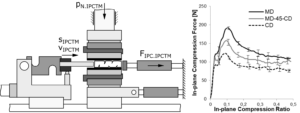
To evaluate the influence of different normal pressures and the fiber orientation on the in-plane compression behavior of paperboard during the deep drawing process, a new method was developed. In addition, the influence of the wrinkle formation on the dynamic coefficient of friction and the bending resistance was examined. To evaluate the eligibility of the in-plane compression testing method, a validation strategy was developed to compare the results from the new alternative tests with the punch force profiles from the deep drawing process within an empirical model.
- Researchpp 2428-2442Phonetip, K., Souvansai, D., and Belleville, B. (2022). "Equilibrium moisture content map for Laos," BioResources 17(2), 2428-2442.AbstractArticlePDF
Providing the equilibrium moisture content values for territories is important for avoiding major problems due to dimensional changes in wooden products. This study evaluated the average equilibrium moisture content values for twelve months (from 1981 to 2020) for Laos and produced an equilibrium moisture content map. A model was used to generate the equilibrium moisture content values based on temperature and relative humidity data obtained from the POWER Data Access Viewer v2.0.0. for 18 provinces (148 districts) based on the geographic coordinates of each district in Laos. The lowest equilibrium moisture content (12% to 13%) values were found in Vientiane Capital City, Vientiane province, Louangprabang, Bokeo, Attapeu, Louang Namtha, Oudomxay, Houaphan, Sayaburi, Savannakhet, Salavan, and Champasak province. The rest of the districts, which had an equilibrium moisture content ranging from 13% to 16%, were mostly found on the eastern part of Laos and a small part of Northern Laos. The monthly swinging average value of the equilibrium moisture content ranged from 10% to 18% across the country. The equilibrium moisture content values for each district in Laos were also defined.
- Researchpp 2443-2456Yang, X., Gao, Y., Zhao, Z., Ge, Z., Liu, X., and Zhou, Y. (2022). "Detection and analysis of an eave purlin of the timber building eroded by carpenter bees based on computed tomography," BioResources 17(2), 2443-2456.AbstractArticlePDF
To explore the harm of carpenter bee nests to timber buildings, an eave purlin of Wu’s house, the seventh batch of national key cultural relics in China, was taken as the research object. A CT (computed tomography) device was used to collect the projection data of wood components, and VGSTUDIO MAX3.2 software was used to reconstruct multiple transverse sections, radial sections, tangential sections, and 3D (three-dimensional) images of an eave purlin. The results showed that carpenter bees eroded a timber building randomly, but they usually nested along the length of eave purlin. The wood in the middle of an eave purlin is more vulnerable to carpenter bees than the end. Carpenter bee nests are usually not connected, and the volume of nests accounts for 3% to 4% of the eave purlin. The eave purlin is applied with an orientation and a torsion force. The position of the maximum hot spots of the stress occurs at holes and the large cracks, indicating that carpenter bee nests have a great impact on the mechanical properties of timber buildings. The research results of this paper provide reference for the safety evaluation and preventive protection of timber buildings.
- Researchpp 2457-2469Yu, C., Jhong, M., Lin, F., Chen, M., and Wang, G. (2022). "Aldehyde content of dialdehyde cellulose determined via nitrate analysis," BioResources 17(2), 2457-2469.AbstractArticlePDF
Dialdehyde cellulose was synthesized via the heterogeneous periodate oxidation of microcrystalline cellulose in an aqueous solution. The aldehyde content of the dialdehyde cellulose was determined via nitrate analysis based on a two-step sequential approach. The approach first employed hydroxylamine to react with the aldehyde groups and to produce oxime groups via Schiff’s replacement reaction. Then, the oxime groups were oxidized via persulfate to produce nitrate. The nitrate concentration was analyzed via two highly sensitive methods, i.e., ion chromatography and ultraviolet light absorption. The aldehyde content was approximately one-fifth of the theoretical value. The resulting aldehyde groups were found primarily distributed over the surface layers. A solubility parameter calculation suggested that the increase of the aldehyde groups caused the detachment and dissolution of the dialdehyde cellulose chains and consequently led to the determination of a relatively low aldehyde content.
- Researchpp 2470-2485Tirak Hizal, K. (2022). "Wood anatomy teaching: Example of the Vocational School of Forestry," BioResources 17(2), 2470-2485.AbstractArticlePDF
The teaching of wood anatomy is difficult because of the Latin and foreign terminology and the great number of concepts, definitions, terms, and topics that must be learned and that pose difficulties in understanding for most students. The aim of this study was to describe developed traditional methods and adapt new methods in order to explain wood anatomy more clearly to students in both online and face-to-face education. The teaching of the Wood Structure and Identification course at the Vocational School of Forestry was observed and evaluated over the period of two academic terms (one during the Covid-19 pandemic). Teaching methods used in the wood anatomy course were described in detail. Lesson materials and homework were evaluated. When the usual methods were diversified and enriched with visuals and samples brought to the classroom, the students showed more interest in the lesson. As a result of the student drawing and modelling assignments, the lesson was reviewed and reinforced, which enabled the students to focus on the subject and consequently, to understand and learn more easily. It has determined that all teaching methods can be applied easily in both education periods, except using real wood samples method in online education.
- Researchpp 2486-2500Perçin, O., and Uzun, O. (2022). "Screw withdrawal strength of heat-treated and laminated veneer lumber reinforced with carbon and glass fibers," BioResources 17(2), 2486-2500.AbstractArticlePDF
The strength of a structural system often depends on the interconnections between the components of the structure. Screws are one of the most widely used fasteners in construction. In this study, the screw withdrawal strength of heat-treated scotch pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) samples reinforced with glass and carbon fibers via Desmodur-vinyl trie ketonol acetate adhesive was investigated. Before manufacturing the laminated veneer lumber, the wood samples were subjected to heat treatment at a temperature of 150 °C, 170 °C, 190 °C, and 210 °C for 2 h. Test results showed that the reinforcement fiber type and heat treatment temperatures had a considerable effect on the screw withdrawal strength. Heat treatment reduced the screw withdrawal strength, while the samples reinforced with both fibers had higher screw withdrawal strengths than those without reinforcement. Reinforcement with glass and carbon fibers increased the screw withdrawal strength up to 38% and 49% in the tangential, 13% and 20% in the radial, and 17% and 25% in the axial direction, respectively, compared to solid wood. In addition, the laminated veneer lumber samples reinforced with carbon fiber had a considerable increase in the screw withdrawal strength compared with the solid wood and glass fiber reinforced samples.
- Researchpp 2501-2524Çakıroğlu, E. O., Demir, A., Aydın, İ., and Büyüksarı, Ü. (2022). "Prediction of optimum CNC cutting conditions using artificial neural network models for the best wood surface quality, low energy consumption, and time savings," BioResources 17(2), 2501-2524.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to predict the CNC cutting conditions for the best wood surface quality, energy, and time savings using artificial neural network (ANN) models. In the CNC process, walnut, and ash wood were used as materials, while three different cutting tool diameters (3 mm, 6 mm, and 8 mm), spindle speed (12000 rpm, 15000 rpm, and 18000 rpm), and feed rate (3 m/min, 6 m/min, and 9 m/min) were determined as cutting conditions. After the cutting processes were completed with the CNC machine, energy consumption and processing time were determined for all groups. Surface roughness and wettability tests were performed on the processed wood samples, and their surface qualities were determined. The experimentally obtained data were analysed in ANN, and the models with the best performance were obtained. By using these prediction models, optimum cutting conditions were determined. Using the findings of the study, the optimum cutting condition values can be determined for walnut and ash wood with the smoothest and best wettable surface. Furthermore, in CNC processes using such materials, minimum energy consumption and shorter processing time can be obtained with optimum cutting conditions.
- Researchpp 2525-2546Gu, H., Liu, Y., Yan, J., Yu, X., Li, Y., Li, C., and Peng, W. (2022). "Chemical component characterization and potential medicinal utilization of extracts and pyrolyzates from Jasminum nudiflorum Lindl. wood," BioResources 17(2), 2525-2546.AbstractArticlePDF
Utilization of lignocellulosic biomass is receiving increasing attention lately. In this study, Jasminum nudiflorum Lindl. (JNL) wood were extracted using methanol, ethanol, and benzene/ethanol (2:1, v:v) separately. Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) were used to study the chemical components of extracts. A thermogravimetric (TG) analyzer and pyrolysis (Py)-GC-MS investigated the characteristics of thermal loss law and pyrolyzates of JNL wood, respectively. The FTIR results showed that many functional groups were detected from the extracts of JNL wood, which were consistent with the chemical structures in the components detected by GC-MS. There were two obvious stages of thermal loss for removing moisture and decomposition of the organic constituents. The components of the extracts and pyrolyzates were esters, acids, aldehydes, alcohols, inositol, furfural, alkanes, phenols, ketones, antibiotics, saccharides, and glycosides. Among them, some components, such as ethyl iso-allocholate, scopoletin, isosorbide dinitrate, and idebenone, have high medicinal value. This study revealed the chemical component characterization and potential medicinal utilization of JNL wood. It provides the scientific basis for enhancing the utilization value of JNL wood.
